Deferred Tax Liability A deferred tax liability represents an obligation to pay taxes in the future. These taxes are owed by a company but are not due to be paid until a future date. Companies that incur such an obligation prepare and maintain two financial reports every year: a tax statement and anRead more
Deferred Tax Liability
A deferred tax liability represents an obligation to pay taxes in the future. These taxes are owed by a company but are not due to be paid until a future date.
Companies that incur such an obligation prepare and maintain two financial reports every year: a tax statement and an income statement.
This is because companies maintain their books as per book accounting rules (GAAP/IFRS), but they have to pay taxes according to tax accounting rules, and they each have to follow their own guidelines.
For example, a tax statement follows the cash basis of accounting, and an income statement follows the accrual basis of accounting.
Companies calculate their profit as per the accounting rules as well as tax laws known as accounting income and taxable income, respectively. Some differences arise due to the application of different provisions of law.
These temporary differences are accounted for, recognized, and carried forward in the books of accounts and create deferred tax.
Example
Here is an example of deferred tax liability.
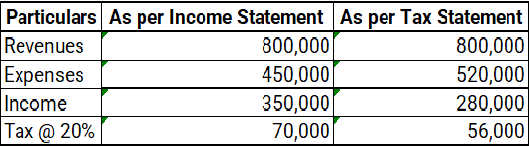
In the given example, tax as per income statement is 70,000, whereas as per tax statement it is 56,000. This temporary difference is termed as deferred tax liability of 14,000.
When accounting income is more than taxable income, it creates Deferred Tax Liability. It will be adjusted in the books of accounts during one or more subsequent year(s).
How Does it Arise?
There are several instances under which a company creates a deferred tax liability. Some other instances are:
Depreciation Methods
- One of the most common reasons for deferred tax liability is when a company uses different depreciation methods in the Income and Tax Statement.
- Assets are depreciated by calculating the straight-line method in the Income Statement, while the written-down value method is used in the Tax Statement.
- Since the straight-line value method produces lower depreciation when compared to the WDV method, accounting income is temporarily higher than taxable income.
- The company recognises deferred tax liability as this difference between accounting income and taxable income.
Treatment of Revenue & Expenses
- Deferred tax liability can also arise when there is a difference in the way revenue and expenses are treated in books of accounts.
- As mentioned earlier, accounting rules follow the accrual basis of accounting while tax laws follow the cash basis of accounting.
- Meaning in the tax statement, income and expenses are recorded when they are received or paid, not when they are incurred or realised.
- This difference in the treatment of revenue and expenses creates deferred tax liability.
Impact on Financial Statements
Recognising deferred tax liability and its subsequent effect on the company’s financial statement is important as it simplifies the process of auditing and analysing financial reports.
Balance Sheet
- Deferred tax liabilities are recorded on the liability side of the balance sheet under non-current liabilities.
Cash Flow Statement
- The deferred tax liability is added back to the net income in calculating cash flow from operating activities to show the actual cash flow.

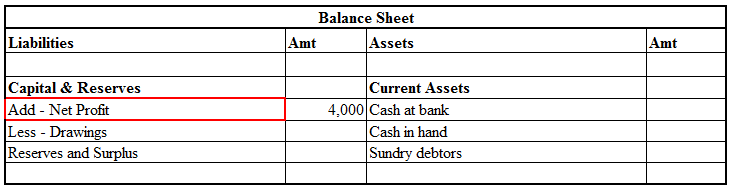
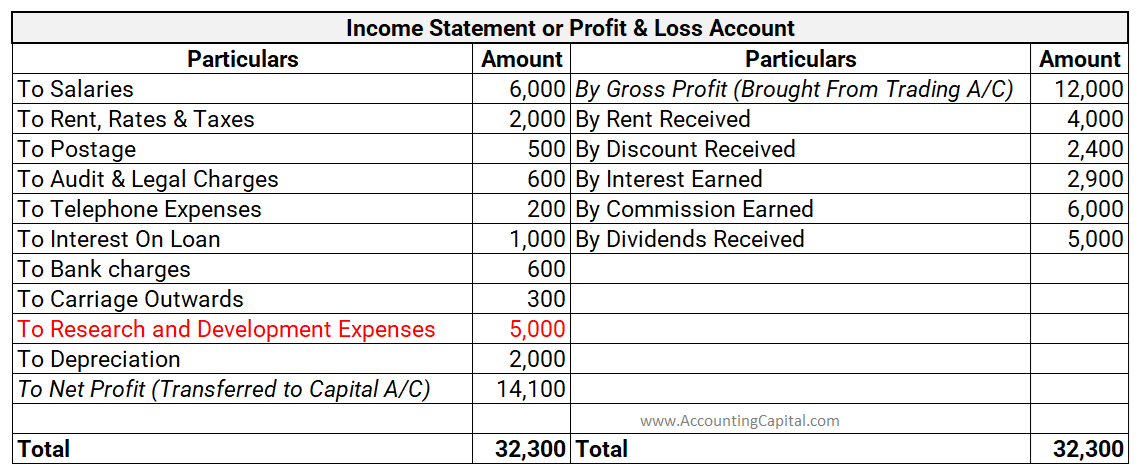
Prepaid expense means a service to be rendered in the future period for which the business has already paid the remuneration. Prepaid expenses are classified as assets. The benefits of this payment will accrue to the business at a later period. For example, insurance is often paid for annually on tRead more
Prepaid expense means a service to be rendered in the future period for which the business has already paid the remuneration. Prepaid expenses are classified as assets. The benefits of this payment will accrue to the business at a later period.
For example, insurance is often paid for annually on the basis of the calendar year. A business may pay insurance every year on 1st January for that entire year. While preparing the financial statements on 31st March, it will recognize the insurance premium for the period 1st April to 31st December of the next financial year as a prepaid insurance expense.
Why are prepaid expenses classified as assets?
First of all, let us understand what an asset is. An asset is anything over which the business has ownership rights and which it can sell for money. The benefits of this asset should accrue to the business.
In light of this definition, let us analyze prepaid expenses as an asset. As the business has already paid for these goods or services, it becomes a legal right of the business to receive the relevant goods or services at a later date. As the benefit of this expense would accrue to the business only at a later date, the prepaid expenses are classified as an asset.
Some examples of prepaid expenses are prepaid insurance, prepaid rent etc
Treatment of Prepaid Expenses
Prepaid expenses are recorded in the balance sheet under the heading “Current Assets” and sub-heading “Other Current Assets”
As per the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles or GAAP, expenses must be recognized in the accounting period to which they relate or in which the benefit due to them is likely to arise. Thus, we cannot recognize the prepaid expenses in the accounting period in which they are incurred.
Prepaid assets are classified as assets and carried forward in the balance sheet to be debited in the income statement of the accounting period to which they relate.
Adjusting Entries
Adjusting entries are those entries that are used to recognize prepaid expenses in the income statement of the period to which they relate. These entries are not used to record new transactions. They ensure compliance with GAAP by recognizing the expenses in the period to which they relate.
Conclusion
The GAAP and basic definition of an asset govern the treatment of prepaid expenses as an asset. The business incurs them in an accounting period different from the accounting period in which their benefit would accrue to the business. The business has a legal right to receive those goods or services.
The business carries them as a current asset on the balance sheet. In the relevant accounting period, they are recognized in the income statement.
See less