A Consignment Account is a Nominal Account. It is classified as a nominal A/c because it is prepared to ascertain the profit earned or loss incurred on the consignment. The accounting rule applied to consignment A/c: Debit all Expenses & Losses and Credit all Incomes & Gains. As per the modeRead more
A Consignment Account is a Nominal Account. It is classified as a nominal A/c because it is prepared to ascertain the profit earned or loss incurred on the consignment.
The accounting rule applied to consignment A/c: Debit all Expenses & Losses and Credit all Incomes & Gains.
As per the modern rules, there is no clear-cut classification of consignment A/c. It is prepared from the perspective of the consignor, hence it cannot be outrightly classified as an expense/revenue.
In the context of accounting, consignment refers to an arrangement of goods wherein the consignor sends the goods to the consignee so that the consignee can sell/distribute the goods on behalf of the consignor.
The relationship between the consignor and consignee is that of a principal and agent. The consignee gets a commission for his services.
You should keep in mind that the consignee does not get ownership of the goods even though the goods are in his possession. The ownership remains with the consignor till the sale is made. On sale, the buyer will become the owner.
A Consignment A/c is an account prepared to record the transactions happening in a consignment business. This account is maintained by the consignor. It shows the profit earned or loss incurred by the consignor on a specific consignment.
A consignor may send goods to more than one consignee. In such a case, a separate consignment A/c is prepared for each consignment.
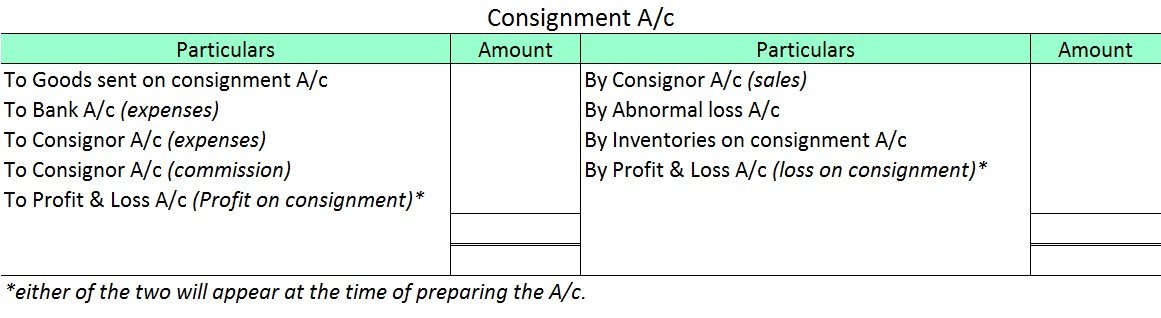
The following items appear on the debit side of the consignment A/c:
- Cost of goods sent on consignment.
- Expenses incurred by the consignor (freight, insurance, etc.)
- Expenses paid by the consignee (storage and warehousing, marketing expenses, packaging and selling expenses, etc.)
- Bad debts in consignment.
- Commission paid to consignee.
The entries appearing on the credit side of the consignment A/c are as follows:
- Gross sales.
- Abnormal loss of goods.
- Inventories on consignment (stock in transit).
The balance in the consignment A/c represents the profit or loss made on the consignment. It is transferred to the P&L A/c and the account is closed.
Below is the format for Consignment A/c:

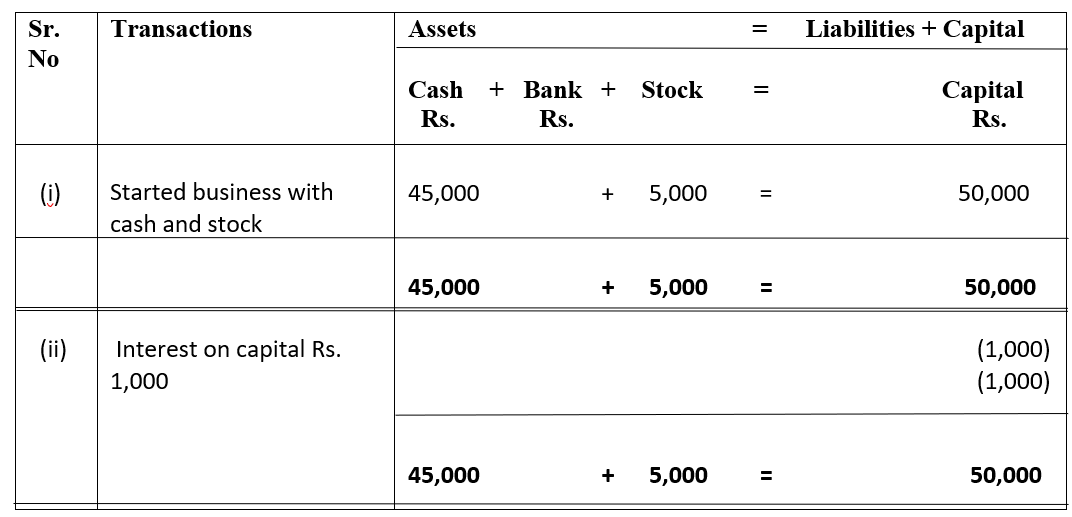
There are two types of ledger accounts in the accounting system – temporary and permanent. Temporary accounts are those whose balances zero out and we do not carry forward balances to the next year. Examples are revenue and expenses accounts or nominal accounts. The balances of such accounts are traRead more
There are two types of ledger accounts in the accounting system – temporary and permanent.
