Credit Note A credit note is a document which generally evidences a sales return. It is created by the seller and sent to the buyer acknowledging the receipt of goods returned by the buyer. On the basis of it, the seller promises to pay back the buyer for the goods returned to him or adjust the amouRead more
Credit Note
A credit note is a document which generally evidences a sales return. It is created by the seller and sent to the buyer acknowledging the receipt of goods returned by the buyer. On the basis of it, the seller promises to pay back the buyer for the goods returned to him or adjust the amount in future transactions.
A credit note is also created when the buyer has sent excess money by mistake against the goods delivered to him.
In Tally, a credit note is created using a credit note voucher. Now, a credit note can only be created only if a sales entry has been made.
Hence first, we will be creating a sales entry and then the credit note.
Creation of sales entry in sales voucher ( If not done before)
The step to create a sale entry in Tally prime is as follows:
Gateway of Tally –> Vouchers –> Press F8 to open sales voucher
Enter the details of sales in the sales voucher like I have entered in my sale voucher and accept.
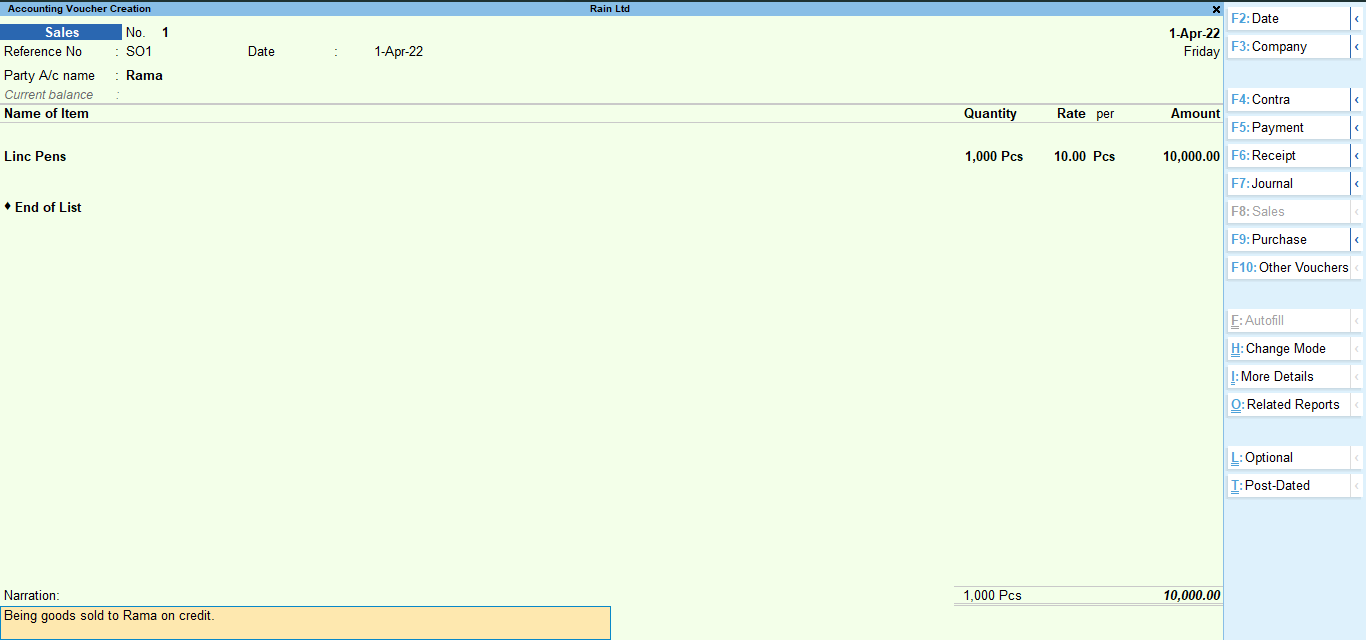
Here, my debtor is Rama and I have sold 1000pcs of Linc pens@Rs. 10 to him
Important things to consider:
- If no ledger accounts, stock items and stock units are created in your company, you can easily create them while in the voucher creation menu itself. Just press Alt + C in the field where you need to enter party name, stock item name or stock unit name and the respective creation menus will open.
- After entering the item details, a new menu will open which will ask for which account to be credited for the sale entry. As we know, a sales account is credited, so you have select the sales account from the menu or simply create a Sales account if not created by pressing Alt + C. Below is that menu:

#2 Creation of credit note
If already in the voucher creation menu, just press Alt + F6 to open the credit note voucher.
Enter the party name and a menu will open, asking for a tracking number. No need to enter any details there.
Next, another menu will open asking for party details. Select the name of the respective debtor.
