If someone can tell me the complete accounting with the percentage that would be great.
The total depreciation of an asset cannot exceed its 3. depreciable value. Depreciable value means the original cost of the asset minus its residual/salvage value. The asset's original cost is inclusive of the purchase price and other expenses incurred to make the asset operational. To put it simplRead more
The total depreciation of an asset cannot exceed its 3. depreciable value.
Depreciable value means the original cost of the asset minus its residual/salvage value. The asset’s original cost is inclusive of the purchase price and other expenses incurred to make the asset operational. To put it simply,

The accumulated depreciation on an asset can never exceed its depreciable value because depreciation is a gradual fall in the value of an asset over its useful life. Only a certain percentage of the asset’s book value/original cost is shown as depreciation every year. So, it is impossible/illogical for the accumulated depreciation of an asset to exceed its depreciable value.
Let me show you an example to make it more understandable,
Amazon installs machines to automate the job of packing orders. The original cost of the machine is $1,000,000. Now let’s assume,
The estimated useful life of the machine – 10 years.
Residual value at the end of 10 years – $50,000.
Method of depreciation – Straight-line method.
The depreciable value of the machine will be $950,000 (1,000,000 – 50,000). The depreciation for each year under SLM will be calculated as follows:
Depreciation = (Original cost of the asset – Residual/Salvage Value) / (Useful life of the asset)
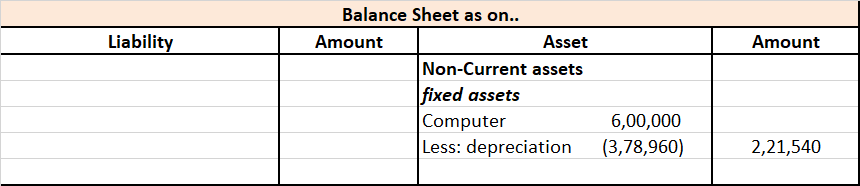
Applying this formula, $95,000 (1,000,000 – 50,000/10) will be charged as depreciation every year. The accumulated depreciation at the end of 10 years will be $950,000 (95,000*10). As you can see, the accumulated depreciation ($950,000) of the machine does not exceed its depreciable value ($950,000).
Thus, the total depreciation of an asset cannot be more than its depreciable value.
See less

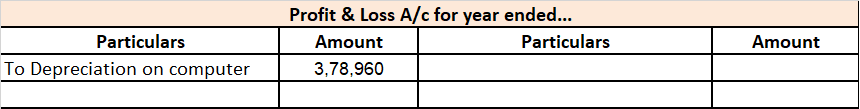
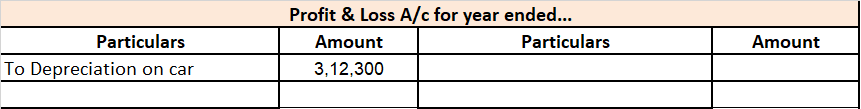
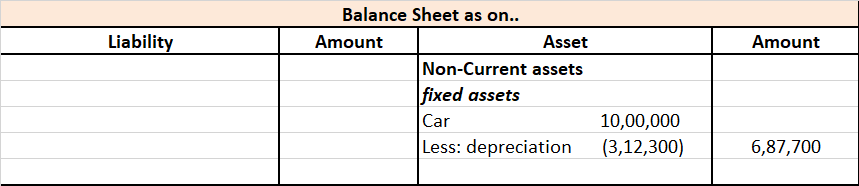
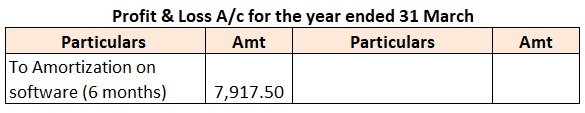
I am assuming that you are asking the question with reference to the sole proprietorship business. In the case of a company, the rates as per the Companies Act, 2013 will apply. A sole proprietor can charge the depreciation in its books of accounts at whatever rate it wants but it should not be moreRead more
I am assuming that you are asking the question with reference to the sole proprietorship business. In the case of a company, the rates as per the Companies Act, 2013 will apply. A sole proprietor can charge the depreciation in its books of accounts at whatever rate it wants but it should not be more than the rates prescribed in the Income Tax Act, 1961.
It is a general practice to take depreciation rate lower than the Income Tax Act, 1961, so that the financial statements look good because of slightly higher profit. There is no harm in it as it is a sole proprietor.
