Fictitious assets are not actually assets. They are expenses/losses not written off in the year in which they are incurred. They do not have any physical presence. Their expense is spread over more than one accounting period. A part of the expense is amortized/written off every year against the compRead more
Fictitious assets are not actually assets. They are expenses/losses not written off in the year in which they are incurred. They do not have any physical presence. Their expense is spread over more than one accounting period.
A part of the expense is amortized/written off every year against the company’s earnings. The remaining part (which is yet to be written off) is shown as an asset in the balance sheet. They are shown as assets because these expenses are expected to give returns to the company over a period of time.
Here are some examples of fictitious assets:
- Preliminary expenses.
- Promotional expenses.
- Loss incurred on the issue of debentures.
- Underwriting commission.
- Discount on issue of shares.
To make it simple I’ll explain the accounting treatment of preliminary expenses with an example.
The promoters of KL Ltd. paid 50,000 as consultation fees for incorporating the company. The consultation fee is a preliminary expense as they are incurred for the formation of the company. The company agreed to write off this expense over a period of 5 years.
At the end of every year, the company will write off 10,000 (50,000/5) as an expense in the Profit & Loss A/c.
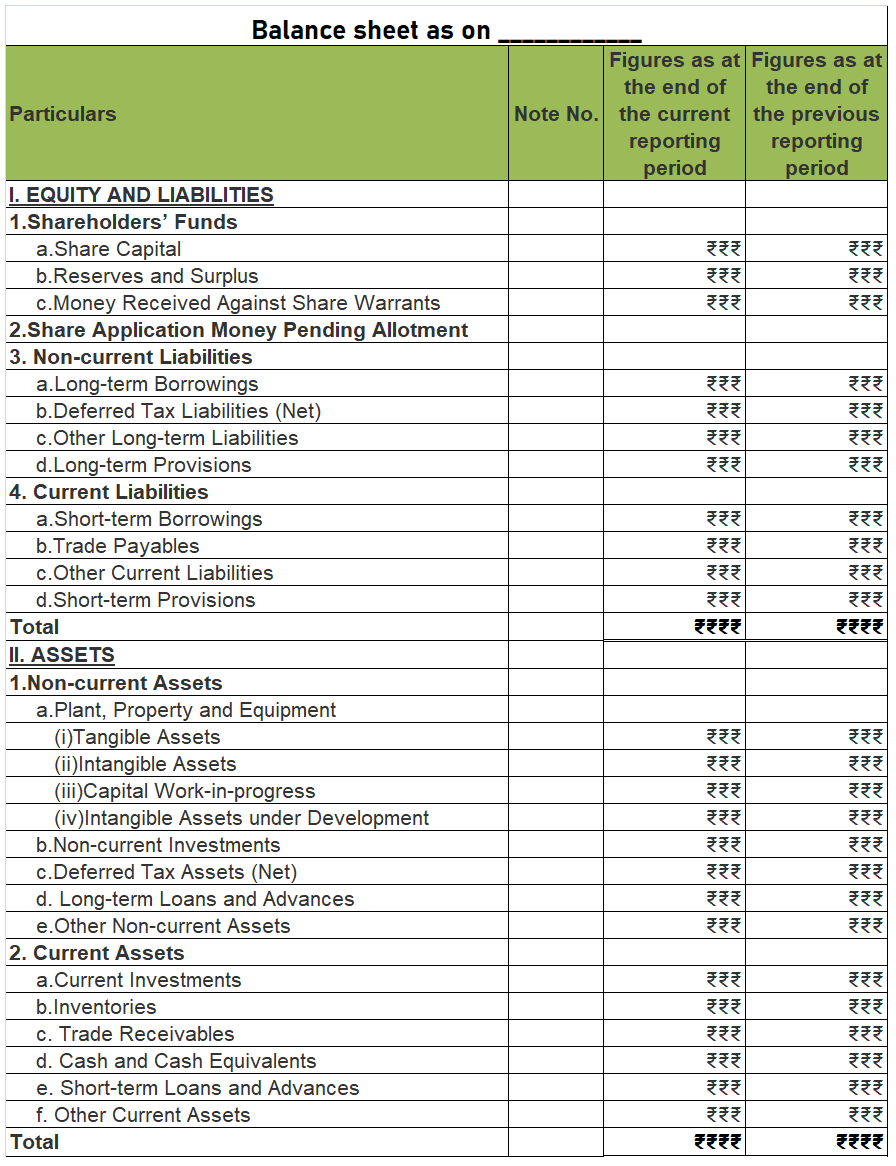
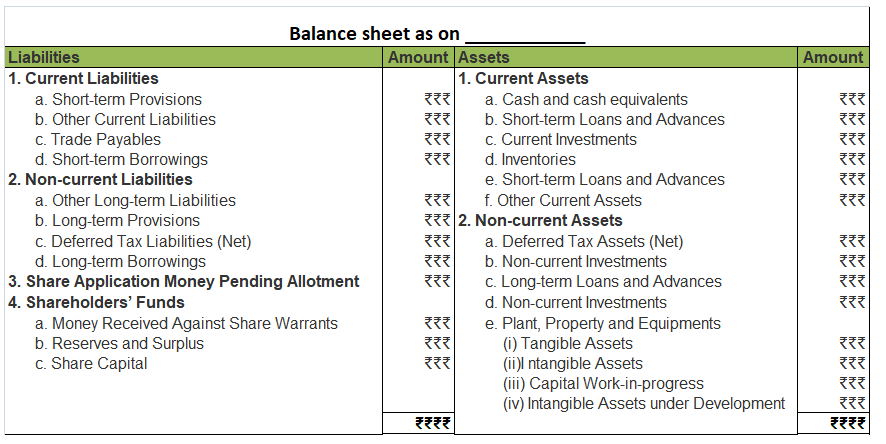
The remaining portion i.e. 40,000 (50,000 – 10,000) will be shown on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet under the head Non – Current Assets and sub-head Other Non – Current Assets.
