The correct option is Option C: Journal Entries. Journal entries are the primary entries in the books of accounts and they are passed when any transaction or event takes place. Every journal entry has a dual effect i.e. two or more accounts are affected. For example, When cash is introduced in the bRead more
The correct option is Option C: Journal Entries.
Journal entries are the primary entries in the books of accounts and they are passed when any transaction or event takes place. Every journal entry has a dual effect i.e. two or more accounts are affected.
For example, When cash is introduced in the business, the journal entry passed is:
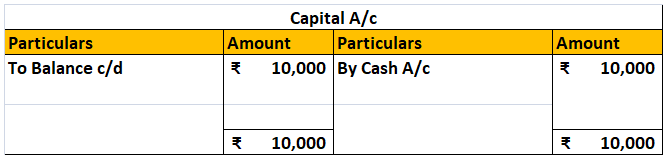
Cash A/c Dr. ₹10,000
To Capital A/c ₹10,000
The accounts affected here are Cash A/c and Capital A/c.
Cash A/c gets debited by ₹10,000,
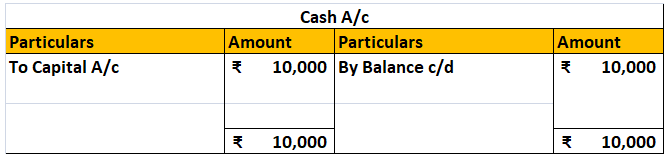
and Capital A/c get credited by ₹10,000.
All the processes of accounting are conducted in an ordered manner known as the accounting cycle.
The first step in an accounting cycle is to identify the transactions and events which are monetary in nature.
The second step is to record the identified transactions in form of journal entries.
And the third step is to make postings in the general ledger accounts as per the journal entries.
Hence, the preparation of the ledger is the third step in the accounting cycle and is prepared from the journal entries.
See less



Goodwill In Accounting Aspect, Goodwill refers to an Intangible asset that facilitates a company in making higher profits and is a result of a business’s consistent efforts over the past years which can be the business's prestige, reputation, good name, customer trust, quality service, etc. GoodwillRead more
Goodwill
In Accounting Aspect, Goodwill refers to an Intangible asset that facilitates a company in making higher profits and is a result of a business’s consistent efforts over the past years which can be the business’s prestige, reputation, good name, customer trust, quality service, etc.
Goodwill has no separate existence although the concept of goodwill comes when a company acquires another company with a willingness to pay a higher price over the fair market value of the company’s net asset in simple words the goodwill can be only realized while at the time of sale of a business.
The formula for Goodwill
Types of Goodwill
there are two types of goodwill.
1. Inherent Goodwill/Self-generated goodwill
Inherent goodwill is the internally generated goodwill that was created or generated by the business itself. it is generally generated from the good reputation of the business.
Inherent Goodwill or Self-generated goodwill is generally not shown in the books or never recognized in the books of Accounts and no journal entry for the inherent goodwill is passed.
2. Purchased Goodwill/Acquired Goodwill
At the time of acquisition of a business by another business, any amount paid over and above the net assets simply refers to the amount of Purchased Goodwill or Acquired goodwill.
A Journal entry is passed in the case of the Purchase of goodwill.
Type of Account
generally, Goodwill is considered and recorded as an Intangible asset(long-term asset) due to its physical absence like other long-term assets.
Modern rule of accounting:
as per the Modern rule of accounting, all Assets or all possessions of a business are comes under the head Asset accounts.
as Goodwill is treated as an Intangible asset it is an Asset Account.
Journal entry for purchase of goodwill as per Modern rule
Goodwill A/c Dr. – Amt
To Cash/Bank A/c – Amt
(The modern approach of accounting for the Asset account is: “Debit the increase in asset and Credit the decrease in the asset“)
The golden rule of accounting
As per the golden rule of accounting, all assets or possessions of a business other than those which are related to any person (debtor’s account) are considered Real accounts.
Such accounts don’t close by the year-end and are carried forward.
As Goodwill is an Intangible asset it is treated as a Real account as per the golden rule of accounting.
Journal entry for purchase of goodwill as per Golden rule
Goodwill A/c Dr. – Amt
To Cash/Bank A/c – Amt
(The golden rule of accounting for the Real account is: “Debit what comes in and Credit what Goes out“)
See less