Trading A/c is a nominal account which follows the rule "Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains". So, all expenses relating to the purchase or manufacturing of goods are shown on the debit side of the Trading A/c. It includes Opening Stock, Purchases, Wages, Carriage Inward, ManRead more
Trading A/c is a nominal account which follows the rule “Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains”.
So, all expenses relating to the purchase or manufacturing of goods are shown on the debit side of the Trading A/c. It includes Opening Stock, Purchases, Wages, Carriage Inward, Manufacturing Expenses, Dock charges, and other direct expenses that are directly related to the manufacturing or purchase.
TRADING ACCOUNT
Trading A/c is prepared for calculating the Gross Profit or Gross Loss arising from the trading activities of a business.
Trading activities are mostly related to buying and selling of goods. However, in between buying and selling, a lot of activities are involved like transportation, warehousing, etc. So, all the expenses that are directly related to manufacturing or purchase of goods are also recorded in the Trading A/c.
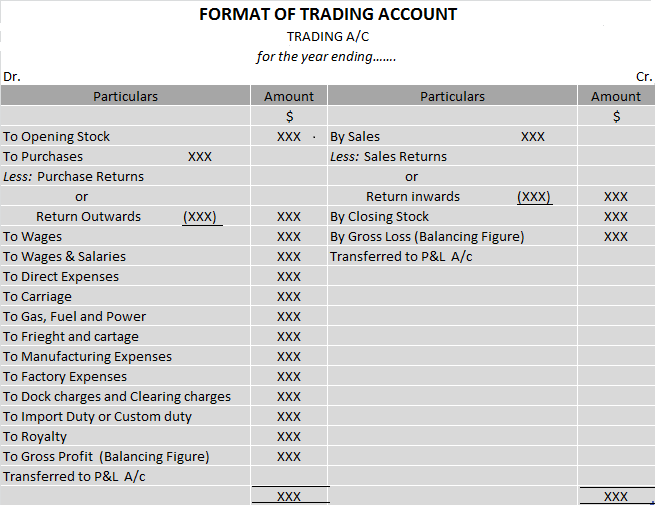
DEBIT SIDE OF TRADING A/C
The items shown on the Dr. side are,
OPENING STOCK – Stock is nothing but goods that are either obtained for resale or manufactured for sale and are yet unsold on any particular date.
The value of stock at the beginning of an accounting year is called Opening stock while the value of the stock at the end of an accounting year is called closing stock.
The closing stock of the last year becomes the opening stock of the current year.
Opening stock includes,
- Opening Stock of Raw materials
- Opening Stock of Semi-finished goods
- Opening Stock of Finished goods
For example – Suppose you are in the business of manufacturing and trading shirts. On 31st March 2023, there was unused raw material worth $10,000 and shirts worth $50,000 remained unsold.
So, we have Closing Stock of Raw material – $10,000
Closing Stock of Finished Goods – $50,000
This closing stock of last year becomes your opening stock during the current year i.e. on 1st April 2023, we have
Opening Stock of raw material – $10,000
Opening Stock of Finished Goods – $50,000
PURCHASES – Goods that have been bought for resale or raw materials purchased for manufacturing the product are terms as Purchases. These goods must be related to the business you are doing.
It includes cash as well as credit Purchases.
Continuing with the above example, suppose you bought raw material worth $ 1,00,000 for manufacturing and shirts worth $50,000 for resale (and not for personal consumption) then both these will be termed as purchases for you. So, your purchases will be $1,50,000 ($1,00,000 + $50,000)
PURCHASES RETURN – When goods bought are returned to the suppliers due to any reason. This is known as Purchase return. Purchase return is deducted from the Purchases.
In the above example, you bought shirts worth $50,000 for resale. Out of which shirts worth $20,000 were defective. So, you returned them to the supplier. This return of $20,000 is your purchase return or return outwards (as goods are going out)
WAGES – Wages are paid to the workers who are directly engaged in the loading, unloading and production of goods.
For example – Paid $10,000 to workers for manufacturing shirts.
However, it would be included in Trading A/c only if the wages are paid for work which is directly related to the manufacturing or purchase of goods otherwise it will be shown in P&L A/c.
