Yes, I agree with your statement that accounting information should be comparable. Comparability is one of the qualitative characteristics of accounting information. It means that users should be able to compare a company's financial statements across time and across other companies. Comparability oRead more
Yes, I agree with your statement that accounting information should be comparable.
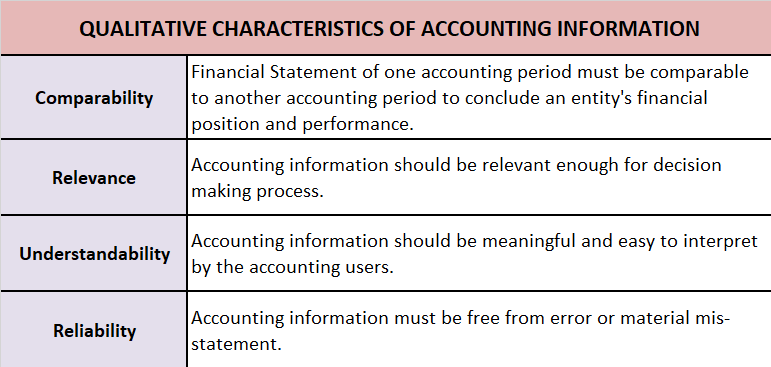
Comparability is one of the qualitative characteristics of accounting information. It means that users should be able to compare a company’s financial statements across time and across other companies.
Comparability of financial statements is crucial due to the following reasons:
1. Intra-Firm Comparison:
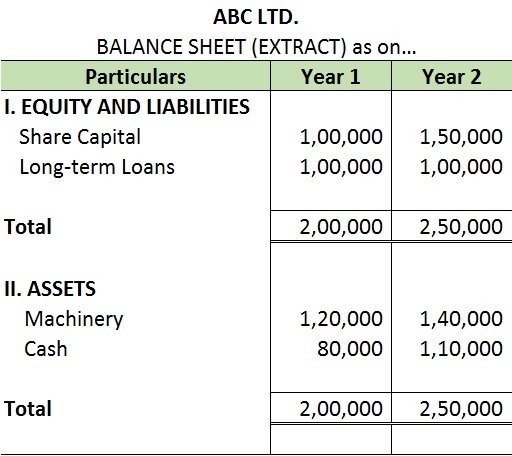
Comparison of financial statements of two or more periods of the same firm is known as an intra-firm comparison.
Comparability of accounting information enables the users to analyze the financial statements of a business over a period of time. It helps them to monitor whether the firm’s financial performance has improved over time.
The intra-firm analysis is also known as Time Series Analysis or Trend Analysis.
To understand intra-firm analysis, I have provided an extract of the balance sheet of ABC Ltd. for two accounting periods.
2. Inter-Firm Comparison:
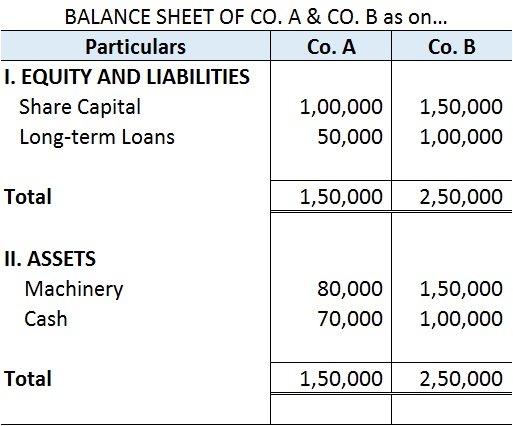
Comparison of financial statements of two or more firms is known as an inter-firm comparison.
Inter-firm comparison helps in analyzing the financial performance of two or more competing firms in an industry. It enables the firm to know its position in the market in comparison to its competitors.
Inter-firm comparison is also known as Cross-sectional Analysis.
I’ve provided the balance sheets of Co. A and Co.B to make an inter-firm comparison.
Here is a piece of bonus information for you,
Sector Analysis – it refers to the assessment of economical and financial conditions of a given sector of a company/industry/economy. It involves the analysis of the size, demographic, pricing, competitive, and other economic dimensions of a sector of the company/industry/economy.
One more important thing to note here is that comparability can only be achieved when the firms are consistent in the accounting principles and standards they adopt. The accounting policies and standards must be consistent across different periods of the same firm and across different firms in an industry.
See less

Assets can be classified as Financial or Non-financial assets. One might wonder why this is necessary. Let us dive into this concept, beginning with understanding what financial and non-financial assets are and why they are classified as such. What are Assets? Assets are things that have a monetaryRead more
Assets can be classified as Financial or Non-financial assets. One might wonder why this is necessary. Let us dive into this concept, beginning with understanding what financial and non-financial assets are and why they are classified as such.
What are Assets?
Assets are things that have a monetary value and are beneficial for a business. Assets are commonly classified as tangible, intangible, current, fixed, financial, non-financial, etc.
Plant and machinery, land, buildings, cash, bank balance, patents, etc are some of the examples of assets that a business has.
What are Financial Assets?
Financial assets are the things of value that are held by a person for their underlying value. They are intangible and do not have a physical form. For example – Stocks, bonds, debentures, options, futures, etc.
The value of these assets may change over time depending upon the market conditions, changes in government policies, fluctuations in interest rates, etc.
In comparison to non-financial or physical assets, financial assets are more liquid as they can be traded and can be converted into cash.
What are Non-financial assets?
Non-financial assets are tangible or intangible assets that have a value but cannot be easily converted into cash. They are not as liquid and generally not traded.
Examples of such assets are buildings, plant and machinery, patents, trademarks, etc.
Why do we separate Financial and Non-Financial Assets?
The following are several important reasons why it is important to segregate the same:
Difference between Financial and Non – Financial Asset
See less