TDS stands for Tax Deducted at Source It is the tax deducted on certain incomes as specified under sections 192 to 194N of the Income Tax Act,1961 by the person who is responsible to pay such income. For example, an employer is liable to deduct the TDS on the salary paid to the employee subject to tRead more
TDS stands for Tax Deducted at Source
It is the tax deducted on certain incomes as specified under sections 192 to 194N of the Income Tax Act,1961 by the person who is responsible to pay such income.
For example, an employer is liable to deduct the TDS on the salary paid to the employee subject to the provisions of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
TDS is deducted either,
- at the time of payment
OR
- At time of credit to the account of the payee or at the time of payment; whichever is earlier
We know that Income tax liability is calculated after the income for a year is earned. In the next year, which is called the Assessment Year, income tax payable is calculated on the income earned in the Previous Year
For example:
Year 2021-2022 – This year (Previous Year) – Income is earned here.
Year 2021-2022 – Next Year (Assessment Year) – Income tax is assessed here.
But, the government collects the income tax from the income of the assessee in the Previous Year itself by the following ways:
- TDS – Tax Deducted at Source
- TCS – Tax Collected at Source
- Advance Tax
Some of the most common sections are given below:
- Section 192 – Salary
- Section 194A – Interest other on securities deposits with the bank, post office etc) – @10%
- Section 194B and 194BB – Winning from lotteries, crossword puzzle – @30%
- Section 194 – DA – Payment in respect of Life Insurance Policy – @5%.
So, according to sections 192 to 194N, some amount of income tax is deducted from the income of the assessee in the Previous Year itself.
In the Assessment Year, the assessee also gets a tax credit for the TDS i.e. the Income Tax liability gets reduced by the amount of Tax Deducted at Source in the Previous Year.
See less
Introduction Income tax means the tax charged on the income of a person which the person has earned during a financial year. As per the Income-tax act, 1961, the income tax on income earned during a financial year is assessed in the following financial year and tax is to be paid on the assessed incoRead more
Introduction
Income tax means the tax charged on the income of a person which the person has earned during a financial year. As per the Income-tax act, 1961, the income tax on income earned during a financial year is assessed in the following financial year and tax is to be paid on the assessed income if payable.
The year in which the income is earned is called the Previous Year and the following year in which the previous year’s income is assessed is known as the Assessment Year
Steps involved in the computation of Income-tax of a person:
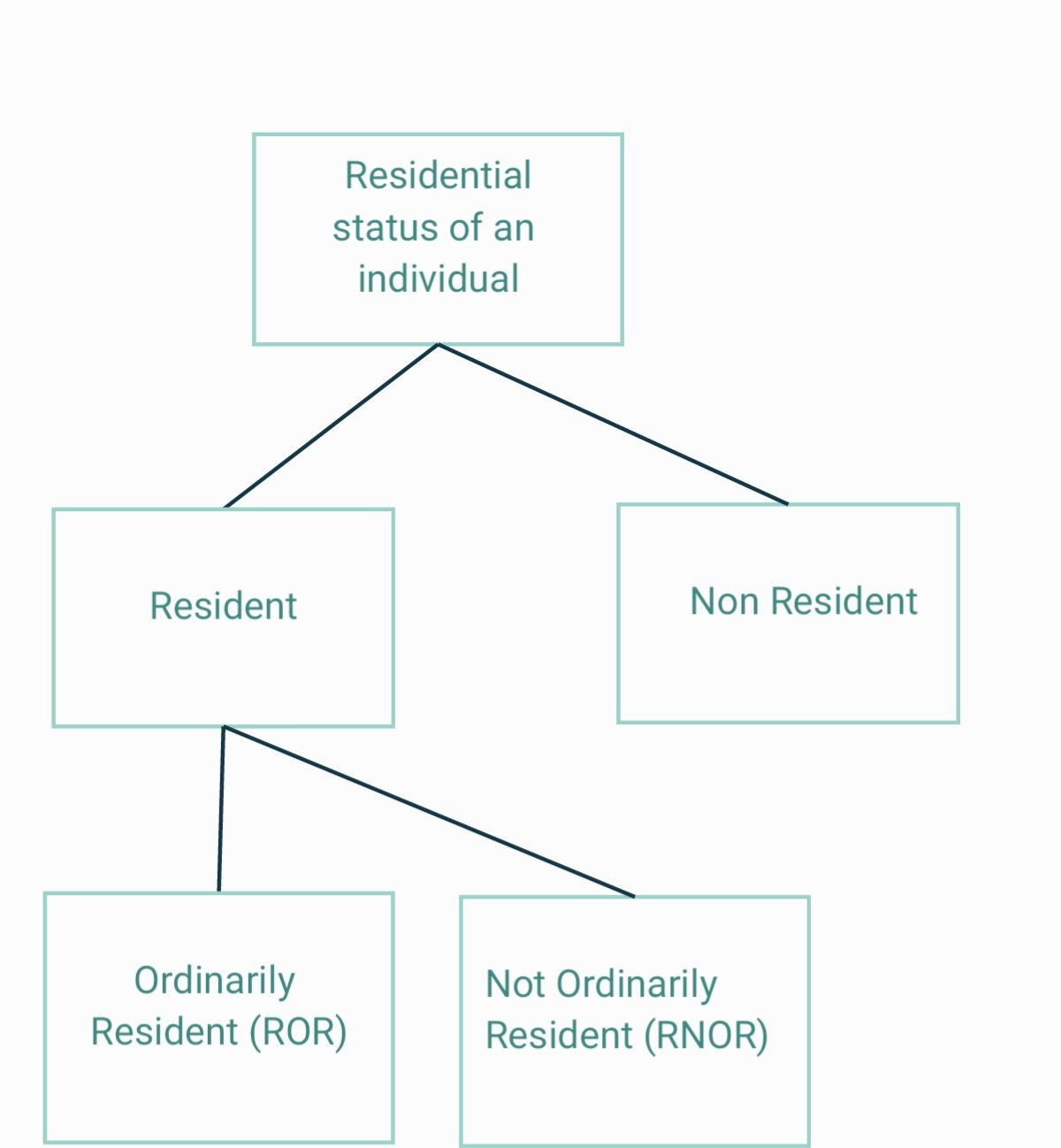
Determination of residential status of the person
The residential status of a person is of great significance for ascertaining the taxability of a person’s income as per the Income-tax act, 1961. As per the act, a person can fall into one of the following criteria:-
Classification and computation of income under the five heads of income
Now, a person’s income can be from various sources. As per section 14 of the Income-tax act, there are five main heads of income for computation of income tax:
Income under each head is to be computed as per provisions of the Income-tax Act, 1961.
