Capital Redemption Reserve is a statutory reserve, which means it is mandatory for a company to create such reserve when it decides to redeem its preference shares. Capital Redemption Reserve cannot be utilised for any purpose other than the issue of bonus shares. Now let’s understand the reason behRead more
Capital Redemption Reserve is a statutory reserve, which means it is mandatory for a company to create such reserve when it decides to redeem its preference shares. Capital Redemption Reserve cannot be utilised for any purpose other than the issue of bonus shares.
Now let’s understand the reason behind it.
We know preference shares are those shares that carry some preferential rights:
- Dividend at a fixed rate
- Right to get repaid before equity shareholders in event of winding up of the company
- Other rights as specified in the Articles of Associations.
Also, unlike equity shares, preference shares are redeemable i.e. repaid after a period of time (which cannot be more than 20 years).
Generally, the creditors of a company have the right to be repaid first. So, in event of redemption of preference shares, the preference shareholders are repaid before creditors and the total capital of the company will but the total debt of the company is unaffected.
The gap between the debt and equity of the company will further widen and this will also increase the debt-equity ratio of the company. It will be perceived to be a risky scenario by the creditors and lenders of the company because the
So to protect the creditor and lender, Section 55 of the Companies Act comes to rescue.
Section 55 of the Companies Act ensure that the creditors and lenders of a company do not find themselves in a riskier situation when the company decides to redeem its preference shares by making it mandatory for a company to either
- issue new shares to fund the redemption of preference shares
OR
- create a capital redemption reserve if it uses profits for redemption
OR
- a combination of both
This will fill up the void created by the redemption of preference shares and the debt-equity ratio will remain unaffected. Keeping an amount aside in Capital Redemption Reserve ensures that such amount will not be used for dividend distribution and capital will be restored because it can be only used to issue bonus shares.
In this way the debt-equity ratio remains the same, the interest of the creditors and lenders secured.
Bonus shares are fully paid shares that are issued to existing shareholders at no cost.
Let’s take a numerical example for further understanding:
ABC Ltd wants to redeem its 1,000 9% Preference shares at a face value of Rs 100 per share. It has decided to issue 8,000 equity shares @Rs 10 per share and use the profit and reserves to fund the deficit.
The journal entries will be as follows:
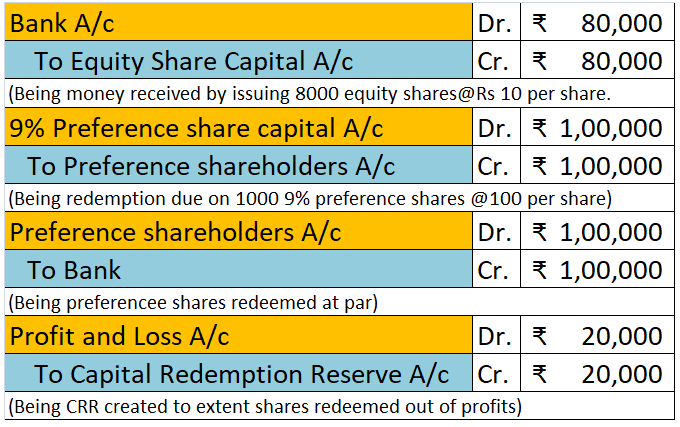
Working note: Rs
9% preference shares due for redemption (1,000 x 10) – 1,00,000
Less: Amount of new shares issued (8,000 x 10) – 80,000
Amount to be transferred to CRR 20,000
Hence, the reduction of total capital by Rs 1,00,000 due to the redemption of preference shares is reversed by issuing equity shares of Rs 80,000 and creating a Capital Redemption Reserve of Rs 20,000.
See less

Non-debt capital receipts As we're aware, there are two main sources of the government’s income — revenue receipts and capital receipts. Revenue receipts are all those receipts that neither create any liability nor cause any reduction in assets for the government, whereas, capital receipts are thoseRead more
Non-debt capital receipts
As we’re aware, there are two main sources of the government’s income — revenue receipts and capital receipts. Revenue receipts are all those receipts that neither create any liability nor cause any reduction in assets for the government, whereas, capital receipts are those money receipts of the government that either create a liability for a government or cause a reduction in assets.
Revenue receipts comprise both tax and non-tax revenues while capital receipts consist of capital receipts and non-debt capital receipts. Non-debt capital receipt is a part of capital receipt.
Definition
Non-debt capital receipts, also known as NDCR, are the taxes and duties levied by the government forming the biggest source of its income. Those receipts of the government lead to a decrease in assets, and not an increase in liabilities. It accounts for just 3% of the central government’s total receipts.
The union government usually lists non-debt capital receipts in two categories:
For Example – Disinvestment and recovery of loans are non-debt creating capital receipts.
See less