RECEIPTS AND PAYMENTS ACCOUNT OF BHARTI CLUB for the year ended 31st March, 2019 Receipts Amount Payments Amount To Balance b/d 10,500 By Salary 25,000 To Subscriptions 70,500 By Travelling Expenses 4,000 To Donations 5,000 By Stationery ...
Before answering your question directly, let’s first understand the two terms, ‘Rent Outstanding’ and ‘Accounting Equation’. Accounting Equation Accounting Equation depicts the relationship between the following items of a business: Assets, Liabilities and Owner’s Equity ( Capital ) It is a simple fRead more
Before answering your question directly, let’s first understand the two terms, ‘Rent Outstanding’ and ‘Accounting Equation’.
Accounting Equation
Accounting Equation depicts the relationship between the following items of a business:
- Assets,
- Liabilities and
- Owner’s Equity ( Capital )
It is a simple formula that implies that the total assets of a business are always equal to the sum of its liabilities and Owner’s Equity (Capital).
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + CAPITAL OR A = L + E
It is also known as the balance sheet equation.
This equation always holds good due to the double-entry system of accounting i.e. every event has a dual effect on items of the balance sheet.
Outstanding Rent
We know rent is an expense for a business and rent outstanding means that rent is due, not paid which implies it is a liability which the business has to settle.
Hence Rent Outstanding is subtracted from the capital balance and added to liabilities.
Let’s take an example to see how rent outstanding affects the accounting equation. Suppose a business has the following figures:
Assets – Rs: 3,00,000
Capital – Rs: 2,00,000
Liabilities – Rs: 1,00,000
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
3,00,000 = 1,00,000 + 2,00,000
Now if Rent outstanding of Rs: 20,000 arises, this will happen:-
Assets – Rs: 3,00,000
Capital – Rs: 2,00,000 – Rs: 20,000 = Rs: 2,80,000
Liabilities – Rs: 1,00,000 + Rs: 20,000 = Rs: 1,20,000
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
3,00,000 = 1,20,000 + 2,80,000.
Hence, when rent outstanding arises, it increases the liability and decreases the Capital by the same amount. Therefore both the sides tally and the accounting equations holds good.
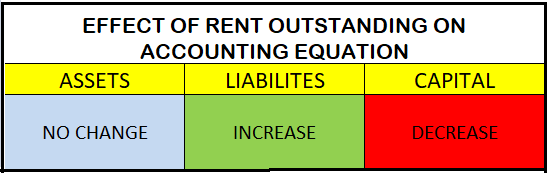
Rent Outstanding is shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet. Also, the rent outstanding of the current year is shown in the debit side profit and loss account and we know the balance of the P/L account if profit, is added to Capital and in case of loss it is subtracted from Capital. Hence, the rent outstanding is subtracted from the capital.
I hope my answer was useful to you.
See less



Here I have prepared the Income & Expenditure A/c and Balance Sheet of Bharti Club: Income & Expenditure A/c for the year ended 31st March 2019 Expenditure Amt Income Amt To Salary 25,000 By Subscriptions (WN 1) 69,900 To Travelling Expenses 4,000 By Donations Read more
Here I have prepared the Income & Expenditure A/c and Balance Sheet of Bharti Club:
Income & Expenditure A/c for the year ended 31st March 2019
Balance Sheet as on 31st March 2019
Working Note 1: Calculation of Subscriptions
Working Note 2: Calculation of Capital Fund
We prepare the previous year’s balance sheet of Bharti Club to identify the capital.
Balance Sheet as on 31st March 2018