Depreciation refers to that portion of the value of an asset that is written off over the useful life of the asset due to wear and tear. Now, when we talk about depreciation, there are multiple methods to calculate depreciation such as: Straight Line Depreciation Method Diminishing Balance Method OrRead more
Depreciation refers to that portion of the value of an asset that is written off over the useful life of the asset due to wear and tear.
Now, when we talk about depreciation, there are multiple methods to calculate depreciation such as:
- Straight Line Depreciation Method
- Diminishing Balance Method Or Written Down Value Method
- Sum of Years’ Digits Method
- Double Declining Balance Method
- Sinking Fund Method
- Annuity Method
- Insurance Policy Method
- Discounted Cash Flow Method
- Use Based Methods
- Output Method
- Working Hours Method
- Mileage Method
- Other Methods
- Depletion Method
- Revaluation Method
- Group or Composite Method
The most commonly used methods are discussed below:
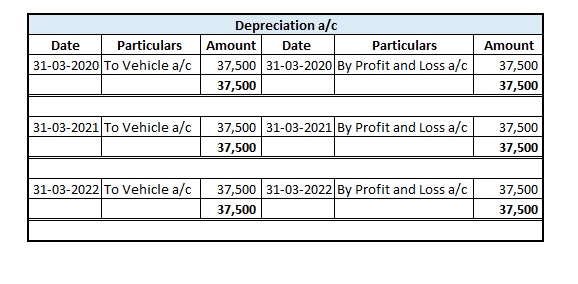
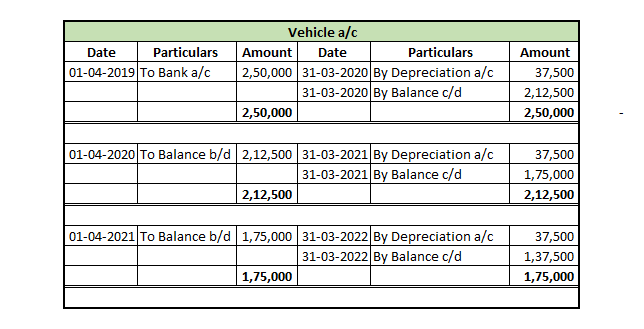
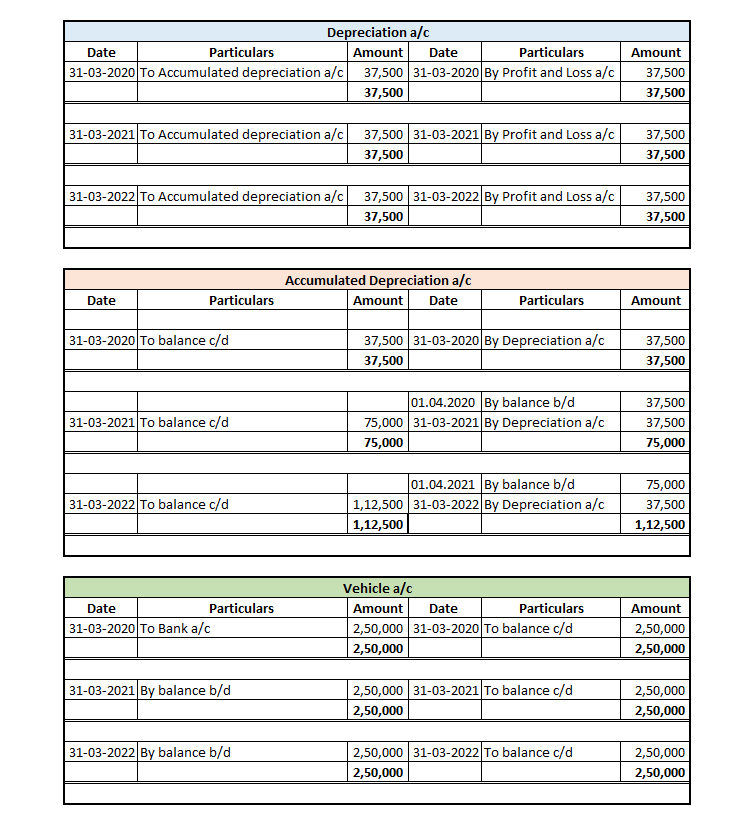
1. Straight Line Depreciation Method: This is the simplest method for calculating depreciation where a fixed amount of depreciation is charged over the useful life of the asset.
