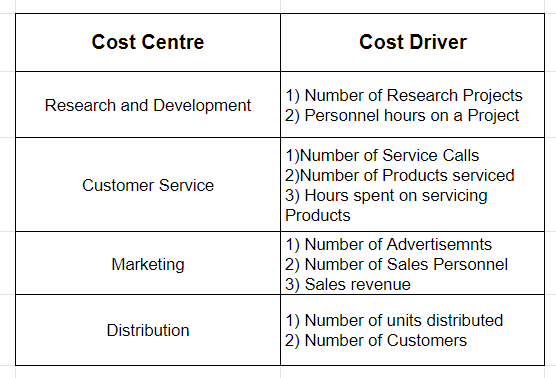
Under Activity-Based Costing, overheads are accurately assigned to different activities and their costs are determined through costing methods. Activities are those events that incur costs whereas overheads are expenditures that cannot be traced to any particular cost unit. A Cost driver refers to tRead more
Under Activity-Based Costing, overheads are accurately assigned to different activities and their costs are determined through costing methods. Activities are those events that incur costs whereas overheads are expenditures that cannot be traced to any particular cost unit.
A Cost driver refers to the factor that causes a change in the cost of an activity. Activity-Based Costing is done to establish a link between the activities and the product. The cost drivers are those links between the activities and the product.
Cost drivers are divided into four categories:
- Resource Cost Driver – It is a measure of the number of resources used by an activity. It assigns the cost of a resource to an activity.
- Activity Cost Driver – It is a measure of the frequency and intensity of demand, placed on activities by cost objects. It assigns activity costs to cost objects.
- Structural Cost Driver – It results from the economic and technological structure of the industry.
- Executional Cost Driver – It reflects the firm’s ability to plan and operate its production operations effectively.
A Cost Centre refers to a department in a business where costs can be allocated. These departments run various processes and incur costs. They can be related to the production of goods or the provision of services. Different centres are allocated different budgets and hence it enables the business to run efficiently by tracking its incomes and expenses easily.
Proper management of cost centres can help the company cut additional costs from each department. It also helps in more accurate forecasts depending on future changes.
Cost centres and Cost Drivers are both important factors while following Activity-Based Costing. Some examples of cost drivers and cost centres are as follows :
See less

To determine if a person is a resident in India as per the Income Tax Act 1961, he has to fulfil any of the 2 following conditions; Condition A Stay in India for 182 days or more in the previous year, or Stay in India for 60 days or more in the previous year and another 365 days or more in the 4 yeaRead more
To determine if a person is a resident in India as per the Income Tax Act 1961, he has to fulfil any of the 2 following conditions;
Condition A
The second condition above is not applicable if he is an Indian citizen leaving India for the purpose of employment, or he is a member of the crew of an Indian ship, or he is only coming to India on a visit.
If he fails to fulfil either of the two conditions, then he is termed as a non-resident.
In India, a resident person can be classified into two:
Condition B
A resident is a resident and ordinarily resident if (B):
If a person satisfies any one condition of (A) but does not follow all conditions of (B), then he is termed as a resident but not ordinarily resident.
EXAMPLE
If Nithin is living in India for 190 days in the previous year and was a resident for the previous two years only staying for 400 days in the previous 7 years, then he fulfils condition (A) but not both conditions of (B) and hence he is a resident but not ordinarily resident.

See less