A Profit and Loss (P&L) statement is a financial statement that records a summary of all expenses and incomes of a business during a period of time. It helps in determining the financial performance of the business. After recording all transactions in an account, if the debit side is greater thaRead more
A Profit and Loss (P&L) statement is a financial statement that records a summary of all expenses and incomes of a business during a period of time. It helps in determining the financial performance of the business.
After recording all transactions in an account, if the debit side is greater than the credit side, then the account is said to have a debit balance. Similarly, if the credit side is greater than the debit side, then the account has a credit balance.
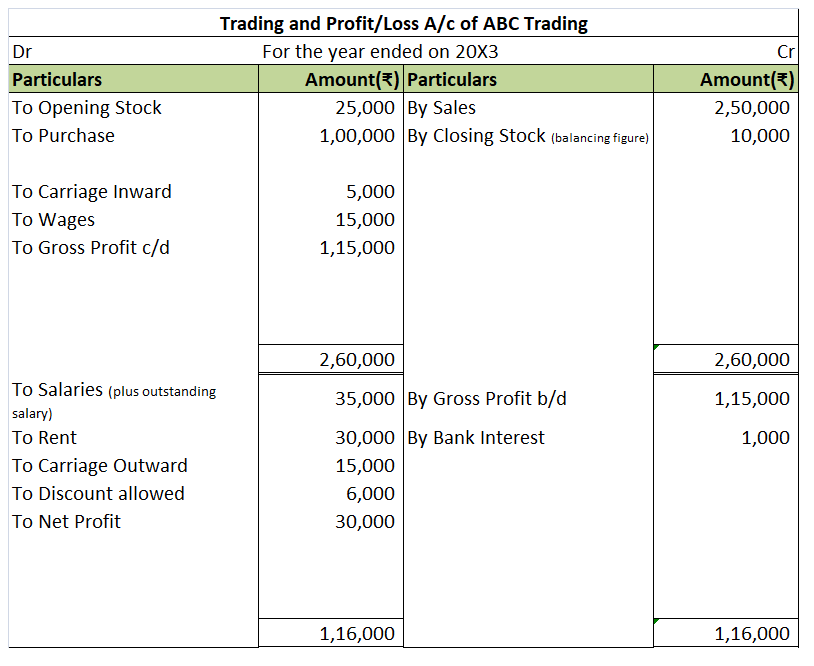
In a P&L account, when the expenses (debit) are greater than the incomes (credit), the business is said to be in a net loss. This loss is what we call the debit balance of a Profit and Loss account. A P&L account with a debit balance can be subtracted from Capital or be shown on the asset side of the Balance Sheet.
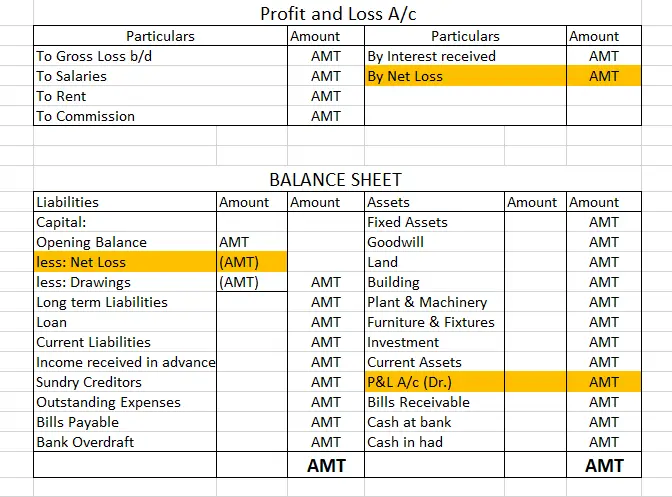
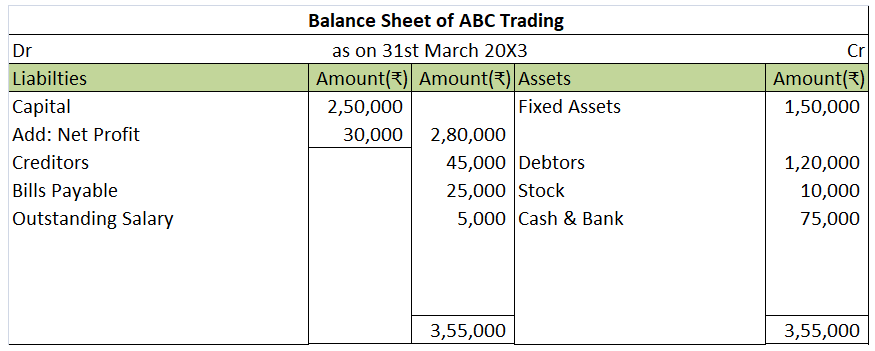
As you can see above, the net loss is shown on the right side of the P&L account. This represents the debit balance of P&L. Once it is transferred to the balance sheet, it is either subtracted from capital or shown on the asset side as shown in the second image. However, they cannot be shown on both sides of the balance sheet at the same time.
However, if the credit side is greater, that is if income is greater than expenses, then the P&L account shows a credit balance which is also known as net profit. This profit is added with Capital to show the final balance in the Balance Sheet.
Debit balance of Profit & Loss account is not preferable for a business. Hence they should put in efforts to either reduce costs or increase their income to gain profits.
See less


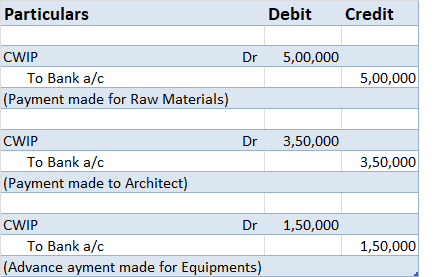
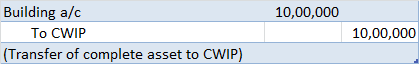
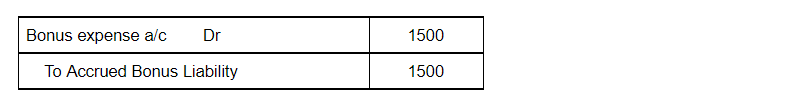 The bonus expense account is debited because according to the modern rule of accounting “Increase in expense is debited”. Accrued bonus liability is credited because according to the rule of accounting, “Increase in liability is credited”.
The bonus expense account is debited because according to the modern rule of accounting “Increase in expense is debited”. Accrued bonus liability is credited because according to the rule of accounting, “Increase in liability is credited”.
In trial balance, the treatment of the general reserve is that it is presented on the credit side. A trial balance is a statement prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts. It features the closing balances of all the assets, liabilities and equity of a business. General reRead more
In trial balance, the treatment of the general reserve is that it is presented on the credit side.
A trial balance is a statement prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts. It features the closing balances of all the assets, liabilities and equity of a business.
General reserve is a free reserve created out of revenue profits of a business to meet future needs and uncertainties. By free reserve, we mean dividends can be freely declared and distributed out of it.
Since the general reserve is an internal liability i.e. liability to the owner or owners or the business, it has a credit balance and is hence shown on the credit side of the trial balance.
See less