Definition Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period. For a business i.e. company/firm, it is a liability towards shareholders/promoters/partners/proprietors, etc. as it is their capital that has earned these profits. When the result of this computationRead more
Definition
Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period.
For a business i.e. company/firm, it is a liability towards shareholders/promoters/partners/proprietors, etc. as it is their capital that has earned these profits.
When the result of this computation is negative it is called a net loss.
Net profit may be shown before or after tax.
Formula :
Total Revenues – Expenses
Or
Total Revenues – Total Cost ( Implicit And Explicit Cost )
Liabilities
It means the amount owed (payable) by the business. liability towards the owners ( proprietor or partners ) of the business is termed an internal liability.
On the other hand, liability towards outsiders, i.e., other than owners ( proprietors or partners ) is termed as an external liability. For example – taxes owned, trade payables, etc.
For example creditors, bank overdrafts, etc.
Assets
An asset is a resource owned or controlled by a company and will benefit the business in current and future periods.
In other words, it’s something that a company owns or controls and can use to generate profits today and in the future.
For example – cash, building, etc.
Why debtors are treated as a liability?
Now let me explain to you why net profits are treated as a liability and not as an asset because of the following characteristics :
• Net Profit shows the credit balance of the Profit And Loss Account.
• It is treated directly in the balance sheet by adding or subtracting from the capital.
• Net Profit is a measure of the profitability of the company after taking into consideration all costs incurred during the accounting period.
• Net profit is the last line in an income statement and is the figure that concerns most people who use such a statement.
• Net income is reported on the income statement (profit and loss account) and forms a key indicator of a company’s performance.
Importance Of Net Profit
Now I will let you know the importance of net profit which is as follows :
Owners
Net profit allows owners to calculate the tax to be paid and how much earnings need to be distributed to the business owners.
Investors
Investors need to see net profit as they need to access the risk before investing they basically judge the revenue-generating capacity of a firm based on net profit.
Competitors
For making the comparison competitors tend to look at the net profit of the company to know how are they performing in the industry so that they can build themselves strong.
Creditors
Creditors look at the net profit for the purpose of obtaining business loans or we can say that determines a prospective debtor’s capacity to pay future debts.
Conclusion
Now after the above explanation, we can say that,
Net Profit is shown on the liability side as it belongs to shareholders so the company has to give it to shareholders so we are showing it under the liability side.
Net Profit with respect to the company is a liability as it has to pay it to shareholders.
Net Profit with respect to shareholders is an asset.
See less
Definition Prepaid expenses are those expenses whose payments are done in advance which can be for the goods or services whose benefit will accrue in the subsequent accounting period. A prepaid expense is a current asset. prepaid expenses are classified under the head current assets in the balance sRead more
Definition
Prepaid expenses are those expenses whose payments are done in advance which can be for the goods or services whose benefit will accrue in the subsequent accounting period.
A prepaid expense is a current asset. prepaid expenses are classified under the head current assets in the balance sheet.
This is because they provide future economic benefits to the company. As such, they are assets that can be used to generate revenue in the future.
For example prepaid rent, prepaid insurance, etc.
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business.
Or in other words, we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cycle period although it is more than the period of 12 months from the date of the balance sheet.
For example, goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn a profit, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Current liabilities are liabilities that are payable generally within 12 months from the end of the accounting period or in other words which fall due for payment in a relatively short period.
For example bills payable, short-term loans, etc.
Why current assets and not a current liability?
Now let me try to explain to you that prepaid expenses are classified as current assets and not as a current liability which is as follows :
Example
Now let us take an example for explaining prepaid expenses which are mentioned below.
An insurance premium of Rs 50000 has been paid for one year beginning (previous year). The financial year ends on 31st march YYYY.
It means the premium for 6 months i.e., 1st April, YYYY(current year) to 30th September, YYYY(current year) amounting to Rs 25000 is paid in advance.
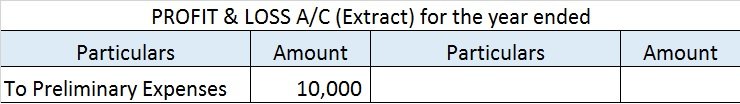
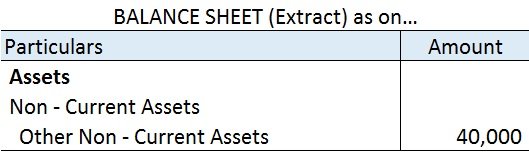
Thus, of premium paid in advance (Rs 25000) is a Prepaid Expense. It will be accounted as an expense in the financial year ending 31st march next year. In the balance sheet as of 31st march YYYY ( current year ) it will be shown as Current Asset.
Here is an extract of the profit /loss account and balance sheet of the above example:
Key points
There are a few things to keep in mind when dealing with prepaid expenses.
See less