Goodwill Patents Preliminary Expense A/c Claims Receivable
Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of both terms. Revenue receipts: The term 'revenue' suggests these are the amounts received by a business due to its operating activities. These receipts arise in a recurring manner in a business. Such receipts don’t affect the balance sheet. They are shown inRead more
Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of both terms.
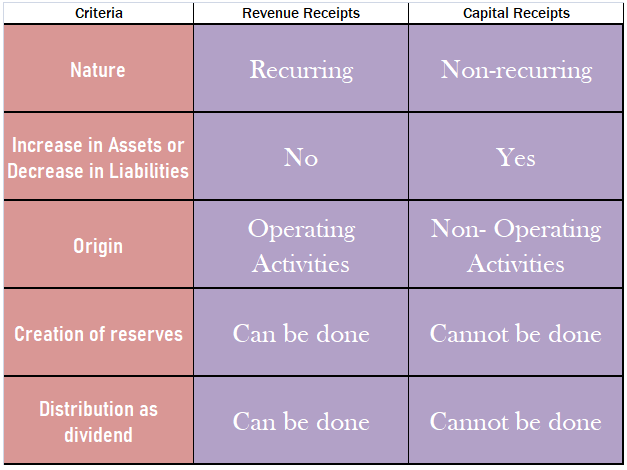
Revenue receipts: The term ‘revenue‘ suggests these are the amounts received by a business due to its operating activities. These receipts arise in a recurring manner in a business. Such receipts don’t affect the balance sheet. They are shown in the statement of profit or loss. Such receipts are essential for the survival of the business.
Examples of revenue receipts are as follows:
- Proceeds from the sale of goods.
- Proceeds from the provision of services
- Rent received
- Interest received from deposits in banks or financial institutions
- Discount received from creditors (shown in the debit side of P/L A/c)
Capital receipts: The term ‘capital’ that such receipts are do not arise due to operating activities, hence not shown in the Profit and loss statement. These are the money received by a business when they sell any asset or undertake any liability. These receipts do not arise in a recurring manner in a business. They don’t affect the profit or loss of the business. They are not essential for the survival of the business.
Examples of capital receipts are as follows:
- Loan from a bank or financial institution. (Increase in liabilities)
- Proceeds from the sale of an asset. (decrease in assets)
- Proceeds from sale of investments. (decrease in assets)
- Proceeds from the issue of equity shares. (Increase in liabilities)
- Proceeds from issue of debentures. (Increase in liabilities)
I have given a table below for more understanding:

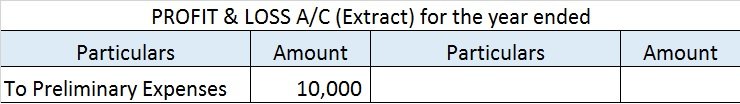


Fictitious assets are expenses or losses not written off entirely in the profit and loss account during the accounting year in which they occur. Fictitious assets have no realizable value or physical existence. In the above, (C) preliminary expense is a fictitious asset. Preliminary expenses are theRead more
Fictitious assets are expenses or losses not written off entirely in the profit and loss account during the accounting year in which they occur. Fictitious assets have no realizable value or physical existence.
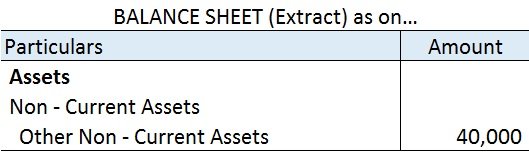
In the above, (C) preliminary expense is a fictitious asset. Preliminary expenses are the expenses incurred before the incorporation of a business. The word ‘fictitious’ means fake, these are not actually the assets of a company even though they are represented in the assets of the balance sheet.
Since the benefit of a fictitious asset is received over a period of time, the whole amount is not charged to the profit and loss account. The amount is amortized over several years. These expenses are non-recurring in nature. These expenses are shown as assets under the head miscellaneous expenditure. Also known as deferred revenue expenditure.
For example: A company incurred $50,000 as promotion costs before the formation of the business. This promotion cost will be deferred over 5 years. In the first year, $10,000 will be charged to the profit and loss account and the remaining $40,000 will be shown as an asset under the heading miscellaneous expenditure. Subsequently, $10000 will be charged to profit and loss for the next 4 years. The amount of $50,000 will be deferred over a span of 5 years.
Some other examples of fictitious assets :
Goodwill
Goodwill is not a fictitious asset because goodwill has a realizable value and can be sold in the market. Goodwill is an intangible asset which does not have a physical existence but can be traded for monetary value. Goodwill has an indefinite life and is sold when the business is sold. Goodwill can be self-generated or purchased. Goodwill is shown as an intangible asset under the heading fixed asset in the financial statements.
Patents
Patents are intangible assets which do not have a physical existence but have realizable value and can be sold in the market. So, patents do not come under the category of fictitious assets. Patents are basically intellectual property. The purchase price of the patent is the initial purchase cost which is amortized over the useful life of the asset. Patents are shown as intangible assets under the heading fixed asset in the balance sheet of the company.
Claim receivable
Claim receivable is an asset if the claim has been authorized by the insurance company. Claim receivable has a monetary value, so does not come under the category of a fictitious asset. If the claim is not yet authorized by an insurance company, it will be shown as a footnote in the financial statements. Authorized claim receivable is shown as a current asset in the financial statement.
See less