Definition Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable. Bad debts will be treated in the following ways : On the debit side of the profit and loss account. In the curreRead more
Definition
Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable.
Bad debts will be treated in the following ways :
On the debit side of the profit and loss account.
In the current assets side of the balance sheet, these are deducted from sundry debtors.
For example loans from banks are declared as bad debt, sales made on credit and amounts not received from customers, etc.
Now I will show you an extract of the profit and loss account and balance sheet
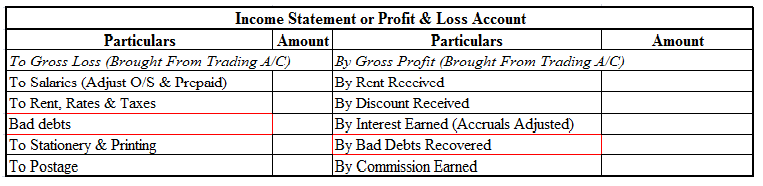
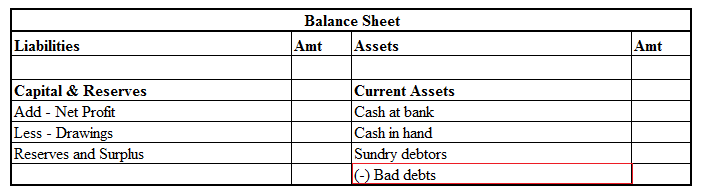
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or the rendering of services in the ordinary course of business.
For example, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Current liabilities are defined as liabilities that are payable normally within 12 months from the end of the accounting period or in other words which fall due for payment in a relatively short period.
For example bills payable, short-term loans, etc.
Accounting treatment
Now let me try to explain to you the accounting treatment for bad debts which is as follows :
- Balance sheet
-
- In the balance sheet either it can be shown on the asset side under head current assets by reducing from that specific assets.
-
- For example, if credit sales are made to a customer who says it’s not recoverable or is partially recoverable then the amount is bad debt. It’s a loss for the business and credited to the personal account of debtors or we can say reduced from debtor those are current assets of the balance sheet.
- Profit and loss account
-
- Bad debts are treated as an expense and debited to the profit and loss account.
- For example, as I have explained above, but before transferring to the balance sheet, bad debt will be debited to the profit and loss account as an expense.
Reasons for bad debts
There are several reasons why businesses may have bad debts some of them are as follows:-
- Offered credit to customers who were unable to pay them back, or they may have been the victim of fraud.
- When there is conflicts or dispute arise with respect to product size, color, quality, delivery, credit term, price, etc therefore debts becomes bad.
- Debtors have poor financial management or they are not able to pay debts on time.
- Debtors’ unwillingness to pay is also a reason for debts to become bad.
- Or there can be more cases where debtors are unable to collect debts and debts turns out to be bad.
Accounting methods
There are two methods for accounting for bad debts which are mentioned below:-
- First, is the direct written-off method which states that bad debts will be directly treated as expenses and expensed to the income statement, which is called the profit and loss account.
- Second, is the allowance method which means we create provisions for doubtful debts accounts and the debtor’s account remains as it is since the debtor’s account and provision for doubtful debts account are two separate accounts.
-
- Debts that are doubtful of recovery are provided estimating the debts that may not be recovered .amount debited to the profit and loss account reduces the current year’s profit and the amount of provision is carried forward to the next year.
-
- Next year, when debts actually become bad debts and are written off, the amount of bad debts is transferred ( debited ) to the provision for doubtful debts account.
-
- The amount of bad debts is not debited to the profit and loss account since it was already debited in earlier years.
-
- Provision for doubtful debts is shown in the debit side of the profit and loss account as well as shown as a deduction from sundry debtors in the assets side of the balance sheet.
Related terms
So there are a few related terms whose meanings you should know
- Further bad debts :
- It means the amount of sundry debtors in the trial balance is before the deduction of bad debts. in this situation, entry for further bad debts is also passed into the books of account.
- That is bad debts are debited and the debtor’s account is credited. And the accounting treatment for them is the same as bad debts which I have shown you above.
- Bad debts recovered :
-
- It may happen that the amount written off as bad debts is recovered fully or partially.
- In that case, the amount is not credited to the debtor’s (personal) account but is credited to the bad debts recovered account because the amount recovered had been earlier written off as a loss.
- Thus amount recovered is a ‘gain’ and is credited to the profit and loss account.
See less




When a company earns profit, it distributes a proportion of its income to its shareholders, and such distribution is called the dividend. The dividend is allocated as a fixed amount per share and shareholders receive dividends proportional to their shareholdings. However, a company can only pay diviRead more
When a company earns profit, it distributes a proportion of its income to its shareholders, and such distribution is called the dividend. The dividend is allocated as a fixed amount per share and shareholders receive dividends proportional to their shareholdings.
However, a company can only pay dividends out of its current year profits or retained earnings (profits of the company that are not distributed as dividend and retained in the business is called retained earnings) of previous years but not out of capital.
Dividends can be paid to shareholders in the form of
For companies, payment of regular dividends boosts the morale of the shareholders, investors trust the companies more and it reflects positively on the share price of the company.
For example, Nestle in India paid an interim dividend of 1100.00% to its shareholders in 2021.
The journal entry for dividend paid is
According to the golden rules of accounting-
According to modern rules of accounting-
For example-
A company paid a dividend of 25 crores to its shareholders in cash, the journal entry according to golden rules will be-
(in crores)
(in crores)
See less