Deferred Revenue Expenditure Capital Expenditure Capital Gain Revenue Expenditure
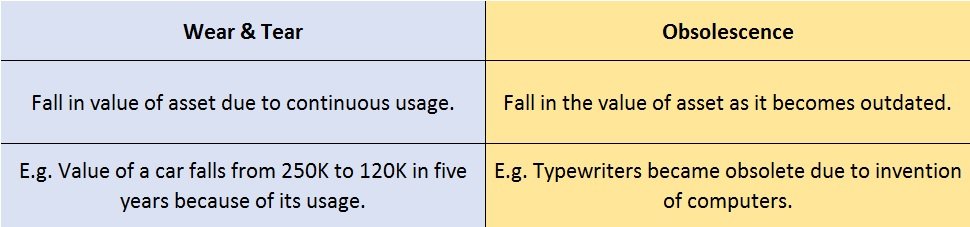
Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence. Normal wear & tear refers to the damage caused to an asset due to its continuous usage. Even when the asset is properly maintained, wear and tear occurs. Hence, it is considered to be inevitableRead more
Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence.
Normal wear & tear refers to the damage caused to an asset due to its continuous usage. Even when the asset is properly maintained, wear and tear occurs. Hence, it is considered to be inevitable and natural.
For example, Kumar has purchased a car for 25,00,000. After five years he wishes to sell his car. Now the market price of his used car is 12,00,000. This reduction in the value of the car from 25,00,000 to 12,00,000 is because of its usage. This fall in the value of the asset due to usage is known as normal wear & tear.
In generic terms, obsolescence means something that has become outdated or is no longer being used. Foreseen obsolescence is nothing but obsolescence that is expected.
In the context of business, whenever the value of an asset falls because it has become outdated or is replaced by a superior version, we call it obsolescence. The fall in the value of the asset due to obsolescence expected by the purchaser of the asset is known as foreseen obsolescence.
When an asset becomes obsolete it doesn’t mean it is not in working condition. Even when an asset is in good working condition it can become obsolete due to the following reasons:
- Technology advancement.
- Change in demand (change in fashion, change in taste and preferences of the consumers, etc.)
For example, before the invention of computers, people used typewriters for getting their paperwork done. With the invention of computers, laptops, etc. it is easier to type as well as save our documents, spreadsheets, etc. Thus typewriters became obsolete with the invention of computers. It has become a technology of the past.
Here is a summarised version of wear & tear and obsolescence:

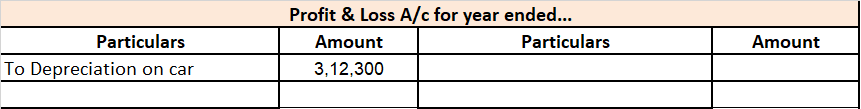
The correct answer is 4. Revenue Expenditure. Depreciation is a non-cash expense and is charged on the fixed asset for its continuous use. Revenue expenditure is a day-to-day expense incurred by a firm in order to carry on its normal business. Depreciation is considered a revenue expense due to theRead more
The correct answer is 4. Revenue Expenditure.
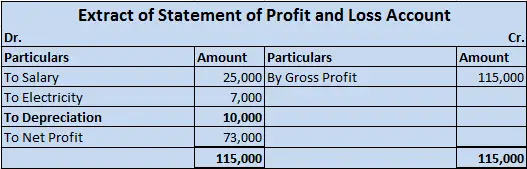
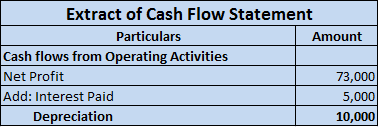
Depreciation is a non-cash expense and is charged on the fixed asset for its continuous use. Revenue expenditure is a day-to-day expense incurred by a firm in order to carry on its normal business. Depreciation is considered a revenue expense due to the regular use of the fixed assets.
