Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
See lessPlease briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
Similarly, someone asked Are loose tools current assets
See lessDefinition Prepaid expenses are those expenses whose payments are done in advance which can be for the goods or services whose benefit will accrue in the subsequent accounting period. A prepaid expense is a current asset. prepaid expenses are classified under the head current assets in the balance sRead more
Prepaid expenses are those expenses whose payments are done in advance which can be for the goods or services whose benefit will accrue in the subsequent accounting period.
A prepaid expense is a current asset. prepaid expenses are classified under the head current assets in the balance sheet.
This is because they provide future economic benefits to the company. As such, they are assets that can be used to generate revenue in the future.
For example prepaid rent, prepaid insurance, etc.
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business.
Or in other words, we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cycle period although it is more than the period of 12 months from the date of the balance sheet.
For example, goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn a profit, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Current liabilities are liabilities that are payable generally within 12 months from the end of the accounting period or in other words which fall due for payment in a relatively short period.
For example bills payable, short-term loans, etc.
Now let me try to explain to you that prepaid expenses are classified as current assets and not as a current liability which is as follows :
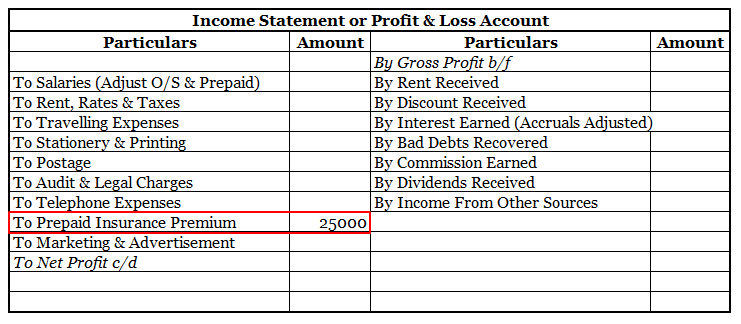
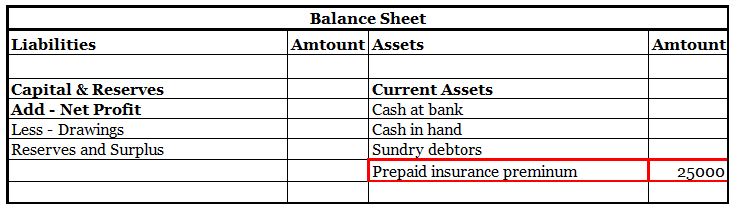
Now let us take an example for explaining prepaid expenses which are mentioned below.
An insurance premium of Rs 50000 has been paid for one year beginning (previous year). The financial year ends on 31st march YYYY.
It means the premium for 6 months i.e., 1st April, YYYY(current year) to 30th September, YYYY(current year) amounting to Rs 25000 is paid in advance.
Thus, of premium paid in advance (Rs 25000) is a Prepaid Expense. It will be accounted as an expense in the financial year ending 31st march next year. In the balance sheet as of 31st march YYYY ( current year ) it will be shown as Current Asset.
Here is an extract of the profit /loss account and balance sheet of the above example:
There are a few things to keep in mind when dealing with prepaid expenses.
See less
Accruals are not the same as provisions both are totally different from each other. Accruals and provision both are vital parts of accounts but work differently Accrual Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irreRead more
Accruals are not the same as provisions both are totally different from each other. Accruals and provision both are vital parts of accounts but work differently
Accrual
Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irrespective of the fact when such an amount has been paid.
An accrual of the expenditure which is not paid will be listed in the books of accounts. These accruals can be further divided into two parts
Accrual Expense
Accrual Expense means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be paid on a later period.
For example- 10,000 for the month of March was paid in April month then this rent will be accounted for in the books in March
These are the following accrued expense
Accrual Revenue
Accrual Revenue means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be received on later period. For example- If interest of 10,000 on bonds for the period of March is received in April months then this amount will be accounted for in March. These are the following accrued revenue
PROVISIONS
Provision refers to making a provision/allowance against any probable future expense that the company might incur in the near future. This amount is uncertain and difficult to predict its surety.
However, as per the prudence concept of accounting a company needs to anticipate the losses that will incur in the near future due to which provision is made.
