Accrual Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irrespective of the fact when such amount has been paid. An accrual of the expenditure which is not paid will be listed in the books of accounts. These accruals can be furtRead more
Accrual
Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irrespective of the fact when such amount has been paid.
An accrual of the expenditure which is not paid will be listed in the books of accounts. These accruals can be further divided into two parts
Accrual Expense-
Accrual Expense means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be paid on a later period.
For example- If rent of 10,000 for the month of March was paid in April month then this rent will be accounted for in the books in March
For example- Interest of 1,000 for the month of March of the loan amount of 10,000 paid in April then will be accounted for in the books in March
These are the following accrued expense
- Accrual Rent– Accrual rent means the amount for using the land of the landlord is paid at a later period than the period when it is put into use.
- Accrual Insurance– Accrual insurance means the amount paid as a premium to the insurance company paid on a later period than the period when it is due
- Accrual Expense- Acrrual expense means the amount for any expense paid on a later period than the period when it pertains to be paid
- Accrual Wages- Accrual wages means the amount which is paid to employees on a later period than the period when the wages get due
- Accrual Loan Interest– Loan Interest means the amount of interest on a loan which is paid on a later period than the period when it is due on
Accrual Revenue-
Accrual Revenue means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be received in the later period.
For example- If interest of 10,000 on bonds for the period of March is received in April months then this amount will be accounted for in March. These are the following accrued revenue
For example- Rent of 10,000 for the month of March received in April month then this rent will be accounted for in the books in March
- Accrual Income- Acrrual expense means the amount for any income received on a later period than the period when it pertains to be received
- Accrual Rent– Accrual rent means the amount for using the land of the entity by the other party is received at a later period than the period when it is put into use.
- Accrued Interest– Accrued interest means the amount of interest received on a later period than the period when it pertains to receive



Prepaid expenses are those expenses that have not been expired yet but their payment has already made in advance. There are many examples of prepaid expenses such as rent paid in advance, interest paid in advance, unexpired insurance You might be wondering what kind of account it is? As the name sugRead more
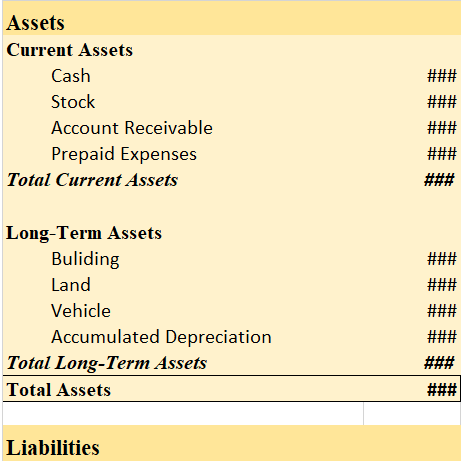
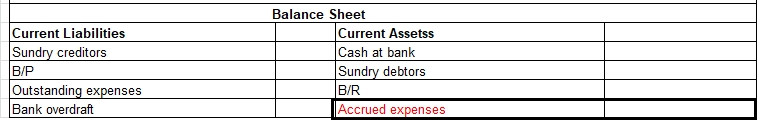
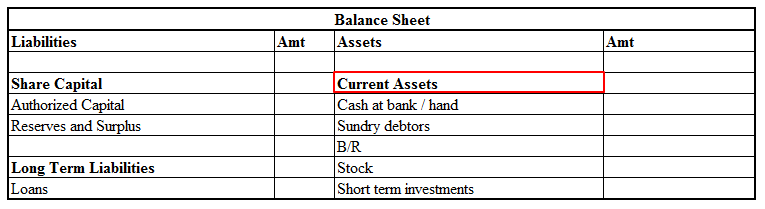
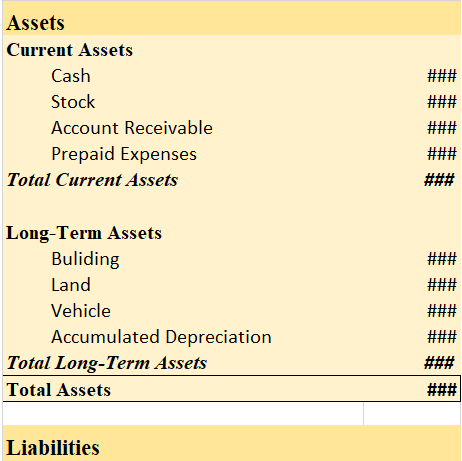
Prepaid expenses are those expenses that have not been expired yet but their payment has already made in advance. There are many examples of prepaid expenses such as rent paid in advance, interest paid in advance, unexpired insurance
You might be wondering what kind of account it is? As the name suggests it should be an expense but actually it’s an asset. When we initially record prepaid expenses we consider them as current assets and show them in the balance sheet. It turns out to be an expense when we use the service/item for what we have paid for in advance.
The entry for the above explanation is as follows:
From the modern rule, we know Assets and expenses increased are debits while decrease in assets and expenses are credit.
As this is asset, increase in asset therefore we debit prepaid expense and on the other hand we pay cash/ bank on behalf of that asset in advance hence there is decrease in assets hence credited. The entry will be as follows:
when this prepaid expense actually becomes expense we pass the adjusting entry. The entry will be as follows:
Let me give you simple example of the above entry.
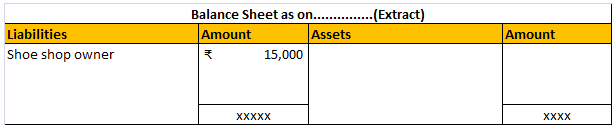
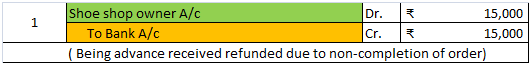
Suppose you pay advance rent of Rs 9,000 for six months for the space you haven’t used yet. So you need to record this as prepaid expense and show it on the asset side of the balance sheet under current assets. Since you paid for the same the entry would be as follows:
As each month passes we will adjust the rent with prepaid rent account. Since the rent was advanced for 6 months, therefore (9,000/6) Rs 1500 will be adjusted each month with the rent expense account. The adjustment entry will be:
The process is repeated until the rent is used and asset account becomes nil.
See less