The word, “deferred” means delayed or postponed and “revenue” in layman’s terms means income. Therefore deferred revenue means the revenue which is yet to be recognised as income. It is actually unearned income. In accrual accounting, income is recognised only when it is accrued or earned. DeferredRead more
The word, “deferred” means delayed or postponed and “revenue” in layman’s terms means income. Therefore deferred revenue means the revenue which is yet to be recognised as income. It is actually unearned income.
In accrual accounting, income is recognised only when it is accrued or earned. Deferred revenue is the income received before the performance of the economic activity to earn it.
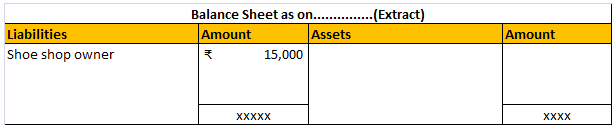
Example: A shoe shop owner gives an order to a shoe manufacturer of 1000 pair of shoes which is to be delivered after 4 months. He also gives him a cheque of ₹15,000 in advance, the rest ₹5000 is to be given at the time of delivery.
So, in this case, the ₹15,000 is actually is unearned revenue i.e. deferred revenue. It will be recognised as revenue when the shoe manufacture completes the order and deliver it.

Till then, the deferred revenue is reported as a liability in the balance sheet. Like this:
After recognition as revenue, it will be reported in the statement of profit or loss:

Hence, to summarise, deferred revenue is:
- Unearned revenue
- Recognised as income till it is earned
- Till then it is recognised and reported as a liability in the balance sheet.
Some examples of deferred revenue are as follows:
- Advance rent received
- Advance payment for goods to be delivered.
- Advanced payment for services to be provided.
Now the question arises why deferred revenue is recognised as a liability. It is due to the fact that the business may not be able to perform the economic activity successfully to earn that revenue.
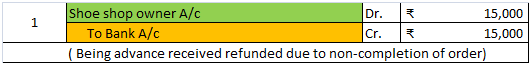
Taking the above example, suppose the shoe manufacturer is not able to honour its commitment and the shoe shop owner can wait no more, then the advanced money of ₹ 15,000 is to be refunded. That’s why deferred revenue is recognised as a liability because it is a liability if we consider the principle of conservatism (GAAP).

Yes, Accounts Payable can have a Debit balance. Accounts payable is a liability and thus, has a credit balance but can have a debit balance in case the creditor is overpaid or when there is purchase return (for already-paid goods) ACCOUNTS PAYABLE Accounts payable refers to all short-term liaRead more
Yes, Accounts Payable can have a Debit balance. Accounts payable is a liability and thus, has a credit balance but can have a debit balance in case the creditor is overpaid or when there is purchase return (for already-paid goods)
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
Accounts payable refers to all short-term liabilities of the business that are to be paid. These are usually paid within a duration of 90 days. It includes both Trade payable (goods and services purchased on credit) as well as expenses payable (used but payment not made yet) like rent payable, electricity bill, etc.
Businesses cannot make every payment on the spot. There can be cases when the business is facing a shortage of funds, can have funds but doesn’t have enough cash (or liquid funds) to make payment or simply doesn’t want to make payment on the spot to reduce its capital requirement.
So, like us businessmen also purchase goods on credit or use services for which payment is to be made soon. All these are liabilities for the business.
However, they must be related to the business to be considered as accounts payable.
DEBIT BALANCE OF ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
Debit balance of accounts payable means money owed by others. There is Debit balance when
OVERPAYMENT is made to the creditors or the supplier. It happens when the wrong amount is paid or payment is made twice for the same transaction.
Suppose you need to pay $10,000 as rent within 30 days. After 25 days you mistakenly made a payment of $12,000.
In this case,
PURCHASE RETURN of already paid goods also result in debit balance of Accounts Payable.
Suppose you bought goods worth $50,000 from Mr A on credit and paid for the same. Later, you returned all the goods because they were defective. Now, there will be Debit balance of Accounts Payable till there is a full refund of $50,000 by Mr A.
How is Accounts Payable Treated Normally?
Accounts Payable are the current liabilities of the firm and are shown under the head Current Liabilities in the Balance Sheet. Its liability, thus has a credit balance which represents the amount owed by the firm to others. It is credited when increases and debited when decreases.
For example – Suppose you purchased goods worth $30,000 and agreed to pay after 30 days. So, Accounts payable will be credited by $30,000 and purchases will be debited by $30,000.
Purchases A/c – $30,000 (debit)
To Accounts Payable A/c – $30,000
After 30 days payment is made in cash, which means the liability decreased. So, Accounts Payable A/c will be debited.
Accounts Payable A/c – $30,00
To Cash – $30,000
See less