To begin with, let me give you a brief explanation of both the terms i.e. Accounting policies and accounting principles- In order to maintain the financial statements, the company’s management adopts various Accounting Policies of its own. This generally includes the rules, the directions as to howRead more
To begin with, let me give you a brief explanation of both the terms i.e. Accounting policies and accounting principles-
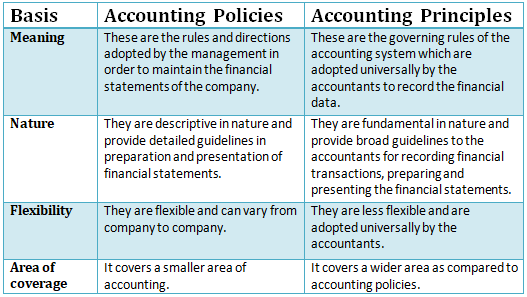
In order to maintain the financial statements, the company’s management adopts various Accounting Policies of its own. This generally includes the rules, the directions as to how the financial statements will be prepared or how the valuation of depreciation would be done, and so on. These are flexible in nature and vary from company to company.
For Example 1, Johnson Co. uses FIFO (first in first out) method to value the inventory. That is to say that, while selling its product, it sells those goods or products which it has acquired or produced first.
It does not consider the LIFO or weighted average cost. The other company may adopt the other method as per its wish.
Example 2, Johnson Co. uses the straight-line method of depreciating an asset, whereas the other company can opt for a written down value method depending upon the need of the company.
So what I am trying to explain from this is that the accounting policies are flexible and can be adopted as per the needs of the company.
Accounting Principles are the rules which the accountants adopt universally for recording and reporting the financial data. It brings uniformity in accounting throughout the practice of accounting. These are generally less flexible in nature.
For Example, “Cost” is a principle. According to this accounting principle, an asset is recorded in the books at the price paid to acquire it and this cost will be the basis for all the subsequent accounting for the asset. However, asset market value may change over time, but for the accounting purpose, it continues to be shown at its book value i.e. at which it is acquired.
Some more examples would be of Matching principle, Consistency principle, Money measurement principle, etc.
Differences
Conclusion
The point is Accounting Principles are the broad direction to reach a goal and to reach that goal helps the accounting policies.
See less
Let me first explain the meaning of both the terms CapEx and OpEx Capital expenditure (in short CapEx) is basically incurred for Fixed assets like building, furniture, machinery, etc., or an intangible asset like Goodwill, patent, etc. This expenses are incurred in order to acquire a new asset or imRead more
Let me first explain the meaning of both the terms CapEx and OpEx
Capital expenditure (in short CapEx) is basically incurred for Fixed assets like building, furniture, machinery, etc., or an intangible asset like Goodwill, patent, etc. This expenses are incurred in order to acquire a new asset or improve an existing one or maintain the asset in use.
Capital expenditure is commonly found in the Cash flow statement under Investing activities as Investment in plant, machinery, equipment, etc.
Operating Expenditure (in short OpEx) are day-to-day expenses incurred by a firm in order to carry its normal business.
Expenses such as rent, advertisement, inventory costs, etc.
Operating Expenses are shown in the income statement of the company as expenses incurred during the period.
For Example: If a company purchases a printer, the printer would be a capital expenditure and the papers used for the printer would be operating expenditure.
Difference between CapEx and OpEx
Example 1: A company wants to lease machinery instead of buying it, in this case buying machinery would be capital expenditure, and leasing the machinery would be an Operating expense.
Example 2: Buying machinery would cost a company for 50000 and leasing the same would cost 35000. So in this case leasing will be more preferred by a company which means operating expenditure would be preferred instead of a capital expenditure.
From the point of view of tax treatment operating expenditure is more preferred over Capital expenditure because the expenses incurred during the year are deducted during the same year which reduces the tax levied on net income.
Some real Examples from the Company Amazon
This is the cash flow statement of Amazon, where the investing activities shows the capital expenditure incurred by the company during the years.
This is the income statement of Amazon, it shows the operating expenditure incurred by the company during the year.
See less