Formula: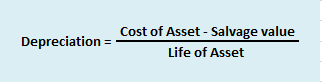
Suppose a company Bear Ltd purchases machinery costing 8,00,000 with useful life of 10 years and salvage value 1,00,000. Then depreciation charged to the machinery each year would be:
Depreciation = (8,00,000 – 1,00,000)/10 = 7,00,000/10 = 7,000 p.a.
2. Diminishing Balance Method Or Written Down Value Method: Under this method, a fixed rate of depreciation is charged every year on the opening balance of the asset which is the difference between the previous year’s opening balance and the previous year’s depreciation. Here the book value of asset reduces every year and so does the depreciation amount.
Formula:
Suppose a company Moon ltd purchases a building for 50,00,000 with a useful life of 5 years and decides to depreciate it @ 10% p.a. on Diminishing Balance Method. Then depreciation charged to the machinery would be:
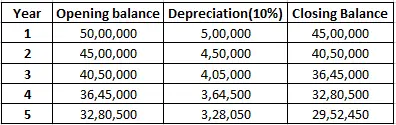
3. Sum of Years’ Digits Method: In this method, the life of asset is divided by the sum of years and multiplied by the cost of the asset to determine the depreciating expense. This method allocates higher depreciation expense in the early years of the life of the asset and lower depreciation expense in the latter years.
Formula:
Suppose a company Caps Ltd purchases machinery costing 9,00,000 having a useful life of 5 years. Then the depreciation cost would be:
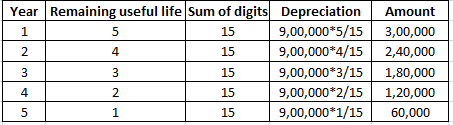
4. Double Declining Balance method: This method is a mixture of straight-line method and diminishing balance method. A fixed rate of depreciation is charged on the reduced value of the asset at the beginning of the year. This rate is double the rate charged under straight-line method.
Formula:
Suppose a company Paper Ltd purchases machinery for 1,00,000 with an estimated useful life of 8 years. Then the depreciation rate would be:
Straight line = 100%/8 = 12.5%
Double declining method = 2*12.5% = 25%
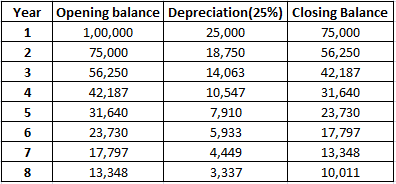
5. Sinking Fund Method: Under this method, the amount of depreciation keeps on accumulating till the asset is completely worn out. Depreciation is the same every year. Profits equal to the amount of depreciation is invested each year outside the company. At the time of replacement of the asset the investments and sold and the proceeds thereof are used to purchase the new asset.
6. Annuity Method: This method calculates depreciation by calculating its internal rate of return (IRR). Depreciation is calculated by multiplying the IRR with an initial book value of the asset, and the result is subtracted from the cash flow for the period.
7. Use Based Methods: Depreciation, under these methods, is based on the total estimated machine hours or total estimated units produced during the life of the machine. It is calculated by dividing the cost of the machine by the estimated total machine hours or estimated lifetime production in units and multiplying by the units produced or machine hours worked.
