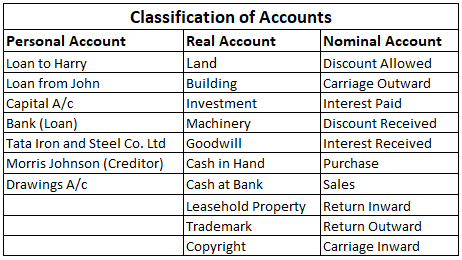
Personal Accounts: The accounts of persons, firms, companies, etc. are personal accounts. There is a further classification to personal accounts- Accounts of Natural Persons: The transactions relating to individual human beings fall under this category. For Example, accounts of Joseph, Richard, MorrRead more
Personal Accounts: The accounts of persons, firms, companies, etc. are personal accounts. There is a further classification to personal accounts-
- Accounts of Natural Persons: The transactions relating to individual human beings fall under this category. For Example, accounts of Joseph, Richard, Morris, etc.
- Accounts of Artificial Persons: The transactions relating to firms, organizations, companies, institutions, associations, etc. fall under this category. For Example, Oil India Ltd, Symbiosis college, Assam Tea company, etc.
- Representative Personal Accounts: The transactions relating to certain person or a group of persons, although the name of the concerned person or persons are not mentioned in the account head, such types of accounts come under this head. Such type of accounts generally include outstanding accounts or prepaid accounts. For Example, accounts like wages outstanding, outstanding salary, commission received in advance, salary prepaid, etc.
Note: When any Prefix or Suffix is used before/ after any nominal account head, such account is classified as Representative personal account under traditional approach.
For Example, Salary A/c is a nominal account whereas salary outstanding A/c is a personal account as the word outstanding is being used as a prefix to Salary A/c.
The Accounting rule for Personal Account is –
Debit the Receiver of the benefit.
Credit the Giver of the benefit.
Real Account: The transactions relating to tangible things i.e. the things that can be seen, touched and physically exchanged and the intangible things that cannot be seen, touched but the presence can be felt comes under this category. For Example, tangible things like Cash, goods, building, machinery, etc. and intangible things like goodwill, patent, trademarks, etc.
The Accounting rule for Real Account is –
Debit what comes in.
Credit what goes out.
Nominal Accounts: The transactions relating to losses, expenses, incomes and gains comes under this category. For Example, Rent paid, wages paid, commission received, interest paid/ received, etc.