For example- A company has debtors of 10,000 but as per the company’s previous records company anticipates that 1% of debtors will become bad debts. So in this case company will make a provision of 1% that is 100 on it.
There are various types of provisions which are-
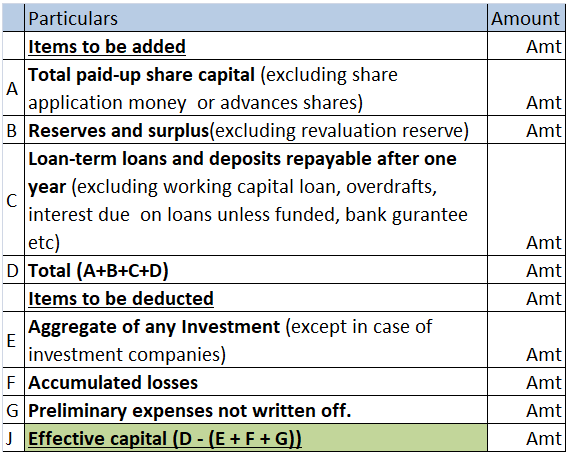
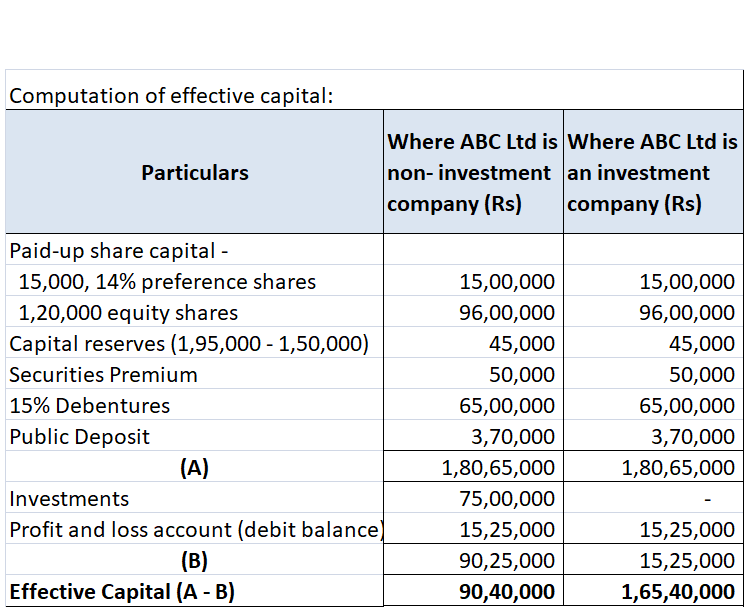
Effective Capital is an amount calculated for purpose of arriving at the maximum limit of managerial remuneration as per the Companies Act, 2013 where profit is inadequate or no profit. Other than that it has no use. Computation of effective capital is given in Explanation I to Schedule II of the CoRead more
Effective Capital is an amount calculated for purpose of arriving at the maximum limit of managerial remuneration as per the Companies Act, 2013 where profit is inadequate or no profit. Other than that it has no use.
Computation of effective capital is given in Explanation I to Schedule II of the Companies Act. Schedule II deals with remuneration payable to managers in case of no profit or inadequate profit in the following manner:
Computation of effective capital is done in the following manner:
ABC Ltd reports its balance sheet as given below:
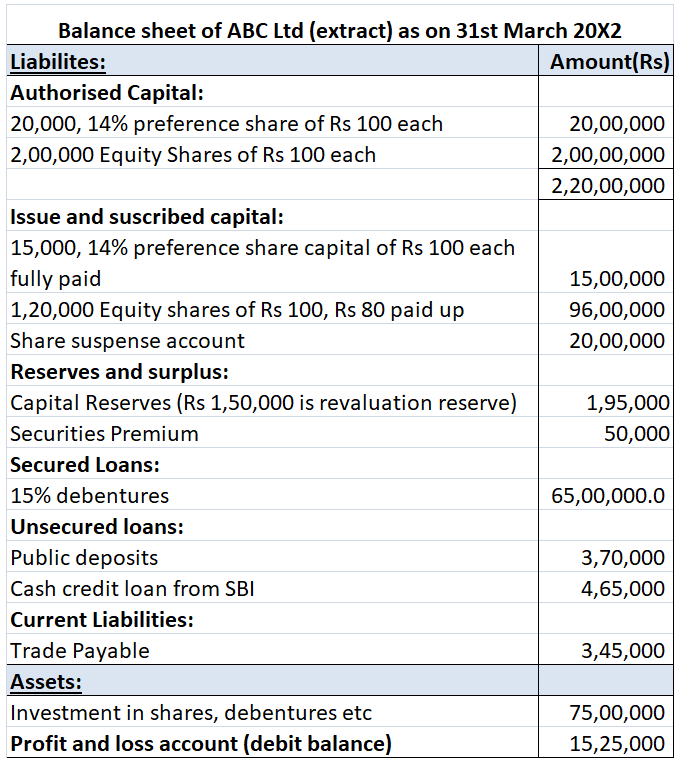
We will compute its effective capital for both an investment company and a non-investment company.
