Definition Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business. Or in other words, we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cRead more
Definition
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business.
Or in other words, we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cycle period although it is more than the period of 12 months from the date of the balance sheet.
For example, goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn a profit, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
List of current assets
The list of current assets is as follows:-
- Cash in hand
- Cash equivalents
- Bills receivables
- Sundry debtors
- Prepaid expenses
- Accrued income
- Closing stock
- Short-term investments ( marketable securities )
- Other liquid assets
Now here are a few definitions for the above list of current assets which are as follows:-
-
Cash in hand
Cash comprises cash on hand and demand deposits with banks.
-
Cash equivalents
Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid investments that are readily convertible into known amounts of cash and which are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value.
-
Bills receivables
It means a bill of exchange accepted by the debtor, the amount of which will be received on the specific date.
-
Sundry debtors
A debtor is a person or entity who owes an amount to an enterprise against credit sales of goods and/or services rendered.
-
Prepaid expenses
Expense that has been paid in advance and benefit of which will be available in the following years or year.
-
Accrued income
Income that has been earned in the accounting period but in respect of which no enforceable claim has become due in that period by the enterprise.
-
Closing stock
Stock or inventory at the end of the accounting period which is shown in the balance sheet and which is valued on the basis of the “ cost or net realizable value, whichever is lower “ principle is called closing stock.
-
Short term investment
Investments that are also known as marketable securities and are held for a temporary period of time i.e, for less than 12 months, and can be easily converted into cash are called short-term investments.
Criteria for classification
Now let us see the classification of assets in the case of companies as per Schedule III of the Companies act 2013.
An asset is a current asset if it satisfies any one of the following criteria which are as follows:-
- It is held primarily for the purpose of being traded.
- It is expected to be realized in or is intended for sale or consumption in the company’s normal operating cycle.
- It is expected to be realized within 12 months from the reporting date.
- It is cash and cash equivalent unless it is restricted from being exchanged or used to settle a liability for at least 12 months after the reporting date.
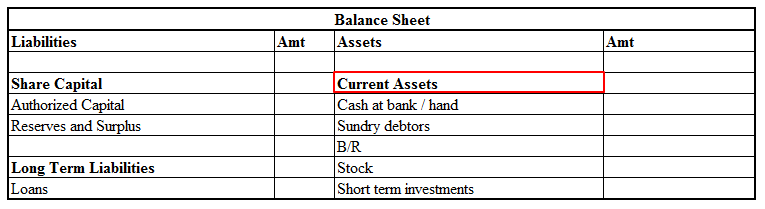
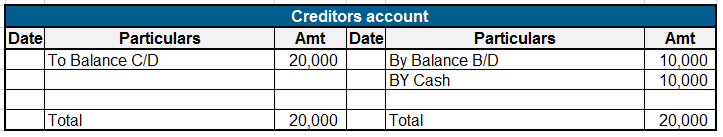
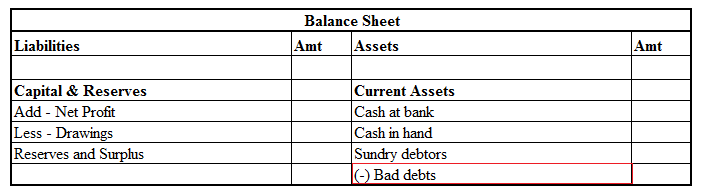
Here is an extract of the balance sheet showing current assets

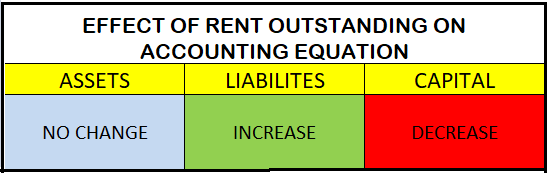
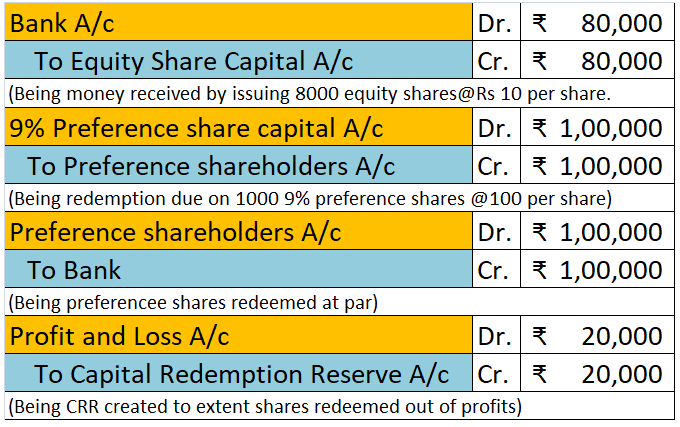
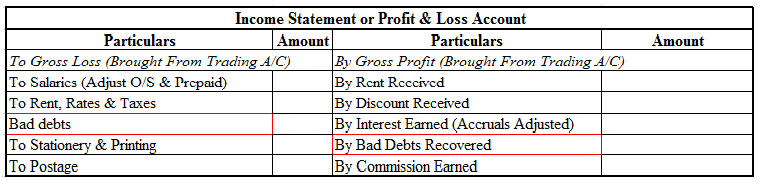
Workmen Compensation Reserve as the name suggests is a reserve created by the company to compensate its employees in the event of any uncertainty in future. It is created to protect the interest of workers in the company. Workmen Compensation Reserve Account is generally given effect in case of admiRead more
Workmen Compensation Reserve as the name suggests is a reserve created by the company to compensate its employees in the event of any uncertainty in future. It is created to protect the interest of workers in the company.
Workmen Compensation Reserve Account is generally given effect in case of admission, retirement of partners or dissolution of firm.
If there is a change in the estimated value of reserve it is given effect during the revaluation of assets and liabilities.
Journal entry if the existing reserve is less than the new estimated amount:
Revaluation A/c (Dr)
To Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c
The reserve is credited because we need to create more than the existing reserve, since the new estimated liability is more than the existing.
Journal entry if the existing reserve is more than the new estimated amount:
Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c (Dr)
To Revaluation A/c
The reserve is debited because we need to decrease the existing reserve, since the new estimated liability is less than the existing.
If a worker claims compensation, it is said to be a liability against the reserve. In case of dissolution, any such liability against workmen compensation reserve takes priority to be paid off according to the law.
Journal entry in case of claim against reserve is:
Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c (Dr)
To Workmen Compensation Claim
The amount is transferred from the reserve to a new liability, hence the reserve is debited and the claim is credited.
If there are not sufficient funds in the firm to pay the liability, partners will have to bring funds from their personal assets to pay the workers.
Journal entry when partner’s have to bring funds:
Partner’s Capital Account (Dr)
To Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c
Partner’s need to bring funds to fulfill the liability, hence there account is debited and since the reserve is increased, hence it is credited.
If there is no liability against the Workmen Compensation Reserve then it is distributed amongst the partners in their existing profit-sharing ratio.
Journal entry for distribution of reserve is:
Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c (Dr)
To Partner’s Capital Account
Since, reserve is more than required it is distributed among partners, hence their account is credited and as the reserve decreases, it is debited.
See less