The correct option is Option C: Journal Entries. Journal entries are the primary entries in the books of accounts and they are passed when any transaction or event takes place. Every journal entry has a dual effect i.e. two or more accounts are affected. For example, When cash is introduced in the bRead more
The correct option is Option C: Journal Entries.
Journal entries are the primary entries in the books of accounts and they are passed when any transaction or event takes place. Every journal entry has a dual effect i.e. two or more accounts are affected.
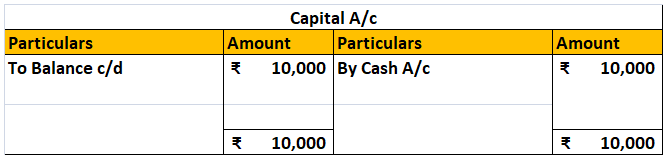
For example, When cash is introduced in the business, the journal entry passed is:
Cash A/c Dr. ₹10,000
To Capital A/c ₹10,000
The accounts affected here are Cash A/c and Capital A/c.
Cash A/c gets debited by ₹10,000,
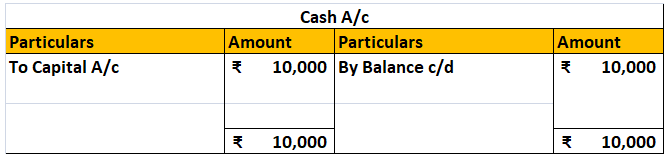
and Capital A/c get credited by ₹10,000.
All the processes of accounting are conducted in an ordered manner known as the accounting cycle.
The first step in an accounting cycle is to identify the transactions and events which are monetary in nature.
The second step is to record the identified transactions in form of journal entries.
And the third step is to make postings in the general ledger accounts as per the journal entries.
Hence, the preparation of the ledger is the third step in the accounting cycle and is prepared from the journal entries.
See less



Ledger Folio A ledger folio, in simple words, is a page number of the ledger account where the relevant account appears. The term 'folio' refers to a book, particularly a book with large sheets of paper. In accounting, it's used to maintain ledger accounts. The use of ledger folio is generally seenRead more
Ledger Folio
A ledger folio, in simple words, is a page number of the ledger account where the relevant account appears. The term ‘folio’ refers to a book, particularly a book with large sheets of paper. In accounting, it’s used to maintain ledger accounts.
The use of ledger folio is generally seen in manual accounting, i.e the traditional book and paper accounting as it is a convenient tool used for tracking the relevant ledger account from its journal entry. Whereas, in computer-oriented accounting (or computerized accounting), it’s not really an issue to track your relevant ledger account.
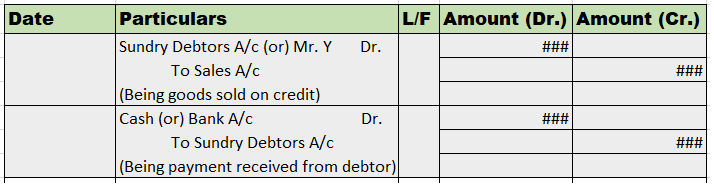
Ledger folio, abbreviated as ‘L.F.’, is typically seen in journal entries. The ledger folio is written in the journal entries, after the ‘date’ and ‘particulars’ columns. It is really convenient when we’re dealing with and recording a large number of journal entries. As we will be further posting them into ledger accounts, thus, ledger folio comes in as a really useful component of journal entries.
Example
We’ll look at how the ledger folio column is used while recording journal entries.
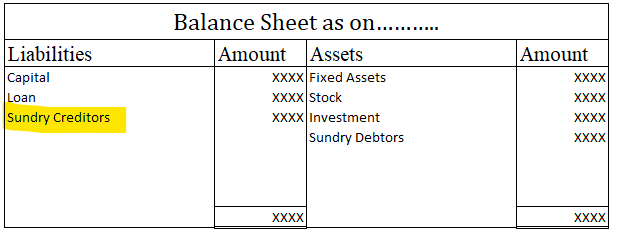
We can find the relevant ledger accounts on the page numbers of the book as mentioned in the above entries, i.e. the cash and sales account on page – 1 whereas, the purchases and sundry creditors on page – 2 of the relevant ledger book.
See less