The term ‘contra’ means 'opposite'. Therefore, a contra revenue account is an account that is opposite of the revenue accounts of a business i.e. sales account. It has the opposite balance of the revenue account i.e. debit balance. The purpose of the contra revenue account is to ascertain the actuaRead more
The term ‘contra’ means ‘opposite’. Therefore, a contra revenue account is an account that is opposite of the revenue accounts of a business i.e. sales account. It has the opposite balance of the revenue account i.e. debit balance.
The purpose of the contra revenue account is to ascertain the actual amount of sales and record the items which have reduced the sales.
These are the contra revenue accounts commonly seen in businesses:
- Sales return account: This account records the amount of goods sold returned by customers. The journal entry for recording sale return is as follow:

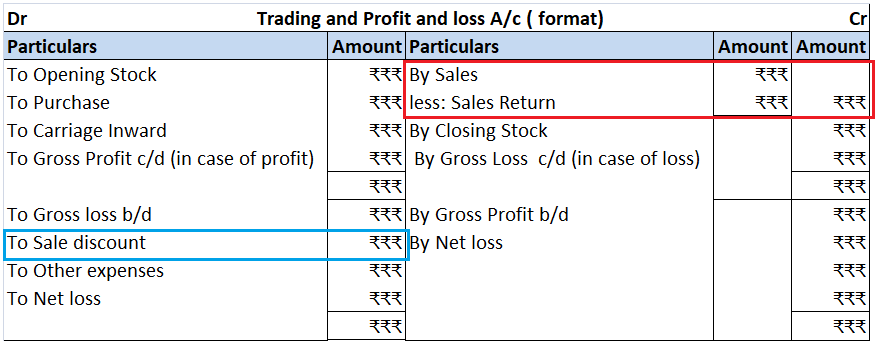
The total sales return is deducted from the sales in the balance sheet. Though being opposite of the sales account, the sale return account is not an expense account. It is considered an indirect loss as it reduces sales.
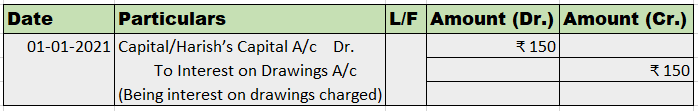
- Sale Discount account: This account records the amount of discount allowed to customers. The journal entry for recording sale discounts is as follows:

Sales discount is an expense hence it is debited to the profit and loss account.
Sales returns and sales discounts are shown in the trading and profit and loss account in the following manner:


Generally, Assets are classified into two types. Non-Current Assets Current Assets Non-Current Asset Noncurrent assets are also known as Fixed assets. These assets are an organization's long-term investments that are not easily converted to cash or are not expected to become cash within an acRead more
Generally, Assets are classified into two types.
Non-Current Asset
Noncurrent assets are also known as Fixed assets. These assets are an organization’s long-term investments that are not easily converted to cash or are not expected to become cash within an accounting year.
In general terms, In accounting, fixed assets are assets that cannot be converted into cash immediately. They are primarily tangible assets used in production having a useful life of more than one accounting period. Unlike current assets or liquid assets, fixed assets are for the purpose of deriving long-term benefits.
Unlike other assets, fixed assets are written off differently as they provide long-term income. They are also called “long-lived assets” or “Property Plant & Equipment”.
Examples of Fixed Assets
Valuation of Fixed asset
fixed assets are recorded at their net book value, which is the difference between the “historical cost of the asset” and “accumulated depreciation”.
“Net book value = Historical cost of the asset – Accumulated depreciation”
Example:
Hasley Co. purchases Furniture for their company at a price of 1,00,000. The Furniture has a constant depreciation of 10,000 per year. So, after 5 years, the net book value of the computer will be recorded as
1,00,000 – (5 x 10,000) = 50,000.
Therefore, the furniture value should be shown as 50,000 on the balance sheet.
Presentation in the Balance Sheet
Both current assets and non-current assets are shown on the asset side(Right side) of the balance sheet.
Difference between Current Asset and Non-Current Asset
Current assets are the resources held for a short period of time and are mainly used for trading purposes whereas Fixed assets are assets that last for a long time and are acquired for continuous use by an entity.
The purpose to spend on fixed assets is to generate income over the long term and the purpose of the current assets is to spend on fixed assets to generate income over the long term.
At the time of the sale of fixed assets, there is a capital gain or capital loss but at the time of the sale of current assets, there is an operating gain or operating loss.
The main difference between the fixed asset and current asset is, although both are shown in the balance sheet fixed assets are depreciated every year and it is valued by (the cost of the asset – depreciation) and current asset is valued as per their current market value or cost value, whichever is lower.
See less