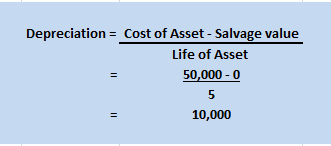
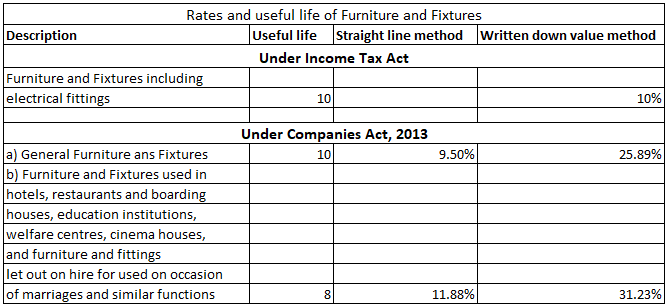
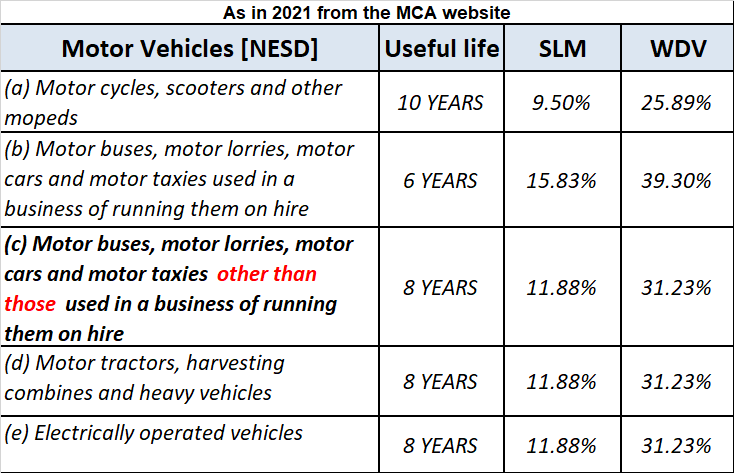
Depreciation is the systematic and periodic reduction in the cost of a fixed asset. It is a non-cash expense. Mostly, depreciation is charged according to the straight-line method or written down method as per the policy of the company.
Depreciation is the systematic and periodic reduction in the cost of a fixed asset. It is a non-cash expense. Mostly, depreciation is charged according to the straight-line method or written down method as per the policy of the company. It is calculated as-
Depreciation = Cost of the asset – Scrap value / Expected life of the asset.
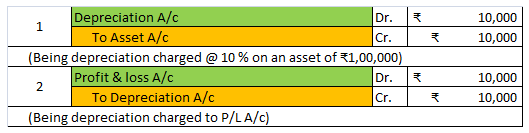
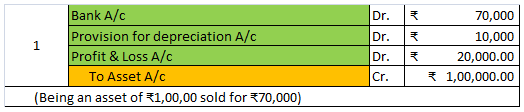
For Example, ONGC bought machinery at the beginning of the year for Rs 10,00,000
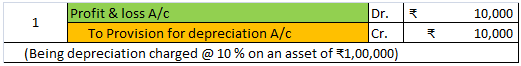
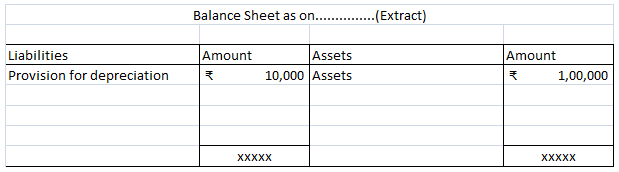
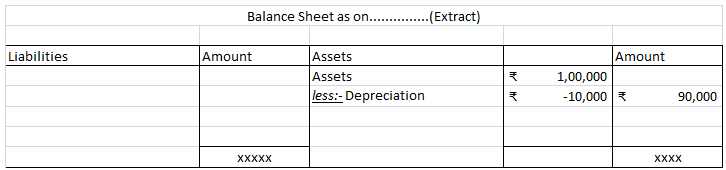
It charges depreciation @10% at the end of the year.
10,00,000 x 10/100 = 1,00,000 will be depreciation for the year and will be shown on the debit side of Profit & Loss A/c.
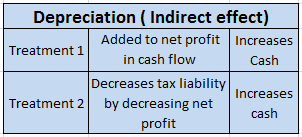
As the fixed assets are used in the day-to-day activities of the firm and hence the depreciation charged on it on the daily basis would be revenue in nature. so depreciation is said to be an item of revenue expenditure.
See less