The Accounting rule for Nominal Account is –
Debit Expenses and Losses.
Credit Gains and Incomes.
Some Common Examples under the three heads are



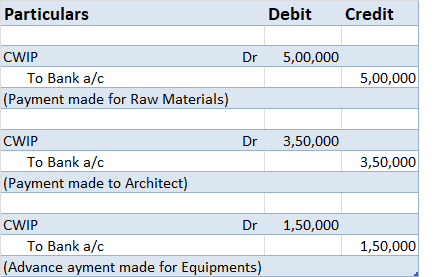
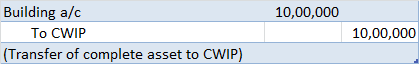
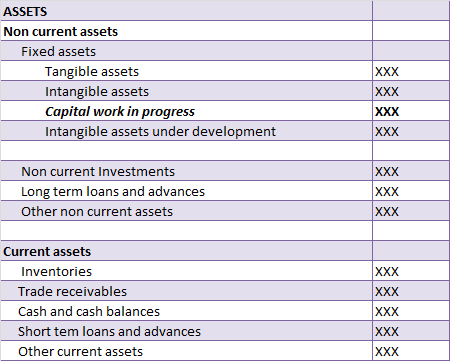
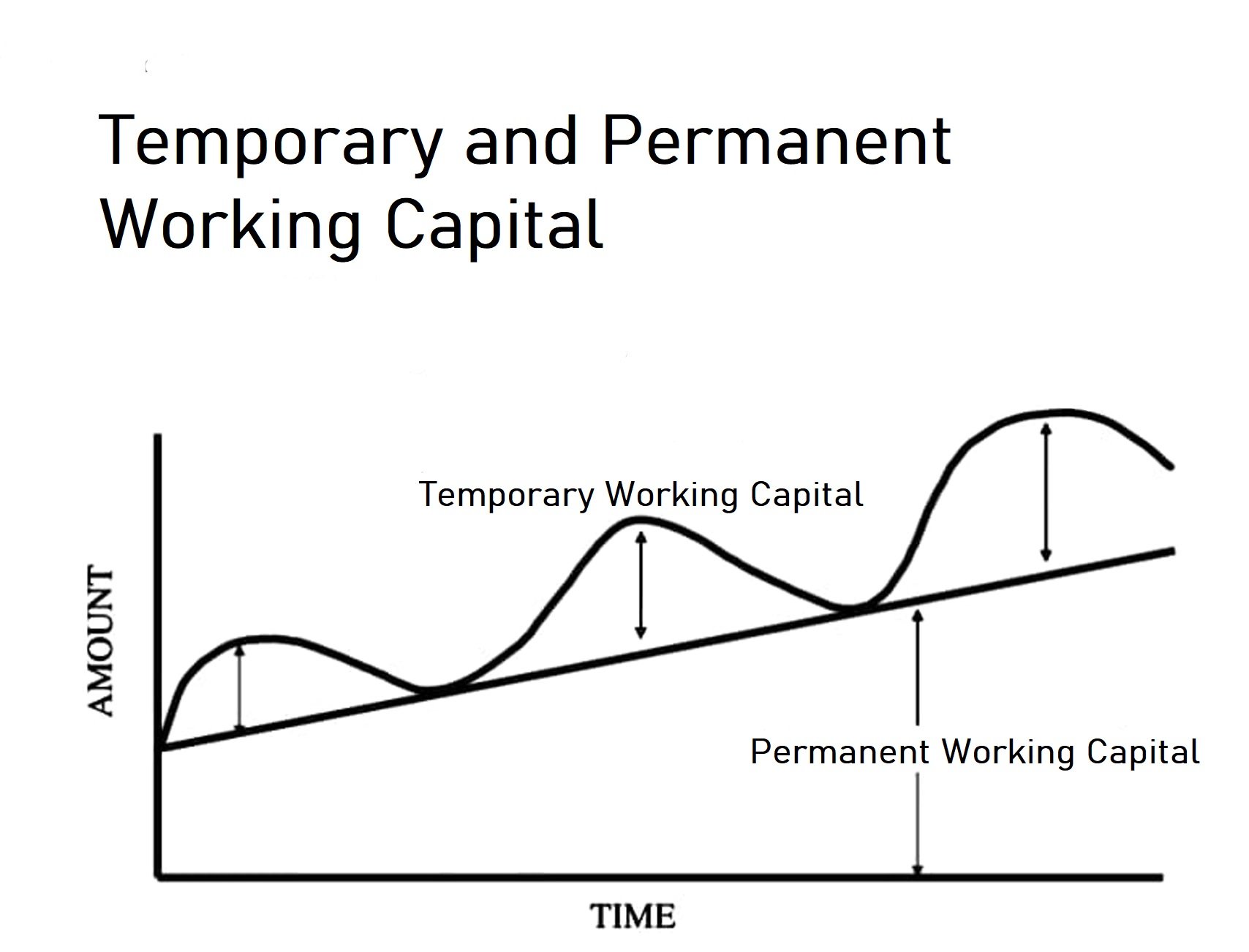
Realization is an important principle in accounting. It is the basis of revenue recognition and it gives to accrual accounting. When we used the word realization, it is usually regarding revenue recognition. Realization of revenue means when revenue to be earned from the sale of goods or rendering oRead more
Realization is an important principle in accounting. It is the basis of revenue recognition and it gives to accrual accounting. When we used the word realization, it is usually regarding revenue recognition.
Realization of revenue means when revenue to be earned from the sale of goods or rendering of services or any other activity or source becomes absolute and certain. An item is to be shown as revenue in the books of accounts only after it is realized.
Realization in case of sale of goods
Realization occurs in the following situations:
i) When the goods are delivered to the customer for a certain price
ii) All significant risks and rewards of ownership have been transferred to the customer and the seller retains no effective control over the goods.
Let’s take an example. Mr Peter received an order of 500 units of goods from Mr Parker on 1st April. The goods were delivered to Mr Parker on 15Th April and payment for goods was received on 30Th April.
The realization of revenue from the sale of goods will be considered to have occurred on 15th April because the goods were delivered to the customer on that date. The entry of sale of goods will be entered on this day.
Realization is not considered to have occurred on 1st April i.e the date of order because the seller had effective control on goods on that date.
Realization in case of rendering of services
The realization of revenue from the rendering of services occurs as per the performance of service.
Now there arise two situations:
Realization of income from other sources:
Realization with regards to other sources of income is considered to have occurred only when there exist no significant uncertainty as to measurability or collectability.
See less