Formula: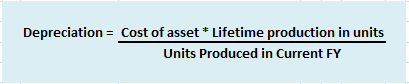
Suppose a company Box Ltd purchases machinery for 25,000 (estimated life 5 years) whose estimated life production is 5,000 units. If it produces 700 units in the first year of operation then depreciation cost would be:
Depreciation = 25,000/5,000*700 = 3,500
See less

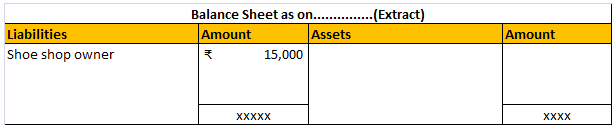

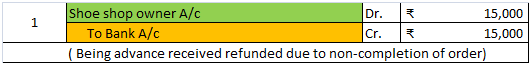
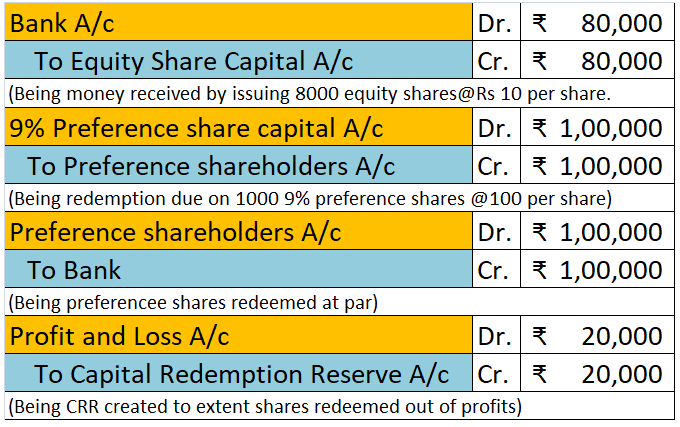


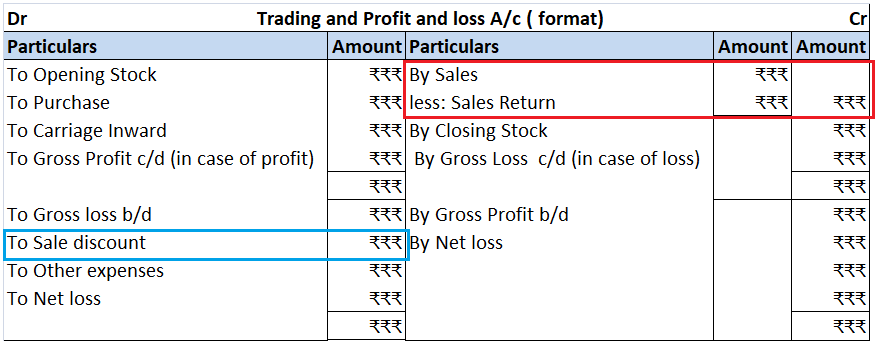
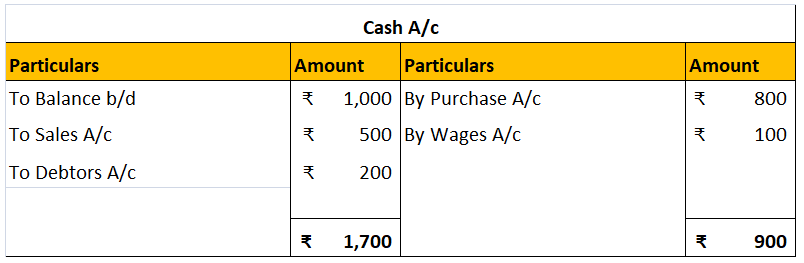
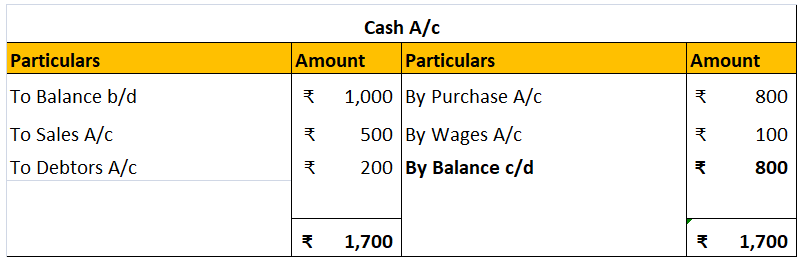

Accruals are not the same as provisions both are totally different from each other. Accruals and provision both are vital parts of accounts but work differently Accrual Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irreRead more
Accruals are not the same as provisions both are totally different from each other. Accruals and provision both are vital parts of accounts but work differently
Accrual
Accrual expense means the transaction that takes place in a particular period must be accounted for in that period only irrespective of the fact when such an amount has been paid.
An accrual of the expenditure which is not paid will be listed in the books of accounts. These accruals can be further divided into two parts
Accrual Expense
Accrual Expense means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be paid on a later period.
For example- 10,000 for the month of March was paid in April month then this rent will be accounted for in the books in March
These are the following accrued expense
Accrual Revenue
Accrual Revenue means any transaction that takes place in a particular period but the amount for it will be received on later period. For example- If interest of 10,000 on bonds for the period of March is received in April months then this amount will be accounted for in March. These are the following accrued revenue
PROVISIONS
Provision refers to making a provision/allowance against any probable future expense that the company might incur in the near future. This amount is uncertain and difficult to predict its surety.
However, as per the prudence concept of accounting a company needs to anticipate the losses that will incur in the near future due to which provision is made.
For example- A company has debtors of 10,000 but as per the company’s previous records company anticipates that 1% of debtors will become bad debts. So in this case company will make a provision of 1% that is 100 on it.
There are various types of provisions which are-
- Provision on Depreciation– Provision for Depreciation means a provision for future depletion of assets has been already created
- Provision for Doubtful Debts– Provision for Doubtful Debts means a provision created against debtors that doesn’t seem to be recovered in the near future
See less