Debtors are treated as an asset. A debtor is a person or an entity who owes an amount to an enterprise against credit sales of goods and/or services rendered. When goods are sold to a person on credit that person is called a debtor because he owes that much amount to the enterprise. Debtors are consRead more
Debtors are treated as an asset.
A debtor is a person or an entity who owes an amount to an enterprise against credit sales of goods and/or services rendered.
When goods are sold to a person on credit that person is called a debtor because he owes that much amount to the enterprise.
Debtors are considered assets in the balance sheet and are shown under the head of current assets.
For example – Ram Sold goods to Sam on credit, Sam did not pay for the goods immediately, so here Sam is the debtor for Ram because he owes the amount to Ram. This amount will be payable at a later date.
Liabilities Vs Assets
Liabilities
It means the amount owed (payable) by the business. Liability towards the owners ( proprietor or partners ) of the business is termed internal liability. For example, owner’s capital, etc
On the other hand, liability towards outsiders, i.e., other than owners ( proprietors or partners ) is termed as an external liability.
For example creditors, bank overdrafts, etc.
Assets
An asset is a resource owned or controlled by a company. The benefit from the asset will accrue to the business in current and future periods. In other words, it’s something that a company owns or controls and can use to generate profits today and in the future.
For example – machinery, building, etc.
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business. They are readily realizable into cash.
In other words, we can say that the expected realization period of current assets is less than the operating cycle period.
For example, goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn a profit, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Why debtors are treated as assets?
Now let me explain to you why debtors are treated as assets and not as liabilities because of the following characteristics :
- We can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cycle period.
- Expected to be converted into cash in the normal course of business.
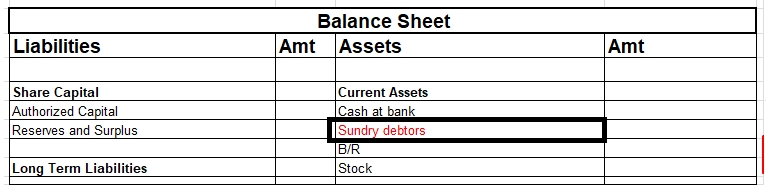
- In the business, debtors are treated as current assets which we can see on the asset side of the balance sheet.
- Debtors have a debit balance.
Conclusion
Now after the above discussion, I can conclude that debtors are considered to be an asset and not a liability.
See less
Effective Capital is an amount calculated for purpose of arriving at the maximum limit of managerial remuneration as per the Companies Act, 2013 where profit is inadequate or no profit. Other than that it has no use. Computation of effective capital is given in Explanation I to Schedule II of the CoRead more
Effective Capital is an amount calculated for purpose of arriving at the maximum limit of managerial remuneration as per the Companies Act, 2013 where profit is inadequate or no profit. Other than that it has no use.
Computation of effective capital is given in Explanation I to Schedule II of the Companies Act. Schedule II deals with remuneration payable to managers in case of no profit or inadequate profit in the following manner:
Computation of effective capital is done in the following manner:
Numerical example:
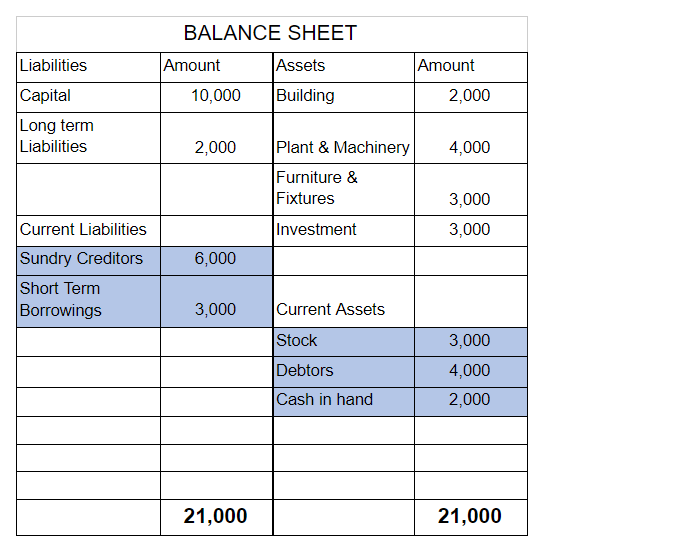
ABC Ltd reports its balance sheet as given below:
We will compute its effective capital for both an investment company and a non-investment company.

See less