Net credit sales can be defined as the total sales made by a business on credit over a given period of time less the sales returns and allowances and discounts such as trade discounts. Net Credit Sales = Gross Credit Sales – Returns – Discounts – Allowances. Credit sales can be calculated from the ARead more
Net credit sales can be defined as the total sales made by a business on credit over a given period of time less the sales returns and allowances and discounts such as trade discounts.
Net Credit Sales = Gross Credit Sales – Returns – Discounts – Allowances.
Credit sales can be calculated from the Accounts receivable/ Bills Receivable/ Debtors figure in the Balance Sheet. It will be normally shown under the Current Assets head in the Balance Sheet.
Credit sales = Closing debtors + Receipts – Opening debtors.
Alternatively, you may observe the bills receivable ledger account to locate the figure of credit sales.
Net Credit Sales and related terms
Before we try to understand the concept of net credit sales with an example, let us discuss the term sales return. Sales return means the goods returned by the customer to the seller. It may be due to defects or any other reasons.
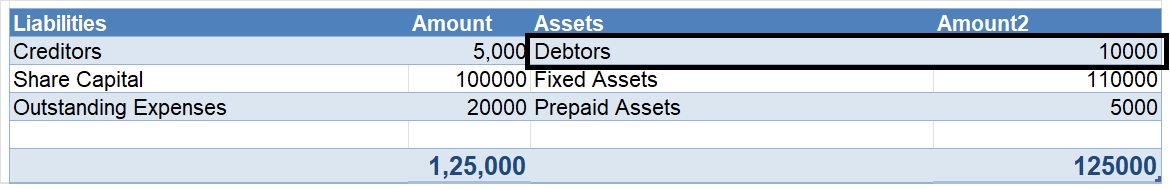
Now let us take an example. John is a retail businessman. He sells smartphones. He buys 100 smartphones from Vivo on credit. The smartphones are worth ₹1.5 lahks. He then returns smartphones worth 20,000 rupees to Vivo. He also gets an allowance of rupees 5,000 from Vivo.
In the above example, the credit sales of Vivo are of rupees 1.5 lakh. The net credit sales is of
1.5 lakh – 20,000 – 5, 000 = 1.25 lakh rupees.
Importance of Net Credit Sales
- Net Credit Sales figure together with the accounts receivable figure acts as an indicator of the credit policy of the company.
- It offers insights into the ability of the company to meet short-term cash obligations.
- The credit policy also affects the total current assets that the company has in the manifestation of Accounts Receivable
Advantages and Disadvantages of Credit Sales.
Advantages
- Increased Sales – The credit Policy facilitates increased sales for the company. The company can attract more customers with a liberal credit policy. For example, Apple got more customers when it started to sell its products on an EMI basis.
- Customer Loyalty / Retention- Regular customers can be retained and made to feel honored by offering them more liberal credit terms.
Disadvantages
- Delay in Cash Collection – Credit Sales imply that the company would get cash on a delayed basis. This money could have otherwise been put to use for some other profitable venture or could have borne interest for the company
- Collection Expenses– The company had to incur additional expenditures for collecting money from debtors.
- Risk of Bad Debts – With credit sales, there is always the risk that the buyer may become bankrupt and may not be able to pay the money due to the seller.

The profits earned by a company are distributed to its shareholders monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly in the form of dividends. The dividend payable by the company is transferred to the Dividend Account and is then claimed by the shareholders. If the dividend is not claimed by the members aRead more
The profits earned by a company are distributed to its shareholders monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly in the form of dividends. The dividend payable by the company is transferred to the Dividend Account and is then claimed by the shareholders.
If the dividend is not claimed by the members after transferring it to the Dividend Account, it is called Unclaimed Dividend. Such a dividend is a liability for the company and it is shown under the head Current Liabilities.
The dividend is transferred from the Dividend Account to the Unclaimed Dividend Account if it is not claimed by the shareholders within 37 days of declaration of dividend.
For the Cash Flow Statement, unclaimed dividend comes under the head Financing Activities.
Items shown under the head Financing Activities are those that are used to finance the operations of the company. Since, money raised through the issue of shares finances the company, any item related to shareholding or dividend is shown under the head Financing Activities.
However, there are two approaches to deal with the treatment of Unclaimed Dividend:
First, since there is no inflow or outflow of cash, there is no need to show it in the cash flow statement.
Second, the unclaimed dividend is deducted from the Appropriations, that is, when Net Profit before Tax and Extraordinary Activities is calculated.
Then, it is added under the head Financing Activities because the amount of dividend that has to flow out of the company (that is Dividend Paid amount which has already been deducted from Financing Activities) remained in the company only since it has not been claimed by the members.
The second approach to the treatment of an Unclaimed Dividend is used when the company has not transferred the unclaimed dividend amount from the Dividend Account to a separate account.
See less