Capital Expenditure Revenue Expenditure Cash Expense Credit Expense
Here I've prepared the Income & Expenditure A/c. Income & Expenditure A/c for the year ended 31st March 2021 Expenditure Amt Income Amt To Salary 4,80,000 By Subscriptions 9,00,000 To Rent 50,000 By Donations 10,000 To Stationery 20,000 To Loss on sale ofRead more
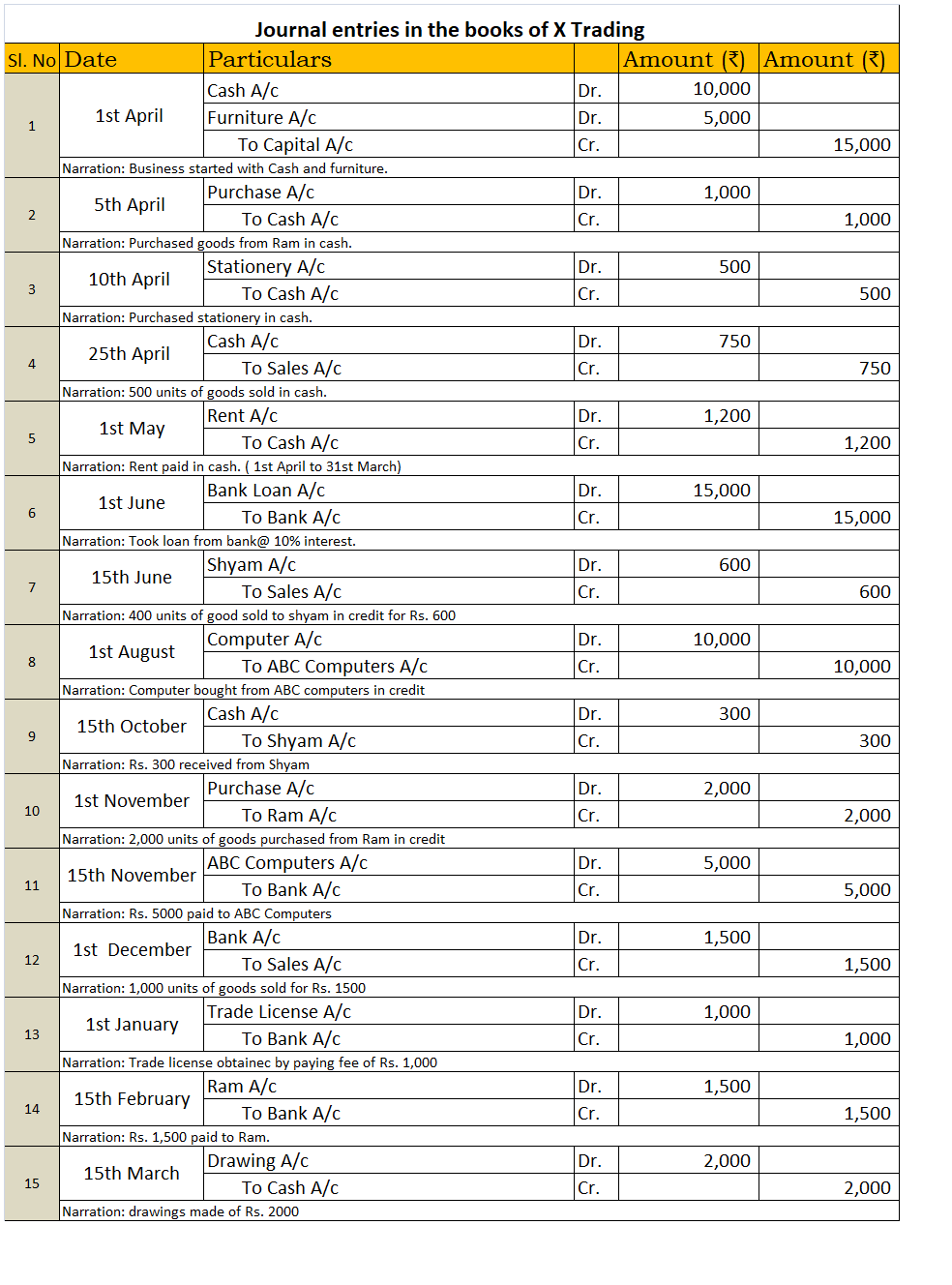
Here I’ve prepared the Income & Expenditure A/c.
Income & Expenditure A/c for the year ended 31st March 2021
| Expenditure | Amt | Income | Amt |
| To Salary | 4,80,000 | By Subscriptions | 9,00,000 |
| To Rent | 50,000 | By Donations | 10,000 |
| To Stationery | 20,000 | ||
| To Loss on sale of furniture (WN) | 10,000 | ||
| To Surplus | 3,50,000 | ||
| 9,10,000 | 9,10,000 |
Working Note: Calculation of Loss on sale of furniture
The following calculation is made to identify the loss incurred on the sale of furniture.
| Particulars | Amt |
| Book Value of Furniture | 40,000 |
| Less: Sale Value of Furniture | 30,000 |
| Loss on Sale of Furniture | 10,000 |
See less

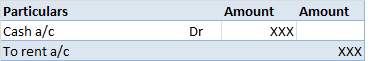
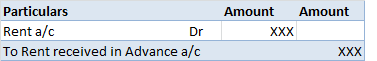
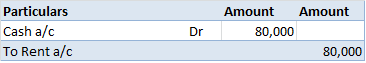
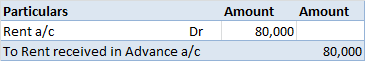
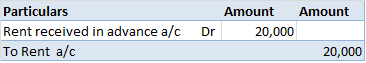
The correct answer is 2. Revenue Expenditure. An honorarium is a voluntary payment paid to a person for the services provided. It is a type of cost incurred for the expenses of guests and volunteers. This is a payment made to the person who is not an employee of the institution. Revenue expendituresRead more
The correct answer is 2. Revenue Expenditure. An honorarium is a voluntary payment paid to a person for the services provided. It is a type of cost incurred for the expenses of guests and volunteers. This is a payment made to the person who is not an employee of the institution.
Revenue expenditures are the short-term expenses and consumed within one accounting year and are also known as operating expenses.
Payment of honorarium to the secretary is treated as revenue expenditure because benefits from the expense are derived in the same accounting period. The honorarium is a type of outside expense and any outside expense is revenue in nature. It is a daily allowance incurred to cover the hotel/stay expense.
Payment of honorarium to the secretary is shown on the Expenditure side of the Income and Expenditure Account.
Capital Expenditure is the expense incurred on acquiring an asset and honorarium cannot be a capital expenditure as benefits derived from it cannot be carried forward to the next year.
It cannot be treated as cash or credit expense although it is paid in cash or credit. In this case, it will be treated as a revenue expense while preparing financial statements.
Payment of honorarium is mainly a topic of not-for-profit organizations.
See less