I am assuming that you are asking the question with reference to the sole proprietorship business. In the case of a company, the rates as per the Companies Act, 2013 will apply. A sole proprietor can charge the depreciation in its books of accounts at whatever rate it wants but it should not be moreRead more
I am assuming that you are asking the question with reference to the sole proprietorship business. In the case of a company, the rates as per the Companies Act, 2013 will apply. A sole proprietor can charge the depreciation in its books of accounts at whatever rate it wants but it should not be more than the rates prescribed in the Income Tax Act, 1961.
It is a general practice to take depreciation rate lower than the Income Tax Act, 1961, so that the financial statements look good because of slightly higher profit. There is no harm in it as it is a sole proprietor.
The Income Tax Act, 1961 has prescribed rates at which depreciation is to be given on different blocks of assets. For motor vehicles, the rates are as follows:
| Particulars | Rates (WDV) | |
| 1 | Motor buses, motor Lorries and motor taxis used in a business of running them on hire. | 30% |
| 2 | Motor buses, motor lorries and motor taxis used in a business of running them on hire, acquired on or after the 23rd day of August 2019 but before the 1st day of April 2020 and is put to use before the 1st day of April 2020. | 45% |
| 3 | Commercial vehicles to use in business other than running them on hire. | 40% |
Let’s take an example to understand the accounting treatment:-So a business can choose to charge depreciation at rates slightly lower than the above rates.
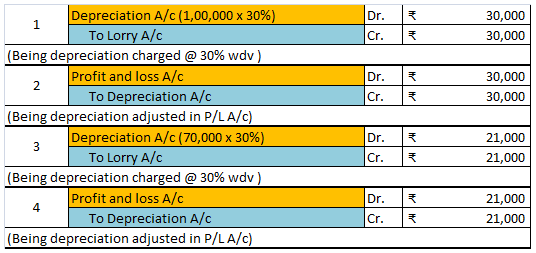
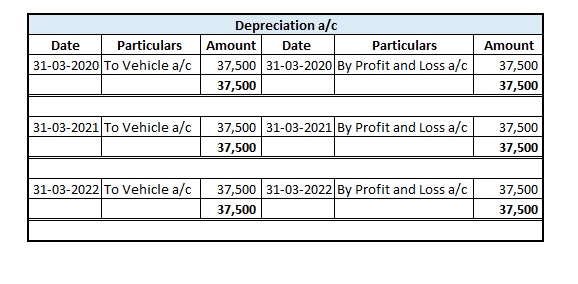
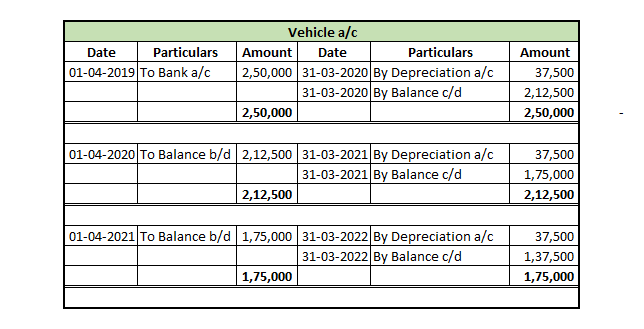
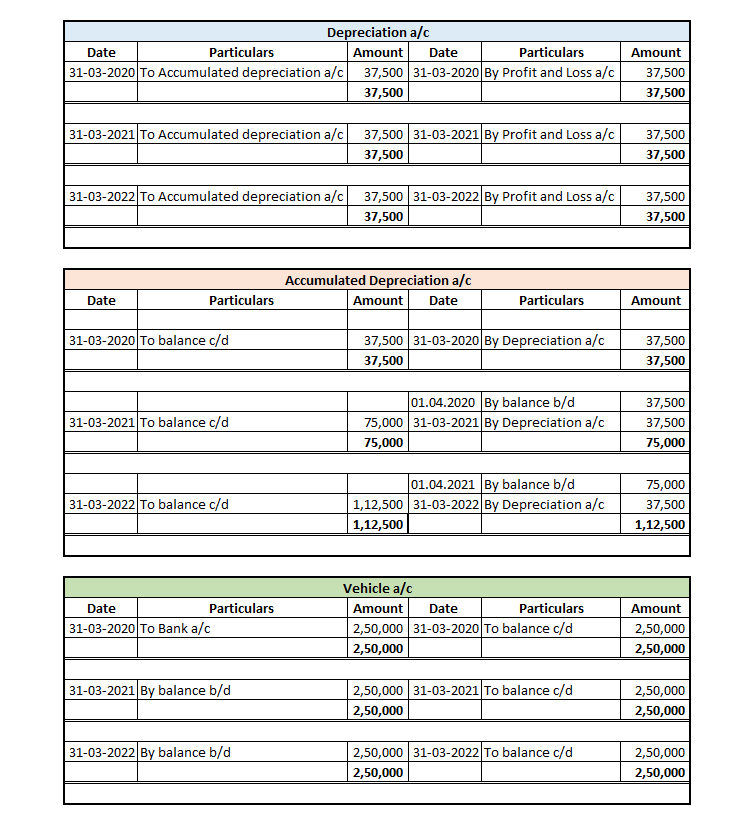
Mr A purchased a lorry for ₹1,00,000 on 1st April 2021 for his business, to be used for transportation of the finished goods. Now, Mr A decided to charge depreciation on the WDV method @30% (prescribed rate is 40%).
Following will be the journal entries.
I hope I was able to answer your question.
See less
Plant and Machinery are the equipment attached to the earth that supports the manufacturing of the company or its operations. These are tangible non-current assets to the company and as a result, have a debit balance. Depreciation is the decrease in the value of an asset that is spread over the expeRead more
Plant and Machinery are the equipment attached to the earth that supports the manufacturing of the company or its operations. These are tangible non-current assets to the company and as a result, have a debit balance.
Depreciation is the decrease in the value of an asset that is spread over the expected life of the asset. Not depreciating an asset presents a false image of the company as the asset is recorded at a higher value and profit is overstated as depreciation expense is not provided for.
There are two ways that a company provide depreciation:
For most of the depreciation methods, we need a rate to provide for depreciation every year. Now, for accounting purposes, the management can use a rate they think is suitable depending on the use and expected life of the machinery.
Depreciation is calculated on the basis of the Companies act, 2013 for the purpose of book-keeping. According to Schedule 2 of the Companies Act, depreciation on plant and machinery is calculated on the basis of either SLM or WDV.
Plant and machinery for those special rates are not assigned useful life is considered to be 15 years and depreciation is calculated @ 18.10% on WDV and @6.33% on SLM.
According to the Income Tax Act, 15% depreciation is provided every year on Plant and Machinery and, an additional 20% depreciation is provided in the first year of installation of machinery.
Depreciation on Machinery is charged on the basis of usage of such machinery. if it is used for 180 days or more then full depreciation is allowed and if it is used for less than 180 days then only 50% depreciation is allowed.
See less