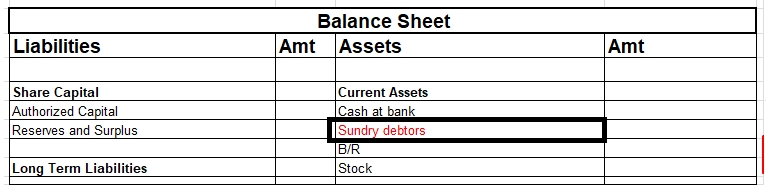
Debtors are treated as an asset. A debtor is a person or an entity who owes an amount to an enterprise against credit sales of goods and/or services rendered. When goods are sold to a person on credit that person is called a debtor because he owes that much amount to the enterprise. Debtors are consRead more
Debtors are treated as an asset.
A debtor is a person or an entity who owes an amount to an enterprise against credit sales of goods and/or services rendered.
When goods are sold to a person on credit that person is called a debtor because he owes that much amount to the enterprise.
Debtors are considered assets in the balance sheet and are shown under the head of current assets.
For example – Ram Sold goods to Sam on credit, Sam did not pay for the goods immediately, so here Sam is the debtor for Ram because he owes the amount to Ram. This amount will be payable at a later date.
Liabilities
It means the amount owed (payable) by the business. Liability towards the owners ( proprietor or partners ) of the business is termed internal liability. For example, owner’s capital, etc
On the other hand, liability towards outsiders, i.e., other than owners ( proprietors or partners ) is termed as an external liability.
For example creditors, bank overdrafts, etc.
Assets
An asset is a resource owned or controlled by a company. The benefit from the asset will accrue to the business in current and future periods. In other words, it’s something that a company owns or controls and can use to generate profits today and in the future.
For example – machinery, building, etc.
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business. They are readily realizable into cash.
In other words, we can say that the expected realization period of current assets is less than the operating cycle period.
For example, goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn a profit, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Now let me explain to you why debtors are treated as assets and not as liabilities because of the following characteristics :
Now after the above discussion, I can conclude that debtors are considered to be an asset and not a liability.
See lessPrepaid expenses are those expenses that have not been expired yet but their payment has already made in advance. There are many examples of prepaid expenses such as rent paid in advance, interest paid in advance, unexpired insurance You might be wondering what kind of account it is? As the name sugRead more
Prepaid expenses are those expenses that have not been expired yet but their payment has already made in advance. There are many examples of prepaid expenses such as rent paid in advance, interest paid in advance, unexpired insurance
You might be wondering what kind of account it is? As the name suggests it should be an expense but actually it’s an asset. When we initially record prepaid expenses we consider them as current assets and show them in the balance sheet. It turns out to be an expense when we use the service/item for what we have paid for in advance.
The entry for the above explanation is as follows:
From the modern rule, we know Assets and expenses increased are debits while decrease in assets and expenses are credit.
As this is asset, increase in asset therefore we debit prepaid expense and on the other hand we pay cash/ bank on behalf of that asset in advance hence there is decrease in assets hence credited. The entry will be as follows:
| Prepaid Expense A/c …….Dr | XXX | |
| To Cash/ Bank | XXX |
when this prepaid expense actually becomes expense we pass the adjusting entry. The entry will be as follows:
| Expense A/c …….Dr | XXX | |
| To Prepaid expense | XXX |
Let me give you simple example of the above entry.
