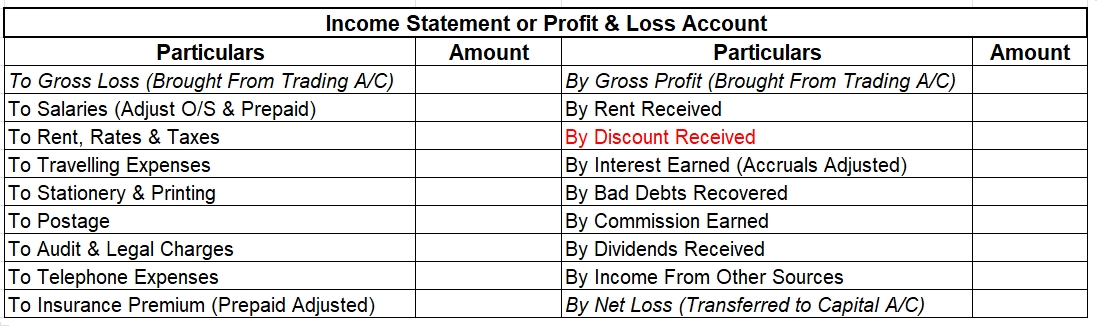
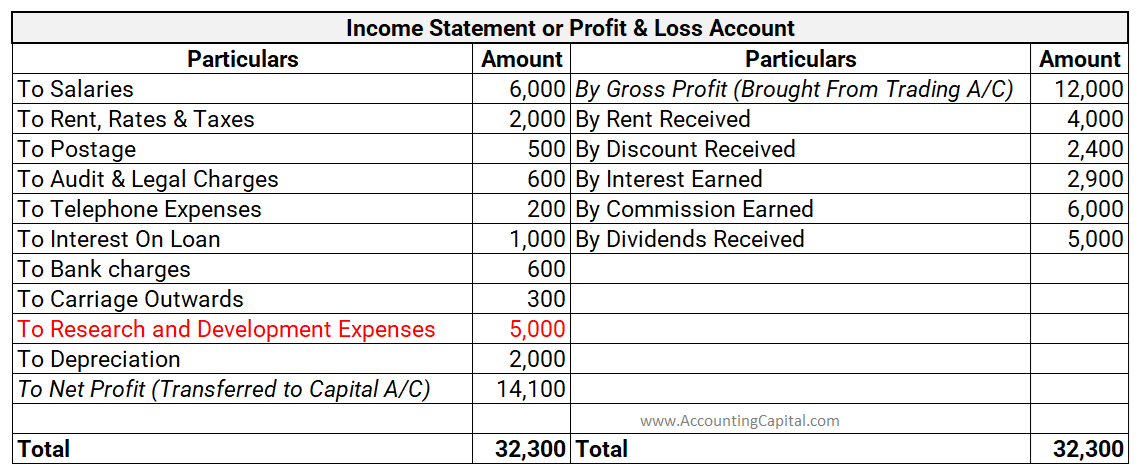
The profit earned by an entity is determined through the profit and loss account. All the expenses are recorded on the debit side of the profit and loss account while all the incomes are recorded on the credit side. The profit is shown as the credit balance of profit and loss A/c. When the sum of itRead more
The profit earned by an entity is determined through the profit and loss account. All the expenses are recorded on the debit side of the profit and loss account while all the incomes are recorded on the credit side.
The profit is shown as the credit balance of profit and loss A/c. When the sum of items on the debit side of a profit and loss account is less than the sum of those on the credit side, it implies profit while when the sum of the items on the credit side is less than the sum of those on the debit side, it implies a loss for the entity.
The Reason for Credit
Profit is recorded as an increase in equity
To understand the reason why profit is recorded as a credit balance, we must first understand the basic principle of debit and credit.
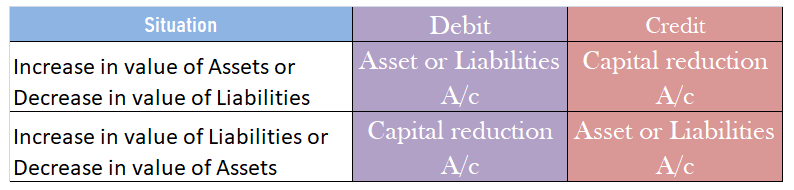
The basic principle of debits and credits is that debits increase asset accounts and decrease liability and equity accounts while credits decrease asset accounts and increase liability and equity accounts.
The revenue that a company earns is credited to the income account and increases equity.