Suppose you hired a manager to take care of your business and paid him $20,000 as salary. This salary is indeed an expense for the business but is not directly related to the manufacturing of goods. Since it is an indirect expense, it can only be recorded in P&L A/c and not in the Trading A/c.
CARRIAGE or CARRIAGE INWARDS or FREIGHT – It refers to the cost of transporting goods from the supplier.
Suppose, you ordered raw material in bulk which was transported to you by a van and you paid its fare. This fare is nothing but your carriage inwards.
However, if carriage or freight is paid on bringing an asset, the amount should be added to the asset account and must not be debited to the trading account.
MANUFACTURING EXPENSES – All expenses incurred in the manufacture of goods such as Coal, Gas, Fuel, Water, Power, Factory rent, Factory lighting etc.
DOCK CHARGES – These are charged by port authorities when unloading goods at a dock or wharf. Such charges paid in connection with goods purchased are considered direct expenses and are debited to Trading a/c.
IMPORT DUTY or CUSTOM DUTY – It is a tax collected on imports and specific exports by a country’s customs authorities. If import duty is paid on the import of goods, then they are shown on the Dr. side of the Trading A/c.
For example – Paid $15,000 as import duty for importing shirts for resale.
ROYALTY – Royalty refers to the amount paid for the use of assets belonging to another person. It includes royalty for the use of intangible assets, such as copyrights, trademarks, or franchisee agreements. It is also paid for the use of natural resources, such as mining leases.
Royalty is charged to the Trading A/c as it increases the cost of production.
GROSS PROFIT – When sales exceed the amount of purchases and the expenses directly connected with such purchases i.e. when Credit side> Debit side.
CREDIT SIDE OF TRADING A/C
SALES – When goods are sold to earn a profit, it is called sales. It can be cash sales or credit sales.
SALES RETURN – When the goods sold are returned by the customer, it is known as a sales return. Sales return is deducted from the sales.
CLOSING STOCK – The goods remaining unsold at the end of the year are termed as closing stock. It is valued at cost price or market price whichever is less.
GROSS LOSS – If purchases and direct expenses exceed sales, then it is a Gross loss. In other words, when Debit side > Credit side.
See less

Profit refers to the excess of total revenue over total expenses. According to the rule "Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains", expenses are recorded on the debit side while revenues are recorded on the credit side. There is profit when Total revenue > Total expenses, whichRead more
Profit refers to the excess of total revenue over total expenses. According to the rule “Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains”, expenses are recorded on the debit side while revenues are recorded on the credit side.
There is profit when Total revenue > Total expenses, which means the balance of the credit side > the balance of the debit side. Since, in accounting Dr. side is always equal to the credit side, a balancing figure (representing profit or loss) is shown on the shorter side, to make both sides equal.
When Credit side > Debit side, Profit(balancing figure) is shown on the Dr. side so that both sides are equal.
PROFIT
Profit refers to the excess of total revenue over the total expenses of the business for an accounting year. In simple words, it shows how much extra the firm earned after deducting all the expenses it incurred during the year.
Profit = Total Revenue – Total Expenses
Suppose, the firm earned a total revenue of $10,000 for the accounting year 2022-23. Also, it incurred total expenses of $6,000 during the year. So, Profit for the AY 2022-23 is $4,000.
ASCERTAINING PROFIT
To ascertain profit earned or loss incurred by the firm during an accounting year, it prepares two accounts.
Points to be noted:
TRADING ACCOUNT
It is the first final account prepared for calculating gross profit or gross loss during the year because of the trading activities of the firm.
Trading activities are related to the buying and selling of goods. In between buying and selling a lot of activities are there like transportation, warehousing, loading, unloading, etc. All expenses that are directly related to buying and selling as well as manufacturing of goods are known as Direct expenses and are also recorded in the trading accounts.
Items included on the debit side:
Items included on the credit side:
Gross Profit is when Cr. side (incomes) > Dr. side (expenses). It is recorded on the debit side as a balancing figure.
PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT
A businessman incurs a lot of expenses during the year which may be directly related or indirectly related to the business.
As the Trading account only considers direct expenses, the businessman prepares the P&L A/c which considers all the expenses incurred during a year to ascertain net profit or loss.
Items written on the Debit side
Items written on the Credit side
Net Profit is when the Cr. side (incomes)> Dr. side(expenses). It is recorded on the Debit side as a balancing figure.
See less