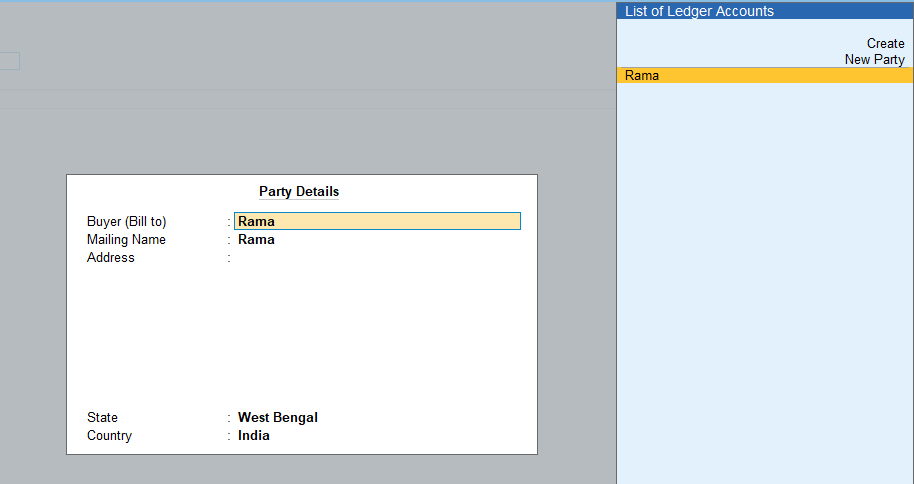
Next enter the details of stock items returned as I have done:
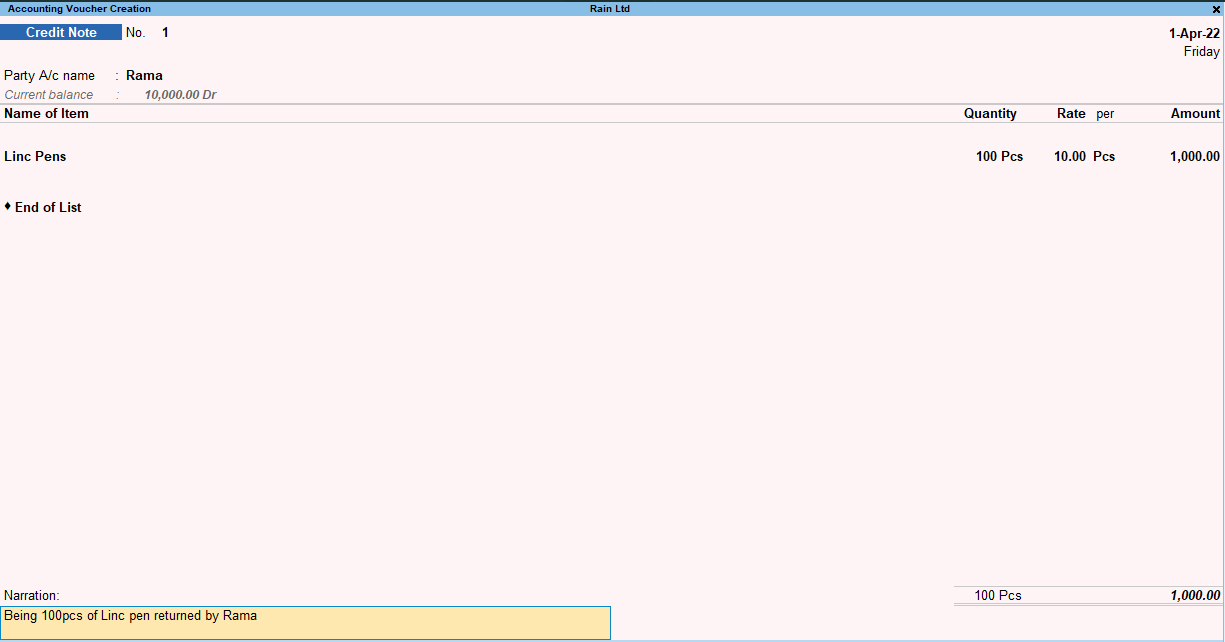
I have made a credit note for 100pcs of Linc pens returned by Rama.
After entering all the details, press Enter and accept.
