Assets can be classified as Financial or Non-financial assets. One might wonder why this is necessary. Let us dive into this concept, beginning with understanding what financial and non-financial assets are and why they are classified as such. What are Assets? Assets are things that have a monetaryRead more
Assets can be classified as Financial or Non-financial assets. One might wonder why this is necessary. Let us dive into this concept, beginning with understanding what financial and non-financial assets are and why they are classified as such.
What are Assets?
Assets are things that have a monetary value and are beneficial for a business. Assets are commonly classified as tangible, intangible, current, fixed, financial, non-financial, etc.
Plant and machinery, land, buildings, cash, bank balance, patents, etc are some of the examples of assets that a business has.
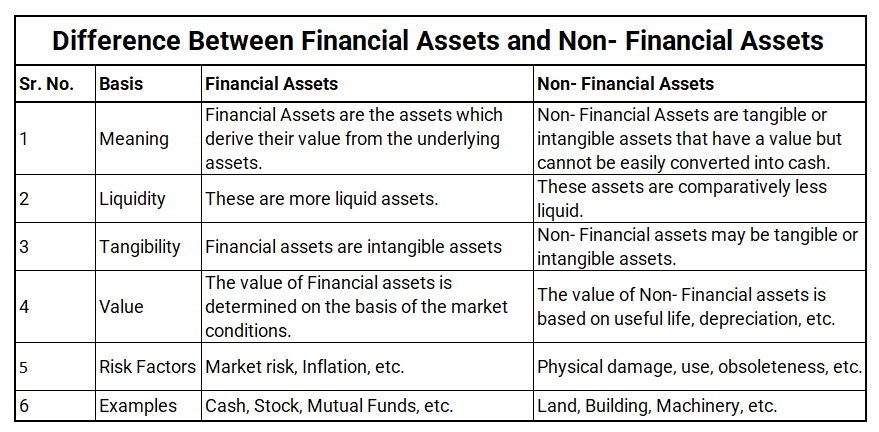
What are Financial Assets?
Financial assets are the things of value that are held by a person for their underlying value. They are intangible and do not have a physical form. For example – Stocks, bonds, debentures, options, futures, etc.
The value of these assets may change over time depending upon the market conditions, changes in government policies, fluctuations in interest rates, etc.
In comparison to non-financial or physical assets, financial assets are more liquid as they can be traded and can be converted into cash.
What are Non-financial assets?
Non-financial assets are tangible or intangible assets that have a value but cannot be easily converted into cash. They are not as liquid and generally not traded.
Examples of such assets are buildings, plant and machinery, patents, trademarks, etc.
Why do we separate Financial and Non-Financial Assets?
The following are several important reasons why it is important to segregate the same:
- It helps in the proper classification of assets on the Financial Statements.
- It helps in liquidity management.
- It helps in Risk assessment.
- Tax management can be done accurately.
Difference between Financial and Non – Financial Asset
See less


A Capital Account is an account that shows the owner's equity in the firm and a Partner's Capital Account is an account that shows the partner's equity in a partnership firm. Partner’s Capital Account includes transactions between the partners and the firm. Examples of such transactions are: CapitalRead more
A Capital Account is an account that shows the owner’s equity in the firm and a Partner’s Capital Account is an account that shows the partner’s equity in a partnership firm.
Partner’s Capital Account includes transactions between the partners and the firm. Examples of such transactions are:
When partners are given interest on their capital contribution in the firm, it is called on Interest on Capital.
In case the partnership firm does not have a Partnership Deed, the Partnership Act does not include a provision for Interest on Capital. However, if the partners want they can mutually decide the rate of Interest on Capital.
Interest on Capital is calculated on the opening capital of the partners and is only allowed when the firm makes a profit, that is, in case a firm incurs losses, it cannot allow Interest on Capital to its partners.
Example:
In a partnership firm, there are two partners A and B, and their capital contribution is Rs 10,000 and 20,000 respectively. Interest on capital is @ 10% p.a. The Interest on Capital for both the partners is:
Partner A- 10,000 * 10/100 = 1,000
Partner B- 20,000 * 10/100 = 2,000
The journal entry for Interest on Capital is an adjusting entry and is shown as:
See less