The correct option is 3.) The term current assets do not include furniture. Explanation A current asset is any asset that can reasonably be expected to be sold, consumed, or exhausted through the normal operations of a business within one accounting year. Thus, current assets don't have life for morRead more
The correct option is 3.)
The term current assets do not include furniture.
Explanation
A current asset is any asset that can reasonably be expected to be sold, consumed, or exhausted through the normal operations of a business within one accounting year. Thus, current assets don’t have life for more than a year.
Example: Cash and cash equivalent, stock, liquid assets, etc.
Furniture is expected to have a useful life for more than a year and they are bought for a long term by a company.
Cash is a more liquid asset of a company making it a more “current” asset. It requires no conversion and is spendable as it is. Thus, making it a vital current asset.
Stock in trade is a current asset because it can be converted into cash within one year and all the stock in trade of a company is expected to be sold within one accounting period and should not stick for a longer period.
Advance payment, on the other hand, is an amount paid to an employee, essentially a short-term loan by the employer. It’s recorded on the asset side of the balance sheet and as these assets are used, they are expended and recorded on the income statement for the period in which they are incurred, making it a short-term asset ending within an accounting year.
Thus, on the asset side of the balance sheet, we can clearly see which current assets are and which are not included in the current asset
Balance Sheet (As at…..)
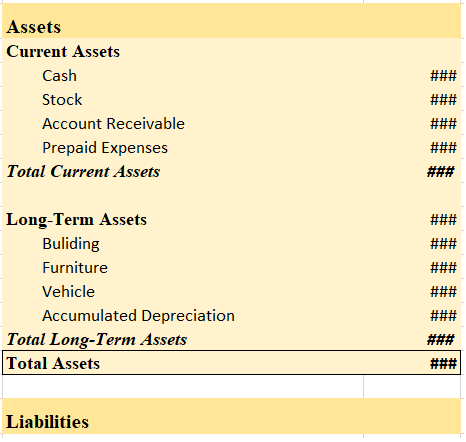
Therefore, (3) Furniture, won’t be included in current assets.
See less
When it is said that furniture is purchased for office use, it means it is an asset for the business and the journal entry for this event will be the following: Furniture A/c Dr. Amt To Cash/Bank / Vendor A/c Cr. Amt (Being furniture purchased for office use) Explanation of the journal as per the goRead more
When it is said that furniture is purchased for office use, it means it is an asset for the business and the journal entry for this event will be the following:
Explanation of the journal as per the golden rules of accounting
The furniture account is a real account because it represents a material asset and the golden rule for real accounts is “Debit what comes in, credit what goes out”. Hence, the furniture account is debited as it is increased. The cash and bank are also real accounts and they are debited because there is an outflow from cash or bank.
If the furniture is purchased on credit then the vendor account is credited. A vendor account represents a person and the golden rule for personal accounts is, “Debit the receiver, credit the giver”. It is credited as the furniture is given by the vendor.
Explanation of journal as per modern rules of accounting
The furniture account is an asset account hence it is debited as asset accounts are debited on increase. Cash and bank accounts are also assets accounts and they are credited as they are decreased on the purchase of furniture.
A vendor account is a liability account as there is an obligation to pay the vendor. It is credited as it is increased. Liability accounts are credited on the increase and vice versa.
When furniture is purchased for personal use
If the furniture is purchased for personal use and the payment is made or is to be made out of business, then the asset will not be recognised as an asset for the business and it will be recorded as a drawing. It will be deducted out of capital. The journal entry will be the following:
See less