Temporary accounts are those whose balances zero out and we do not carry forward balances to the next year. Examples are revenue and expenses accounts or nominal accounts. The balances of such accounts are transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore are not balanced.
Permanent accounts are those whose balances are carried forward to the next accounting year in form of opening balances. These accounts are balanced and such balances are transferred to the balance sheet. Examples are assets, liability and capital accounts or personal and real accounts.
Balancing an account means equaling both the debit and the credit side of the account. Generally, there is a difference between the accounts recorded as a carry down balance in the case of permanent accounts and as a transfer balance in the case of temporary accounts.
Balancing serves as a check to the double-entry rule of accounting.
Balanced accounts
As discussed above, the balanced accounts are shown in the balance sheet and the balancing figure for such accounts are carried forward to the next accounting period.
Unbalanced accounts
As per the above discussion, the balancing figures of unbalanced accounts are transferred to the profit and loss account and no balances are carried forward to the next accounting period.
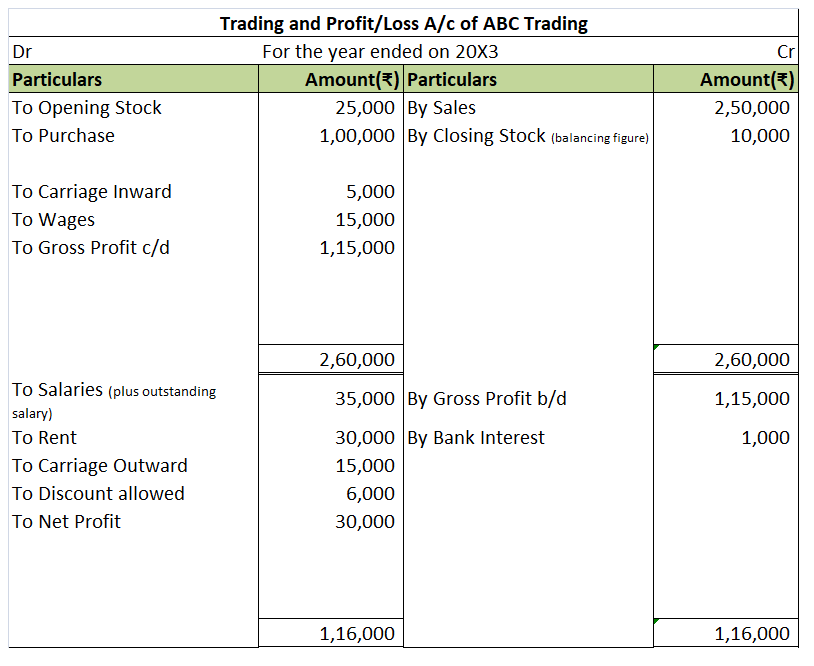
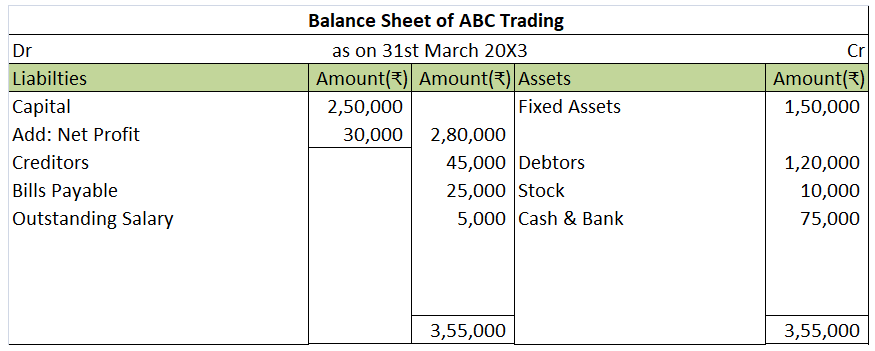
Suppose a company Shine Ltd. has machinery costing 5,00,000 at the beginning of the accounting period and charges depreciation of 10% on the asset. The company also has creditors amounting to 50,000 at the beginning of the period and purchases goods amounting to 30,000 on credit. It has a cash balance of 95,000 at the beginning of the period and earns interest amounting to 10,000.
Following ledgers would be prepared to record the above entries:
The above ledgers can be shown as follows:
The balance of the machinery account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore depreciation account is an unbalanced account.
The balance of creditors account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore purchases account is an unbalanced account.
The balance of the cash account will be shown in the balance sheet and therefore it is a balanced account.
The balance is transferred to the profit and loss account and therefore interest account is an unbalanced account.
See less