Revenue and income are two accounting terms that are often used interchangeably. However, it is important to understand that these two terms are different. Let us know the difference between the two through the discussion below: What is Revenue? Revenue is the total amount of a business's sales. ItRead more
Revenue and income are two accounting terms that are often used interchangeably. However, it is important to understand that these two terms are different. Let us know the difference between the two through the discussion below:
What is Revenue?
Revenue is the total amount of a business’s sales. It is the total amount earned by a business before deducting any expenses. Revenue is recognized in accounting as soon as a sale happens, even if the payment hasn’t been received yet.
For example, XYZ Ltd sold 100 pens at a selling price of 10 per pen. The total revenue of the business is hence 1,000.
What is Income?
Income is the amount earned by a business after deducting any direct or indirect expenses. It is the amount that is left after subtracting all expenses, taxes and other costs from Revenue.
Which is a broader term between the two?
Revenue is a broader term as it includes the total earnings a business generates before deducting any expenses. It includes all sales of goods or services during a specific period.
On the other hand, income is calculated after deducting certain expenses like taxes, interest, etc. This makes it more specific and refined than revenue.
Revenue provides a measure of a company’s ability to generate sales and income reflects the efficiency in managing costs and generating profits.
See less

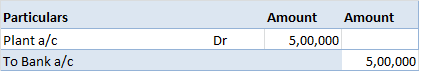

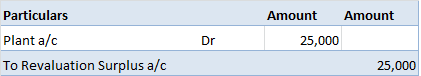
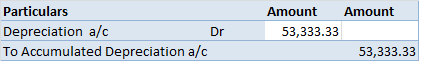
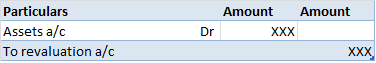
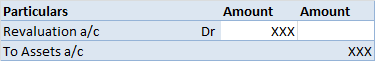
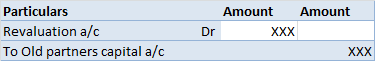
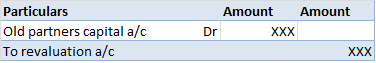


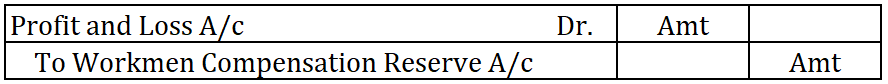

Definition The trial balance is a list of all the closing balances of the general ledger at the end of the year. Or in other words, I can say that it is a statement showing debit and credit balances. A trial balance is prepared on a particular date and not in a specific period. Types of error in theRead more
Definition
The trial balance is a list of all the closing balances of the general ledger at the end of the year. Or in other words, I can say that it is a statement showing debit and credit balances.
A trial balance is prepared on a particular date and not in a specific period.
Types of error in the trial balance
Now let me explain to you that what are the errors of trail balance which are as follows :
• Error of principle
• Compensating error
• Transactions completely omitted
• Error of recording
• Error of posting
A trial balance is not conclusive proof of the accuracy of the books of accounts since certain types of errors remain even when it tallies. They are explained below :
Error of principle
This error arises due to the incorrect application of the principle of accounting is not disclosed by the trial balance.
Compensating error
It means the group of errors committed in such a way that one mistake is compensated by another and the trial balance still agrees.
Transaction completely omitted
When the transaction is entirely omitted from recording in the books of account cannot be detected.
Error of recording
When both aspects of recording a transaction twice in the books of account take place.
Error of posting
Posting the correct amount on the correct side but in the wrong account is not reflected in the trial balance.
Steps to locate errors
Differences in the trial balance, howsoever minor they may be, must be located and rectified. The following steps are useful in locating errors are :
• Two columns of the trial balance should be totaled again.
• The list of sundry debtors and creditors should be checked to find out whether all balances of debtors and creditors have been correctly written in the trial balance or not.
• It should be checked that the balances of every account including cash and bank balances ( from the cash book ) have been written in the correct column of the trial balance.
• If the errors remain undetected, try to locate the errors by trial and error techniques such as finding an account showing a balance difference from the trial balance.
• Ledger balances should be balanced again.
• Check the totals of subsidiary books.
• Check the posting of nominal accounts.
• And at last if not possible to locate the difference in the trial balance is temporarily transferred to a suspense account.
Importance
As the trial balance is prepared at the end of the year so it is important for the preparation of financial statements like balance sheets or profit and loss.
Purpose of trial balance
• To verify the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger accounts
This means trial balance indicates that equal debits and credits have been recorded in the ledger accounts.
It enables one to establish whether the posting and other accounting processes have been carried out without any arithmetical errors.
• To help in locating errors
There can be some errors if the trial balance is untallied therefore to get error-free financial statements trial balance is prepared.
• To facilitate the preparation of financial statements
A trial balance helps us to directly prepare the financial statements and then which gives us the right to not look or no need to refer to the ledger accounts.
Rules of trial balance
When we prepare a trial balance from the given list of ledger balances, the following rules to be kept in mind that are as follows :
• The balance of all
• Assets accounts
• Expenses accounts
• Losses
• Drawings
• Cash and bank balances
Are placed in the debit column of the trial balance.
• The balances of
• liabilities accounts
• income accounts
• profits
• capital
Are placed in the credit column of the trial balance.
See less