Accruals are not the same as provisions both are totally different from each other. Accruals and provision both are vital parts of accounts but work differently Accrual Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irreRead more
Accruals are not the same as provisions both are totally different from each other. Accruals and provision both are vital parts of accounts but work differently
Accrual
Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irrespective of the fact when such an amount has been paid.
An accrual of the expenditure which is not paid will be listed in the books of accounts. These accruals can be further divided into two parts
Accrual Expense
Accrual Expense means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be paid on a later period.
For example- 10,000 for the month of March was paid in April month then this rent will be accounted for in the books in March
These are the following accrued expense
- Accrual Rent– Accrual rent means the amount for using the land of the landlord is paid at a later period than the period when it is put into use.
- Insurance– Accrual insurance means the amount paid as a premium to the insurance company paid on a later period than the period when it is due
- Expense- Acrrual expense means the amount for any expense paid on a later period then the period when it pertains to be paid
- Wages- Accrual wages means the amount which is paid to employees on a later period than the period when the wages get due
Accrual Revenue
Accrual Revenue means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be received on later period. For example- If interest of 10,000 on bonds for the period of March is received in April months then this amount will be accounted for in March. These are the following accrued revenue
- Accrual Rent– Accrual rent means the amount for using the land of an entity by another party is received on a later period than the period when it was put into use.
- Accrued Interest– Accrued interest means the amount of interest received on a later period than the period when it pertains to receive
PROVISIONS
Provision refers to making a provision/allowance against any probable future expense that the company might incur in the near future. This amount is uncertain and difficult to predict its surety.
However, as per the prudence concept of accounting a company needs to anticipate the losses that will incur in the near future due to which provision is made.
For example- A company has debtors of 10,000 but as per the company’s previous records company anticipates that 1% of debtors will become bad debts. So in this case company will make a provision of 1% that is 100 on it.
There are various types of provisions which are-
- Provision on Depreciation– Provision for Depreciation means a provision for future depletion of assets has been already created
- Provision for Doubtful Debts– Provision for Doubtful Debts means a provision created against debtors that doesn’t seem to be recovered in the near future

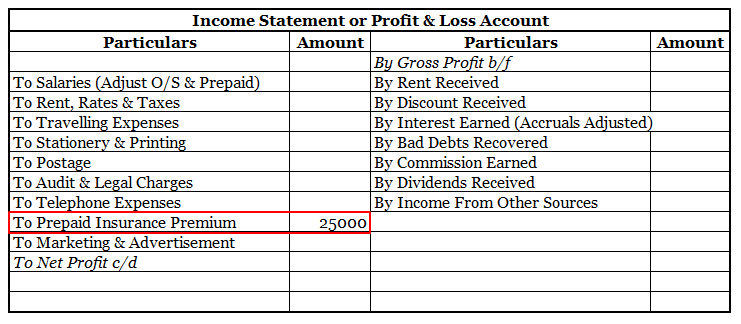
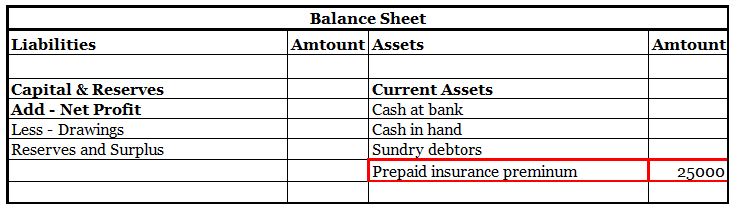
Definition Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable. Bad debts will be treated in the following ways : On the debit side of the profit and loss account. In the curreRead more
Definition
Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable.
Bad debts will be treated in the following ways :
On the debit side of the profit and loss account.
In the current assets side of the balance sheet, these are deducted from sundry debtors.
For example loans from banks are declared as bad debt, sales made on credit and amounts not received from customers, etc.
Now I will show you an extract of the profit and loss account and balance sheet
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or the rendering of services in the ordinary course of business.
For example, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Current liabilities are defined as liabilities that are payable normally within 12 months from the end of the accounting period or in other words which fall due for payment in a relatively short period.
For example bills payable, short-term loans, etc.
Accounting treatment
Now let me try to explain to you the accounting treatment for bad debts which is as follows :
Reasons for bad debts
There are several reasons why businesses may have bad debts some of them are as follows:-
Accounting methods
There are two methods for accounting for bad debts which are mentioned below:-
Related terms
So there are a few related terms whose meanings you should know
See less