Yes, Capital Work in Progress is Tangible Asset. To attain an understanding of the same, we first need to understand what are tangible assets. Assets that have a physical existence, that is they can be seen, touched are called Tangible Assets. Capital work in progress is the cost incurred on fixed aRead more
Yes, Capital Work in Progress is Tangible Asset.
To attain an understanding of the same, we first need to understand what are tangible assets. Assets that have a physical existence, that is they can be seen, touched are called Tangible Assets.
Capital work in progress is the cost incurred on fixed assets that are under construction as on the balance sheet date. Since the asset cannot be used for operation it cannot be classified as a Fixed Asset.
For example:
If an asset takes 1.5 years to be constructed as on 1.4.2020 then on the balance sheet date 31.3.2021, the cost incurred on the asset will be classified as Capital Work in Progress.
Common examples of Capital Work in Progress include immovable assets like Plant and Machinery, Buildings.
It is shown under the head Non-Current Assets in the balance sheet. Examples of cost included in Capital Work in Progress can be:
- Advance payment to the contractor
- Material used/purchased
- Cost of labor incurred, etc.
Since the assets under the head Capital Work in Progress are in the process of completion and not completed, hence they are not depreciable until completed. Once the asset is completed it is moved under the head Fixed Assets.
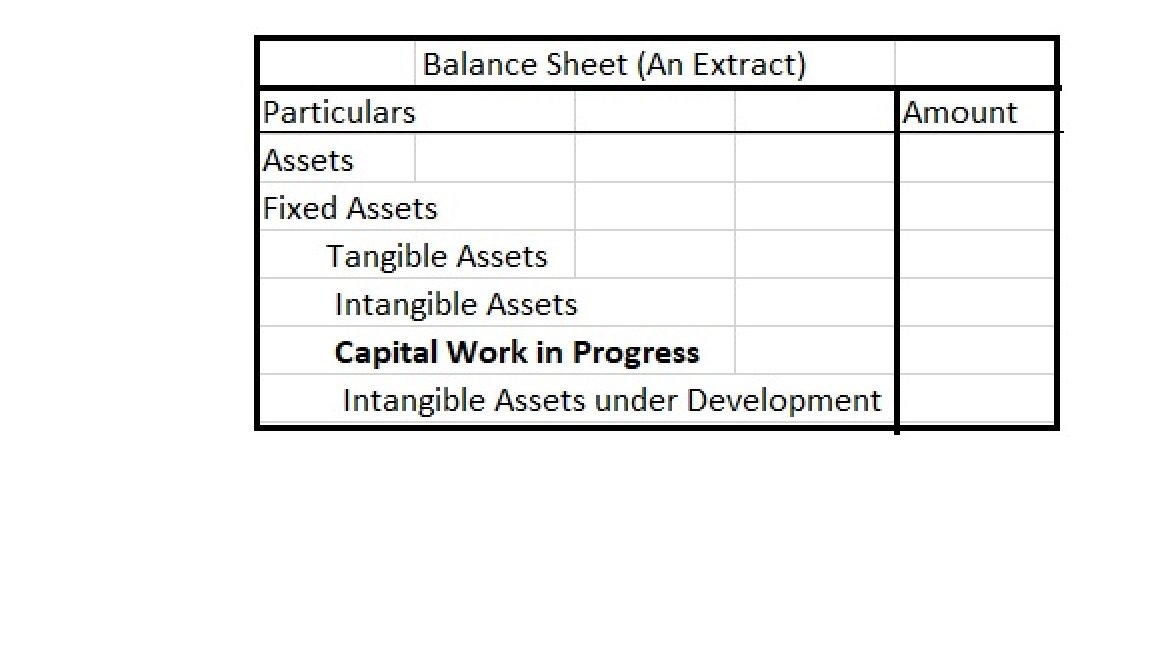
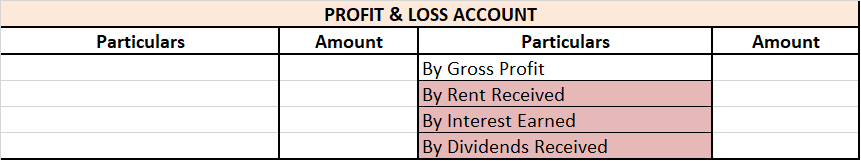
Capital Work in Progress is shown in the Balance Sheet as:

Simply explaining the meaning of the useful life of an asset, it is nothing but the number of years the asset would remain in the business for purpose of revenue generation, making it more simple, the amount of time an asset is expected to be functional and fit for use. It is also called economic lRead more
Simply explaining the meaning of the useful life of an asset, it is nothing but the number of years the asset would remain in the business for purpose of revenue generation, making it more simple, the amount of time an asset is expected to be functional and fit for use. It is also called economic life or service life
It is a useful concept in accounting as it is used to work out depreciation. By knowing this useful life of an asset an entity can easily analyze how to allot the initial cost of an asset across the relevant accounting period rather than doing it unfairly manner.
How do we calculate the useful life of an asset?
The useful life of an asset is not an accounting policy, but an accounting estimate. calculating useful life is not an exact phenomenon but an estimate that is done because it directly impacts how much an asset is to expense every year.
Factors affecting “how long an asset is expected to be useful” depends on some stated points as below:
As per the companies act 2013, some of the useful life of assets are stated below
To know more about the different categories of assets you can follow the given link useful life of assets.
POINT TO BE NOTED:- There lies a huge difference in the useful life v/s the physical life of an asset. It is very important to note that amount of time an asset is used in a business is not always be same as an asset’s entire life span.
See less