Suppose you pay advance rent of Rs 9,000 for six months for the space you haven’t used yet. So you need to record this as prepaid expense and show it on the asset side of the balance sheet under current assets. Since you paid for the same the entry would be as follows:
| Prepaid Rent A/c …….Dr | 9,000 | |
| To Cash/ Bank | 9,000 |
As each month passes we will adjust the rent with prepaid rent account. Since the rent was advanced for 6 months, therefore (9,000/6) Rs 1500 will be adjusted each month with the rent expense account. The adjustment entry will be:
| Rent A/c …….Dr | 1,500 | |
| To Prepaid rent | 1,500 |
The process is repeated until the rent is used and asset account becomes nil.
See less
Working capital is defined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities of a business. Current assets include cash, debtors and stock whereas current liabilities include creditors and short term loans etc. FORMULA Current Assets - Current Liabilities = Working Capital Zero workinRead more
Working capital is defined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities of a business. Current assets include cash, debtors and stock whereas current liabilities include creditors and short term loans etc.
Current Assets – Current Liabilities = Working Capital
Zero working capital is when a company has the exact same amount of current assets and current liabilities. When both are equal, the difference becomes zero and hence the name, Zero working capital. Working Capital may be positive or negative. When current assets exceed current liabilities, it shows positive working capital and when current liabilities exceed current assets, it shows negative working capital.
Zero working capital can be operated by adopting demand-based production. In this method, the business only produces units as and when they are ordered by the customers. Through this method, all stocks of finished goods will be eliminated. Also, raw material is only ordered based on the amount of demand.
This reduces the investment in working capital and thus the investment in long term assets can increase. The company can also use the funds for other purposes like growth or new opportunities.
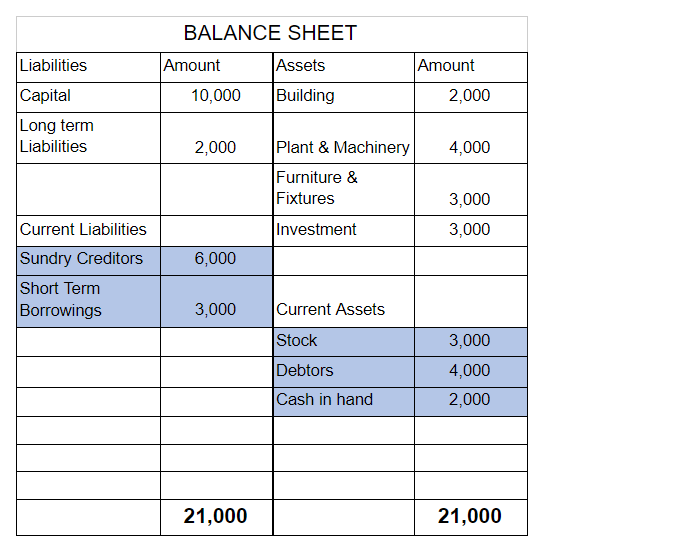
Suppose a company has Inventory worth Rs 3,000, Debtors worth Rs 4,000 and cash worth Rs 2,000. The creditors of the company are Rs 6,000 and short term borrowings are Rs 3,000.
Now, total assets = Rs 9,000 ( 3,000 + 4,000 + 2,000)
And total liabilities = Rs 9,000 ( 6,000 + 3,000)
Therefore, working capital = 9,000 – 9,000 = 0
Profits earned by a firm are not completely distributed to its owners, some of the profits are retained for various purposes. Reserves are profits that are apportioned or set aside to use in the future for a specific or general purpose. Reserves follow the Conservative Principle of accounting. ReveRead more
Profits earned by a firm are not completely distributed to its owners, some of the profits are retained for various purposes. Reserves are profits that are apportioned or set aside to use in the future for a specific or general purpose. Reserves follow the Conservative Principle of accounting.
Revenue reserve is created from the net profits of a company during a financial year. Revenue reserve is created from revenue profit that a company earns from the daily operations of the business.
