No, Goodwill cannot be called a fictitious asset. A fictitious asset does not have any physical existence or realizable value. Although it is recorded in the assets column, it is not really an asset, rather it is an expense that is incurred during the accounting period. Its benefit, however, is realRead more
No, Goodwill cannot be called a fictitious asset.
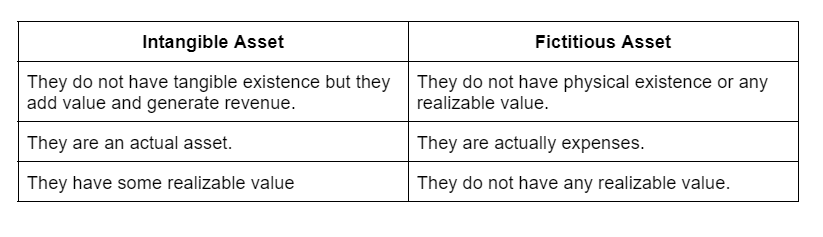
A fictitious asset does not have any physical existence or realizable value. Although it is recorded in the assets column, it is not really an asset, rather it is an expense that is incurred during the accounting period. Its benefit, however, is realized for extended periods. This is why they are recorded as assets. They are recorded in a single year and are amortized over the years. A fictitious asset is neither tangible nor intangible.
Examples of Fictitious Assets
- Preliminary expenses
- Promotional expenses
- Discount on issue of shares/debentures etc.
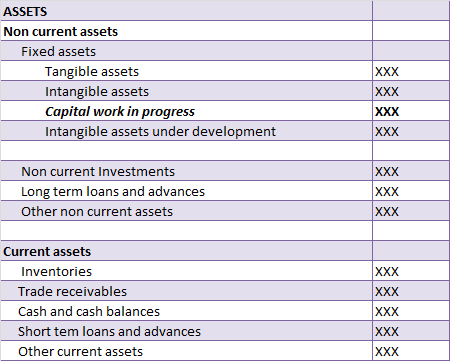
Now, goodwill is an intangible asset that relates to the purchase of a company. It is the amount that a company pays over the net worth of the company being purchased. This can be because of its brand value, good customer base, etc. As a company’s reputation improves, its goodwill increases accordingly. Therefore, It does not have a tangible existence but it does have a monetary value. They are also recorded on the asset side of the balance sheet under the head “Intangible assets”.
Reason for not being a fictitious asset
Since goodwill is an asset and not an expense, it cannot be called a fictitious asset. Moreover, goodwill has a realizable value. Unlike fictitious assets, goodwill can be purchased or sold. Therefore, goodwill is termed as an intangible asset but not a fictitious asset. The major difference between an intangible asset and a fictitious asset is:



The profits earned by a company are mainly divided into two parts: Dividend, and Retained Earnings The part of profit distributed to its shareholders is called a dividend. The part of the profit that the company holds for future expansion or diversification plans is called retained earnings. As theRead more
The profits earned by a company are mainly divided into two parts:
The part of profit distributed to its shareholders is called a dividend. The part of the profit that the company holds for future expansion or diversification plans is called retained earnings.
As the name suggests, retained earnings are the profit that is retained in the company. Retained earnings can be used for various purposes:
As the profits of the company belong to shareholders, retained earnings are considered as profits re-invested in the company by the shareholders.
The formula to calculate the cost of retained earnings is:
(Expected dividend per share / Net proceeds) + growth rate
The expected dividend per share is divided by net proceeds or the current selling price of the share, to find out the market value of retained earnings.
The growth rate is then added to the formula. It’s the rate at which the dividend grows in the company.
For example:
The net proceeds from share is Rs 100, expected dividend growth rate is 2% and expected dividend is 5.
Cost of retained earnings
= (Expected dividend per share / Net proceeds) + Growth rate
= (5 / 100) + 0.02
= 0.07 or 7%
See less