The expenses that a company incurs to earn that revenue are debited to the expense account and decrease equity.
The difference between revenue and expenses is the profit, which is recorded as an increase in equity.
Increase in equity due to revenue – decrease in equity due to expense = profit
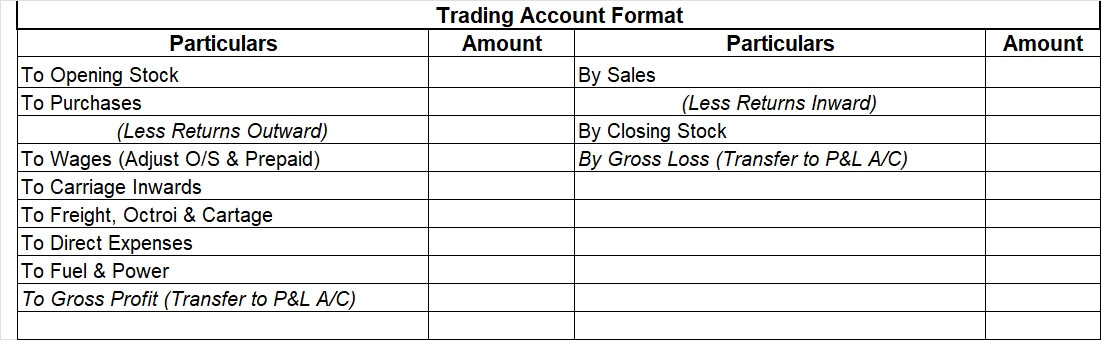
Gross Profit Vs Net Profit
Revenue is the total income that a business or profession earns. Profit is the excess revenue that remains after reducing all expenses from it.
Gross profit is the profit that a company earns after reducing the cost of goods sold from sales revenue while net profit is the profit that a business earns after reducing the total of all its direct and indirect expenses from its direct as well as indirect allowable business income.
Conclusion
The basic principle of debit and credit governs the classification of profit as a debit or credit. Since profit increases our equity, it is a credit.
In the case of a company, it belongs to the shareholders. It is usually recorded in the retained earnings account. Profit can be reinvested in the business or can be distributed as a dividend. In the case of a sole proprietorship, the profit belongs to the owner and is recorded in the owner’s capital account.
See less

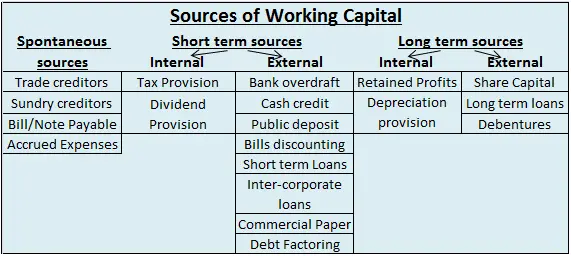
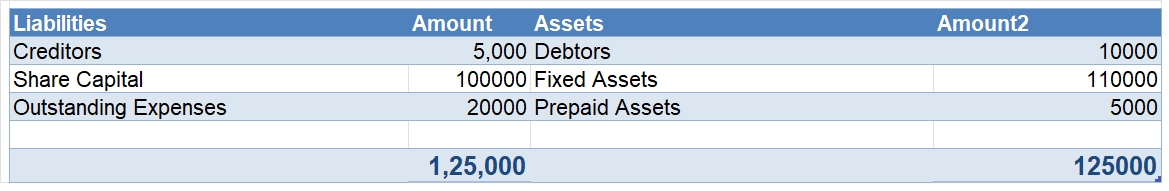
A revenue reserve is a type of reserve where a portion of the net profit is set aside for future requirements. It serves as a great source of internal finance for the company to meet its short term requirements. The funds put into this reserve are earned from the daily operations of a company. RevenRead more
A revenue reserve is a type of reserve where a portion of the net profit is set aside for future requirements. It serves as a great source of internal finance for the company to meet its short term requirements. The funds put into this reserve are earned from the daily operations of a company. Revenue reserves are shown on the liabilities side of a balance sheet under reserves and surplus. Some examples of revenue reserve are :
Retained Earnings is that part of the net profit which is left after the distribution of dividends to shareholders. This amount can be invested in the company to gain profits. It is not technically a reserve as it is held after distribution of dividends but it can still be used as one.
On the other hand, a capital reserve is not a part of the revenue reserve. It is created from capital profits to finance long term projects of a company. It is used for specific purposes only.
See less