Depreciation is an accounting process of allocating the value of an asset over its estimated useful life. When a company purchases an asset, depreciation will be calculated at the end of every financial year on the asset. The company records the amount of depreciation in a separate ledger, i.e., AccRead more
Depreciation is an accounting process of allocating the value of an asset over its estimated useful life.
When a company purchases an asset, depreciation will be calculated at the end of every financial year on the asset. The company records the amount of depreciation in a separate ledger, i.e., Accumulated Depreciation. This expense will be debited instead of depreciation in the Asset ledger.
Accumulated Depreciation
Accumulated depreciation is the accumulated reduction in the cost of an asset over time.
Depreciation is the reduction in the value of an asset over a specific timeframe, whereas accumulated depreciation is the sum of total depreciation on an asset since we bought it.
we will understand this concept with a simple example.
suppose machinery depreciates as follows
Year 1 – Depreciation is 5,000
Year 2 – Depreciation is 5,000
Year 3 – Depreciation is 5,000
Accumulated Depreciation in Year 3 = 5,000 + 5,000 + 5,000
Therefore, overall 3 years of depreciation are accumulated at the last year-end.
Journal entry for accumulated depreciation
Example: Excellence Co. has purchased a new motor vehicle which costs $8,000 for their cab business. The motor vehicle is depreciated at @20% per annum. At the end of the year, Excellence Co. will record this accumulated depreciation journal entry.
Year 1
Depreciation A/c Dr. – $1600
To Accumulated depreciation A/c – $1600
Year 2
Depreciation A/c Dr. – $1600
To Accumulated Depreciation A/c – $1600
Therefore, the Accumulated depreciation for the 2nd year end is $3200.
At the time of the sale of the motor vehicle, the amount of accumulated depreciation will be reduced from the total value of the asset.
Provision for depreciation
Provision for depreciation is very similar to accumulated depreciation. Instead of reducing the amount of depreciation from the value of an asset, a separate provision A/C will be created, and the depreciation amount will be credited to the provision account, i.e., Provision for Depreciation account every year, and the asset will be shown the same value without reducing the depreciation from it.
Journal entry for provision for depreciation
Example: Yesman Co. purchased Machinery worth $40000 at the beginning of the current year for their production. The machinery will be depreciated at @10% per annum. At the end of the year, Yesman Co. will record this provision for depreciation journal entry.
Year 1
Depreciation A/c Dr. – $4000
To Provision for Depreciation A/c – $4,000
Year 2
Depreciation A/c Dr. – $4000
To Provision for Depreciation A/c – $4000
Therefore, the Provision for depreciation balance will be $8000 at the 2nd year-end.
At the time of sale of the machinery, the amount of provision for depreciation created till the date will be reduced from the asset’s value.
Conclusion
Provision for depreciation and accumulated depreciation refers to the amount of depreciation accumulated over the useful life of an asset.
The terms accumulated depreciation and provision for depreciation are different in hearing, but these are similar from the financial perspective.
See less
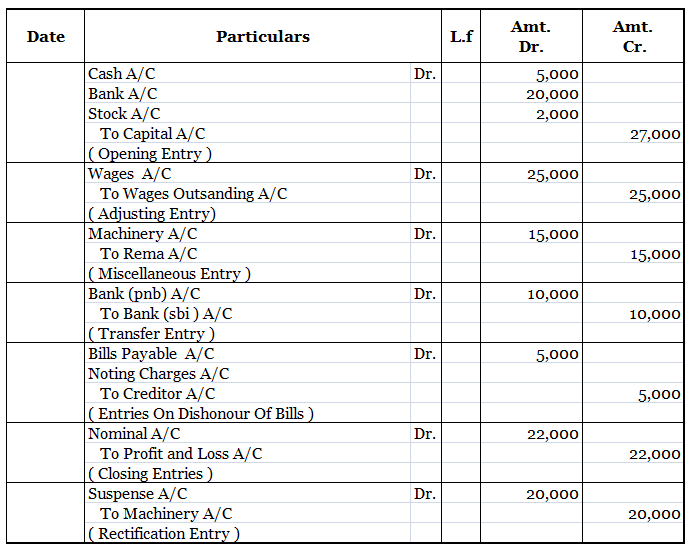
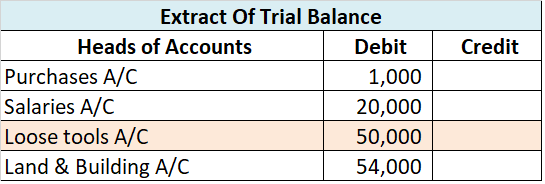
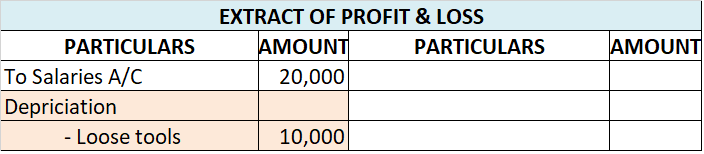
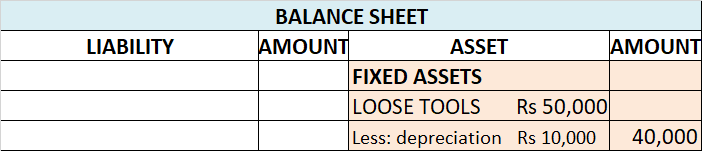
Interest on capital Interest on capital is interest payable to the owner/partners for providing a firm with the required capital to commence the business. Normally, it is charged for a full year on the balance of capital at the beginning of the year unless some fresh capital is introduced during theRead more
Interest on capital
Interest on capital is interest payable to the owner/partners for providing a firm with the required capital to commence the business. Normally, it is charged for a full year on the balance of capital at the beginning of the year unless some fresh capital is introduced during the year.
When the business firm faces a loss, the interest on capital will not be provided. It is permitted only when the business earns a profit. Such payment of interest is generally observed in partnership firms. It is provided before the division of profits among the partners in a partnership firm.
If an owner or partner introduces additional capital to the business then, it is also taken into account for providing interest on capital.
Interest on capital in the accounting equations
Interest on capital is an expense from a business point of view, as it is payable to the owner and is not paid in cash. Being an income from the owner’s point of view, it is added to his capital account. And being a business expense from the business point of view, it is therefore deducted from the capital.
Hence, it further doesn’t create any change in the accounting equation mathematically but it’s mandatory to be shown as it plays a vital role in the profit and loss a/c and even helps the business save tax.
Example
Z started a business with cash and stock of ₹45,000 and ₹5,000 respectively. Further, he received interest on capital of ₹1,000. The accounting equation for the following transactions will be as follows:
Accounting Equation
See less