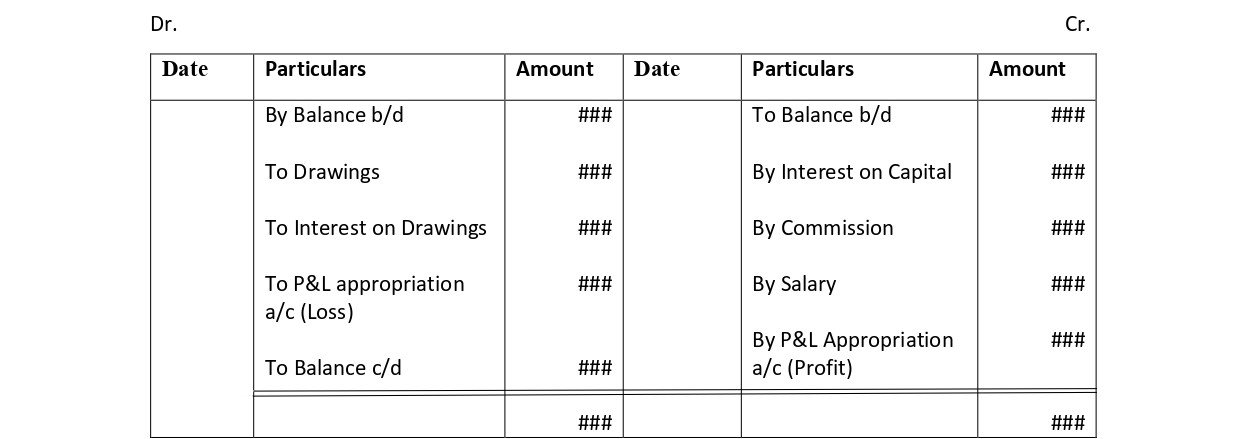
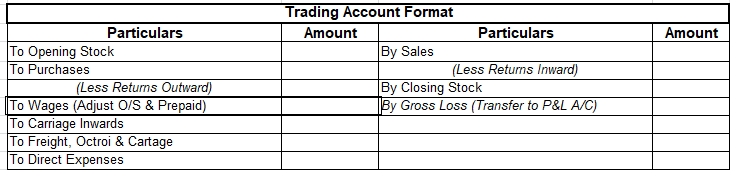
Here are the financial statements of KL Ltd.,
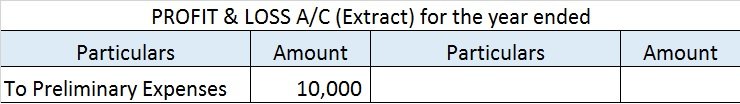
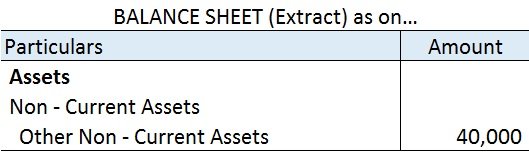
Note: As per AS 26 preliminary expenses are fully written off in the year they are incurred. This is because such expenses do not meet the definition of assets and must be written off in the year of incurring.
Source: Some fictitious assets examples are from Accountingcapital.com & others from Wikipedia.
See less

One of the main purposes of accounting is to provide financial data to its users so that decisions are taken at an appropriate time. These users of accounting information are broadly classified into (a) internal users and (b) external users. Since the question concentrates on internal users I’ll beRead more
One of the main purposes of accounting is to provide financial data to its users so that decisions are taken at an appropriate time. These users of accounting information are broadly classified into (a) internal users and (b) external users. Since the question concentrates on internal users I’ll be explaining internal users of accounting information in detail.
Internal users are people within an organization/business who need accounting information to make day-to-day decisions.
The various internal users of accounting information include:
Owners are the people who contribute capital to the business and therefore they are interested to know the profit earned or loss incurred by the business as well as the safety of their capital. In the case of a Sole Proprietorship, the proprietor is the owner of the business. In the case of a Partnership, the partners are considered as the owners of the firm.
The use for them: To know how the business is doing financially, owners need to know the profit and loss reflected in the financial statements.
Management is responsible for setting objectives, formulating plans, taking informed decisions, and ensuring that pre-planned objectives are met within the stipulated time period.
The use for them: To achieve objectives, management needs accounting information to make decisions related to determining the selling price, budgeting, cost control and reduction, investing in new projects, trend analysis, forecasting, etc.
Employees and workers are the ones who implement the plans set by the management. Their well-being is dependent on the profitability of the business.
The use for them: They are interested to check the financial statements so that they can get a better knowledge of the business. Some organizations also give their employees a share in their profits in the form of a bonus at the year-end. This also creates an interest in the employees to check the financial statements.
See less