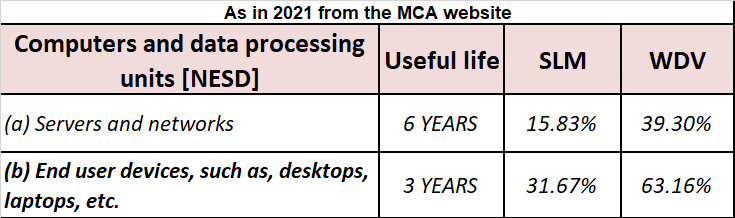
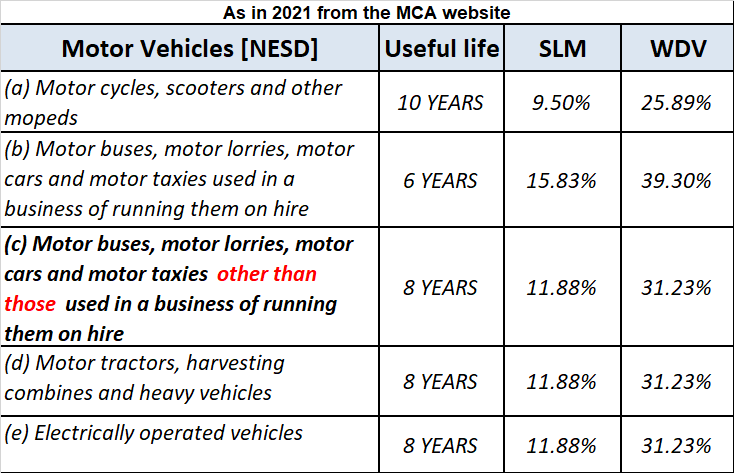
The Income Tax Act, 1961 has prescribed rates at which depreciation is to be given on different blocks of assets. For motor vehicles, the rates are as follows:
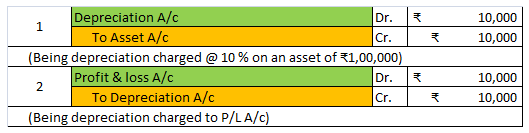
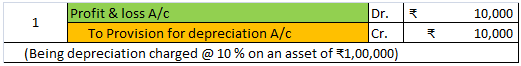
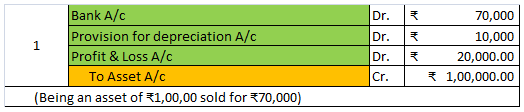
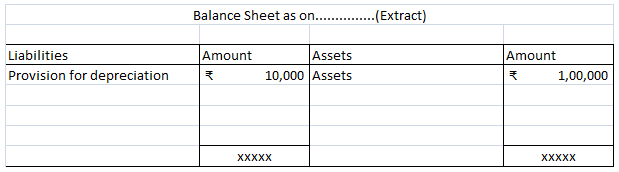
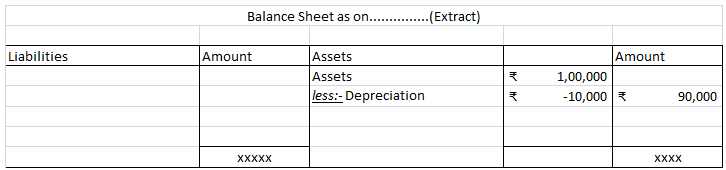
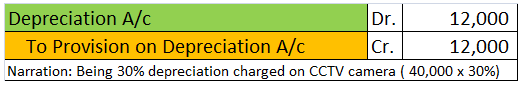
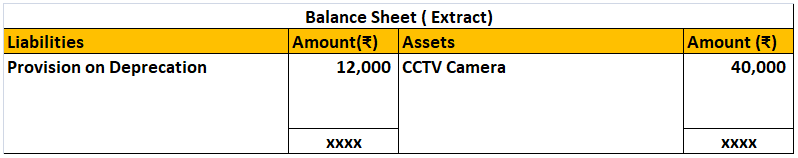
Let’s take an example to understand the accounting treatment:-So a business can choose to charge depreciation at rates slightly lower than the above rates.
Mr A purchased a lorry for ₹1,00,000 on 1st April 2021 for his business, to be used for transportation of the finished goods. Now, Mr A decided to charge depreciation on the WDV method @30% (prescribed rate is 40%).
Following will be the journal entries.
I hope I was able to answer your question.
See less