Various types of reserves are:
Different parts of profit are apportioned to create a different reserve and those reserves can only be used for purposes as defined.
While accounting for Revenue Reserve, the profit decided to transfer to Revenue Reserve are first transferred to Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and then to Revenue Reserve Account. In the balance sheet, Revenue Account is shown under the Capital and Reserves head.
| Liabilities | Amount | Amount |
| Share Capital | ||
| Reserve and Surplus | ||
| General Reserve | ||
| Capital Redemption Reserve | ||
| Securities Premium Account | ||
| Profit and Loss Account |
Uses of Revenue Reserve:
Example:
Given that Revenue Reserve Account stands at Rs 1,00,000 and the company wants to distribute Rs. 40,000 as dividend to its shareholders. The treatment of this transaction in the financial statements will be-
Particulars Amount (Rs.)
Revenue Reserve Account 1,00,000
(less) Dividend distributed (40,000)
The amount shown in Balance Sheet 60,000
See less
Yes, non-current assets are also known as fixed assets. These are long-term assets that are not intended for sale but are used by a company in its business operations. Examples of non-current assets include property, plant, and equipment, as well as intangible assets like patents and trademarks. TheRead more
Yes, non-current assets are also known as fixed assets. These are long-term assets that are not intended for sale but are used by a company in its business operations.
Examples of non-current assets include property, plant, and equipment, as well as intangible assets like patents and trademarks. These assets are recorded on a company’s balance sheet and are reported at their historical cost or at their fair market value, depending on the type of asset.
See less
All expenses whose benefits are received over the years or the expenses or losses that are to be written off over the years are classified as Deferred revenue expenses. It includes fictitious expenses like preliminary expenses, loss on issue of debentures, advertising expenses, loss due to unusual oRead more
All expenses whose benefits are received over the years or the expenses or losses that are to be written off over the years are classified as Deferred revenue expenses. It includes fictitious expenses like preliminary expenses, loss on issue of debentures, advertising expenses, loss due to unusual occurrences like loss due to fire, theft, and research and development expenses, etc.
DEFERRED REVENUE EXPENSES
There are certain expenses which are revenue in nature (i.e. expenses incurred to maintain the earning capacity of the firm and generate revenue) but whose benefits are received over a period of years generally between 3 to 7 years. It means its benefit is received not only in the current accounting period but over a few consecutive accounting periods.
CHARACTERISTICS
EXAMPLES
ADVERTISING EXPENSES refers to the expenses incurred for promoting the goods or services of the firm through various channels like TV, Social media, Hoardings, etc.
As the benefit of advertising is not received not only in the period when such expenses were incurred but also in the coming few years, it is classified as Deferred revenue expense.
For example – Suppose the company incurred $10 lakh on advertising to introduce a new product in the market and estimated that its benefit will last for 4 years. In this case, $250,000 will be written off every year, for 4 consecutive years.
EXCEPTIONAL LOSSES are losses that are incurred because of some unusual event and don’t happen regularly like loss from fire, theft, earthquake, flood or any other natural disaster, confiscation of property, etc.
Since these losses can’t be written off in the year they occurred they are also treated as Deferred revenue expenditure and are written off over the years.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT EXPENSES are expenses incurred on researching and developing new products or improving the existing ones. Its benefits are received for many years and thus are classified as Deferred revenue expenses.
For example – Expenses incurred on the creation of intangible assets like patents, copyrights, etc.
PRELIMINARY EXPENSES are those expenses which are incurred before the incorporation and commencement of the business. It includes legal fees, registration fees, stamp duty, printing expenses, etc.
These expenses are fictitious assets and are written off over the years.
TREATMENT
It is debited to the P&L amount (amount written off that year) and the remaining amount on the Aeest side of the Balance Sheet.
In the above example of advertising expenses, in Year 1, $250,000 will be debited in the P&L A/c and the remaining amount of $750,000 is shown on the Asset side of the Balance Sheet.
In Year 2, $250,00 in P&L A/c and the remaining $500,000 in Balance Sheet.
In Year 3, $250,000 in P&L A/c and the remaining $250,000 in the Balance Sheet and in the last Year 4, only the remaining amount of $250,000 in P&L A/c and nothing in the Balance Sheet.
See less