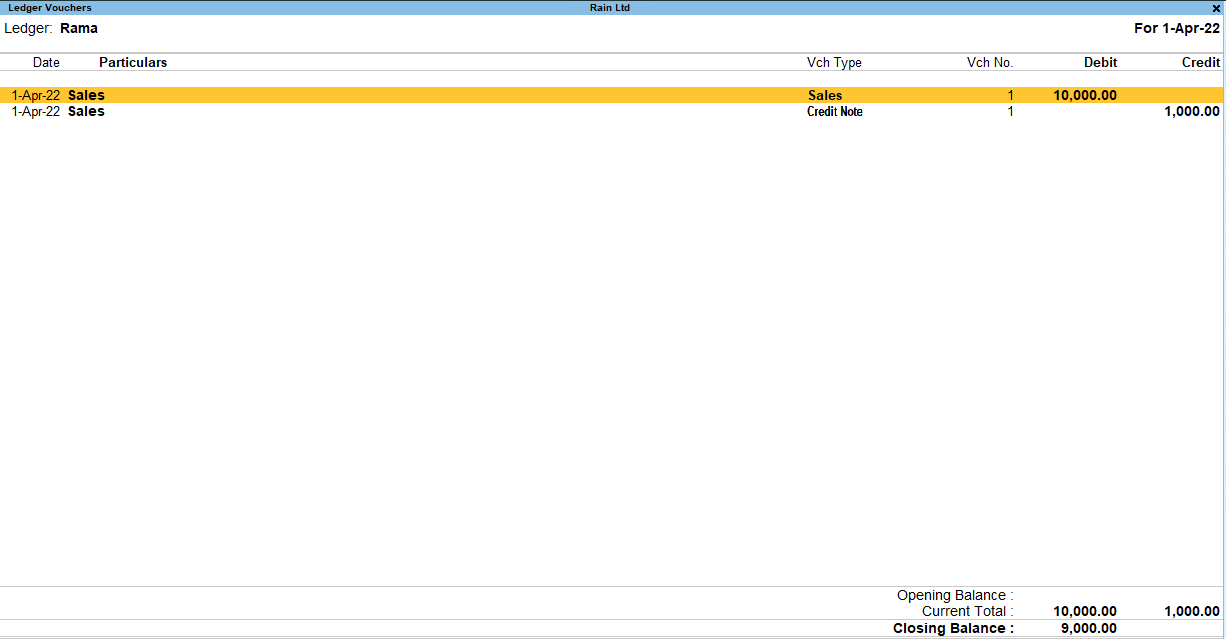
You can verify the effect of this sales voucher by performing the following steps.
Gateway of Tally –> Display more reports –> Account Books –> Ledger –>Select the debtor account from the list of ledgers.
After opening the ledger, if you see that the debtor account is credited by an amount through a credit note voucher, then it can be said that you have performed the steps correctly.

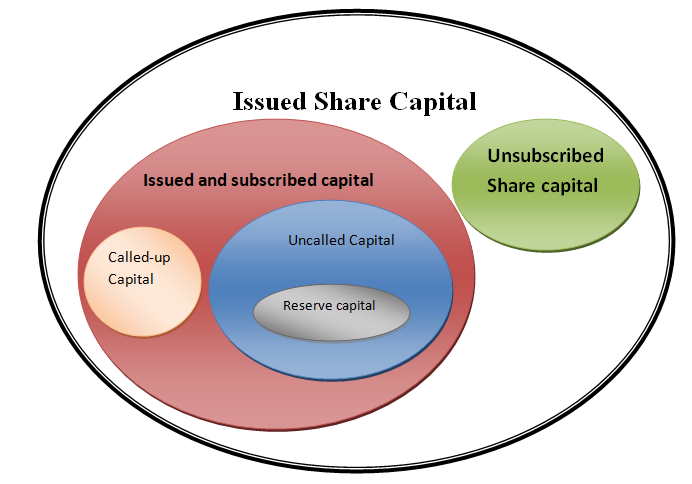
Capital Work in Progress refers to the total cost incurred on a fixed asset that is still undergoing construction as on the balance sheet date. These costs are not allowed to be used as an operating asset until the asset is ready to use. Until the construction of the asset is completed, the costs arRead more
Capital Work in Progress refers to the total cost incurred on a fixed asset that is still undergoing construction as on the balance sheet date. These costs are not allowed to be used as an operating asset until the asset is ready to use. Until the construction of the asset is completed, the costs are recorded as capital work in progress.
Depreciation is the systematic allocation of the cost of an asset over its useful life. Depreciation is charged on an asset from the date it is ready to use. Since Capital Work in Progress is not yet ready to use, depreciation cannot be charged on it.
Example
If a company owns a Machinery worth Rs. 45,000 out of which Rs. 15,000 is part of capital work in progress, then depreciation on such machinery would be calculated only on the part of machinery that is ready to use that is Rs. 30,000 (45,000-15,000).
When an asset is undergoing construction, the journal entry for each expense would be recorded as
Further, when all construction of the above asset is completed, it is transferred to fixed asset account. This would be recorded as
After transfer to Fixed Asset account, depreciation can be calculated and shown as below
If the construction of an asset is complete but has not been put to use till now, depreciation is still calculated as it is ready for use. It can be done through various methods like straight-line method, written down value method etc.
See less