Fluctuating Capital Fluctuating capital is a capital that is unstable and keeps changing frequently. In the fluctuating capital, the capital of each partner changes from time to time. In partnership firms, each partner will have a separate capital account. Any additional capital introduced during thRead more
Fluctuating Capital
Fluctuating capital is a capital that is unstable and keeps changing frequently. In the fluctuating capital, the capital of each partner changes from time to time. In partnership firms, each partner will have a separate capital account. Any additional capital introduced during the year will also be credited to their capital account. In the fluctuating capital method, only one capital a/c is maintained i.e no current accounts like in the fixed capital a/c method. Therefore, all the adjustments like interest on capital, drawings, etc. are completed in the capital a/c itself.
It is most commonly seen in partnership firms and it is not essential to mention the Fluctuating Account Method in the partnership deed.
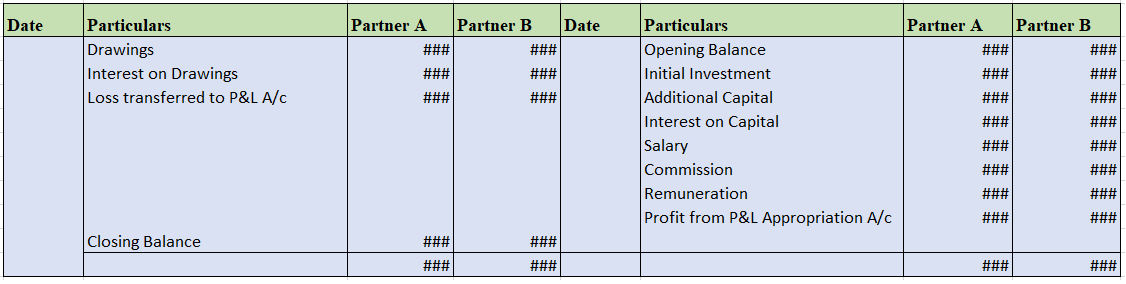
- All the adjustments resulting in a decrease in the capital will be debited to the partner’s capital, such as drawings made by each partner, interest on drawings, and share of loss.
- Similarly, the activities or adjustments that lead to an increase in the capital are credited to the partner’s capital account, such as interest on capital, salary, the share of profit, and so on.
Fluctuating Capital Account Format
See less

Journal Entry for Calls in Advance Calls in advance mean excess money received by the company than what has been called up. Calls in advance are treated as Current Liability and shown in the Balance Sheet on the liability side. Journal Entry will be : Here we will "Debit" Bank A/c as it will increaRead more
Journal Entry for Calls in Advance
Calls in advance mean excess money received by the company than what has been called up. Calls in advance are treated as Current Liability and shown in the Balance Sheet on the liability side.
Journal Entry will be :
Here we will “Debit” Bank A/c as it will increase assets of the company and “Credit” Calls in Advance A/c because it will increase the company’s current liabilties.
For Example:
Mr.Z shareholder of ABC Ltd was allotted 2,000 equity shares of Rs.10 each. He paid call money at the time of allotment.
Journal Entry is as follows:
Here, the company received an excess amount of Rs.6,000 (2,000*3) from a shareholder Mr.Z who paid the call money in advance. ABC Ltd will record this under Calls in Advance A/c. While passing journal entry ABC Ltd will debit its Bank A/c by Rs.6,000 and credit calls in advance account by Rs.6,000.
When share calls are called up, calls received in advance are adjusted. The company will hold only the required amount which will make allotted shares fully paid.
Once the amount is transferred to relevant call accounts, calls in advance account will be written off.
See less