Let’s understand what a cashbook is: A petty cash book is a cash book maintained to record petty expenses. By petty expenses, we mean small or minute expenses for which the payment is made in coins or a few notes like tea or coffee expense, bus or taxi fare, stationery expense etc. Such expenses areRead more
Let’s understand what a cashbook is:
- A petty cash book is a cash book maintained to record petty expenses.
- By petty expenses, we mean small or minute expenses for which the payment is made in coins or a few notes like tea or coffee expense, bus or taxi fare, stationery expense etc.
- Such expenses are numerous in a day for a business and to account for such small expenses along with major bank and cash transactions may create an extra hassle for the chief cashier of a business.
- So, the cash is allocated for petty expenses and a petty cashier is appointed and the task of recording the petty expenses in the petty cashbook is delegated to him.
The manner in which entries are made
When cash is given to the petty cashier, entry is made on the debit side and in the petty cashbook and credit entry in the general cashbook.
Entries for all the expenses are made on the credit side.
Generally, the petty cashbook is prepared as per the Imprest system. As per the Imprest system, the petty expenses for a period (month or week) are estimated and a fixed amount is given to the petty cashier to spend for that period.
At the end of the period, the petty cashier sends the details to the chief cashier and he is reimbursed the amount spent. In this way, the debit balance of the petty cashbook always remains the same.
Format and items which appear in the petty cashbook
The format of the petty cashbook depends upon the type of petty cash book is prepared and the items appearing in it are nothing but petty expenses. Let’s see an example:-
A business incurred the following petty expenses for the month of April:-
- Stamp – Rs. 10
- Postage – Rs. 50
- Cartage- Rs. 100
- Telephone expense – Rs. 500
- Refreshments – Rs. 250
Now we will prepare two types of cashbooks:
- Ordinary Petty Cashbook:
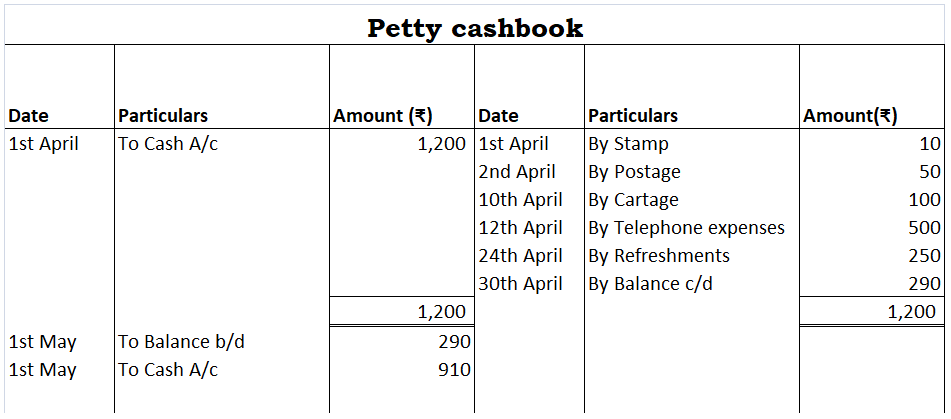
Here, the Petty cash book is of the same format as the general cash book.
The cash allocated for petty expenses is recorded on the debit side of the petty cash book and on the credit side of the general cash book.
- Analytical Petty Cashbook
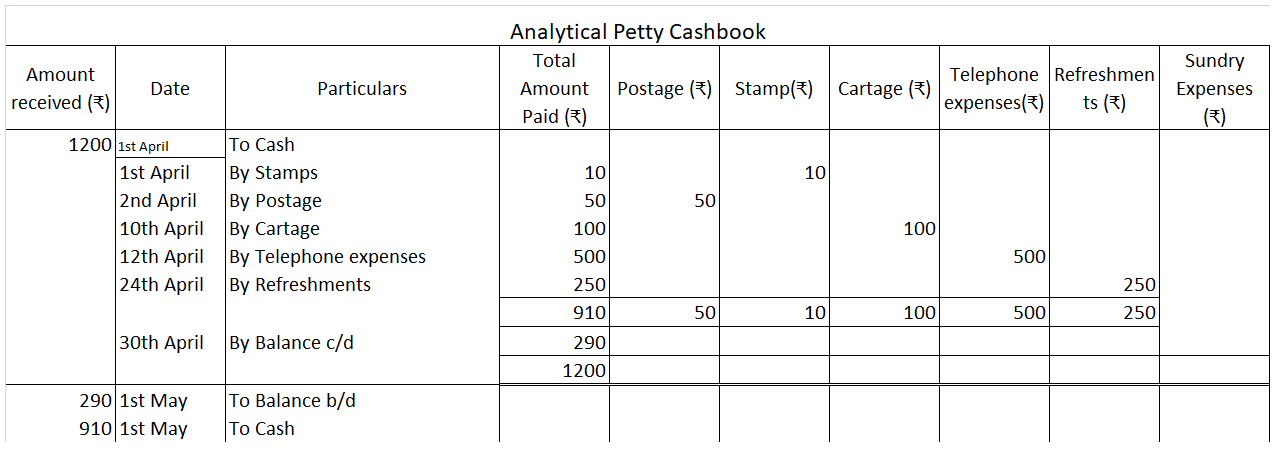
Here, there are separate amount columns for each type of expense. As the name suggests, this type of petty cashbook helps to analyse the petty cash spending on basis of the type of expense.
See less

As per AS-10 ( Revised ): Property, Plant and Equipment, depreciation on an asset should begin when the asset is in the location and condition necessary for it to be capable of operating in the manner as intended by the management. This means a firm should start charging depreciation when the assetRead more
As per AS-10 ( Revised ): Property, Plant and Equipment, depreciation on an asset should begin when the asset is in the location and condition necessary for it to be capable of operating in the manner as intended by the management.
This means a firm should start charging depreciation when the asset is ready to be used as per the management’s desire.
Let’s take an example to understand this clearly:
A business bought a drinking water cooler for its office use on 1st April 2021. Now, this water cooler needs to be installed and wiped with Isopropyl Alcohol before it can be put to use.
The business completed all the required procedures by 1st May 2021, but it opened the machine for office use from 1st August 2021.
So the question arises, from when to start charging depreciation?
The answer is 1st May 2021– The date when the machine was ready to use.
It doesn’t matter whether the company started the use of an asset or not. Once an asset is in
the depreciation should begin.
See less