Clubbing of income of spouse, minor child etc
Some individual taxpayers divert some portion of their income to their spouses and minor child in order to reduce their tax liability as the slab rate of income tax for individuals is progressive.
Such diverted income is to be clubbed with the income of the assessee as per the provisions of the Income-tax act.
Set-off and carry forward of losses
Losses suffered under the heads of the income like ‘Profit and Gains from Business and Profession’, ‘Income from House property’ can be set off against the income earned under other heads as per provision of the act.
If set off is not possible in the current assessment year then the loss can be carried forward to the next assessment year.
Computation of Gross Total Income
Gross Total Income is arrived at by computing the total of income under all five heads of income after giving necessary deductions as applicable under each head of income.
Deductions from Gross Total Income to arrive at Total Income
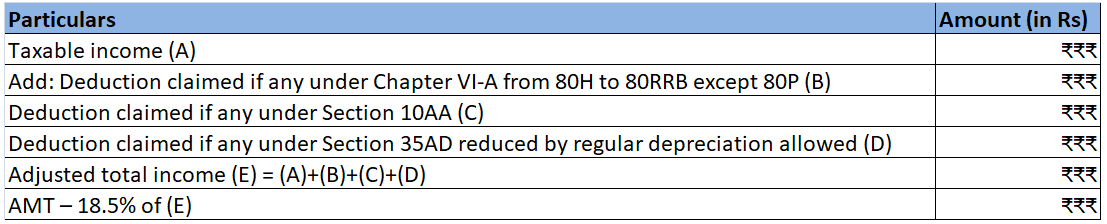
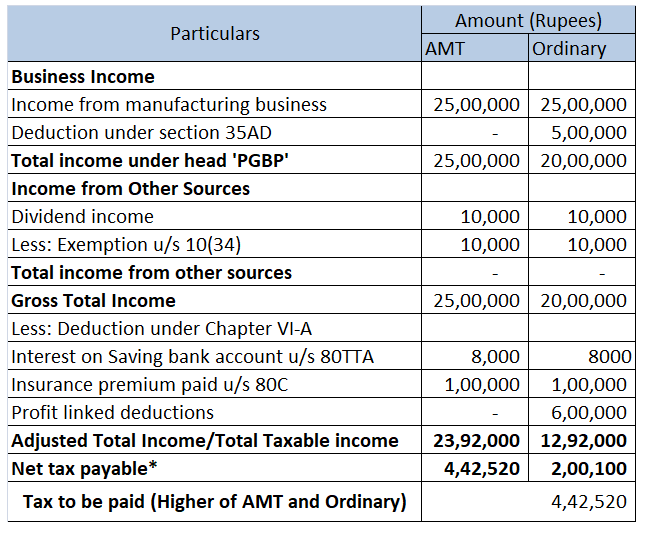
Income tax act, 1961 allows specific deduction from the Gross Total Income under sections 80C to 80U. These deductions are provided to encourage certain kinds of investments like life insurance premiums etc and provide relief on certain spending like medical expenses, interest expenses on home loans etc which leads to the overall welfare of the people.
After allowing the deductions from Gross Total Income, we arrive at Total Income.
Application of the rates of taxes on total income
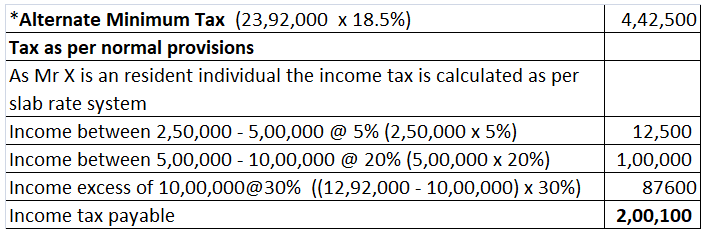
Tax is calculated at a rate on the total income. The rate and calculation of income tax depend on the type of assessees.
Individuals and HUFs
For individuals who are below the age of 60 years and HUFs:
For individuals over 60 years and 80 years of age, the basic exemption limit is ₹3,00,000 and ₹5,00,000 respectively.
Also, as per section 115BAC, individuals and HUFs have the option to choose an alternative slab rate of tax as per which the income tax is charged at concessional rates. But, the various exemptions and deductions like housing rent allowance, leave travel concession, standard deduction on salary income cannot be availed. This slab rate system was introduced recently to reduce the complexity of filling IT returns by small taxpayers.
Rates of tax related to other types of assessees is not provided for sake of simplicity.
Advance tax and tax deducted at source
After calculating the tax on total income as per specified rates, the income tax amount is to be reduced by the advance tax and tax deducted at the source.
Tax payable/ Tax refundable
After performing all the steps above, we arrive at Income tax payable or tax refundable.
See less