The term "principal book of accounts'' refers to the set of ledgers that an entity prepares to group the similar transactions recorded as journal entries under an account. So to put it simply, the principal book of accounts mean ledgers. Ledgers are prepared by posting the debits and credits of a joRead more
The term “principal book of accounts” refers to the set of ledgers that an entity prepares to group the similar transactions recorded as journal entries under an account.
So to put it simply, the principal book of accounts mean ledgers.
Ledgers are prepared by posting the debits and credits of a journal entry to the respective accounts.
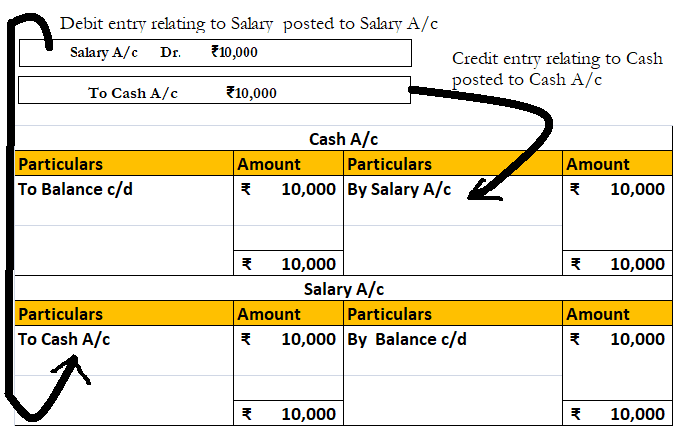
A ledger groups the transactions concerning the same account. For example, Mr B is a debtor of X Ltd. Hence all the transactions entered into with Mr. will be grouped into the ledger Mr B A/c in the books of X Ltd.
Ledgers are of utmost importance because all the information to any account can be known by its ledger.
Preparation of ledger is very important because all the information to any account can be known by its ledger. Ledgers also display the balance of each and every account which may be debit or credit. This helps in the preparation of the trial balance and subsequently the financial statements of an entity.
Hence, it is the most important book of accounts and calling it the ‘books of final entry’ is also justified.
See less

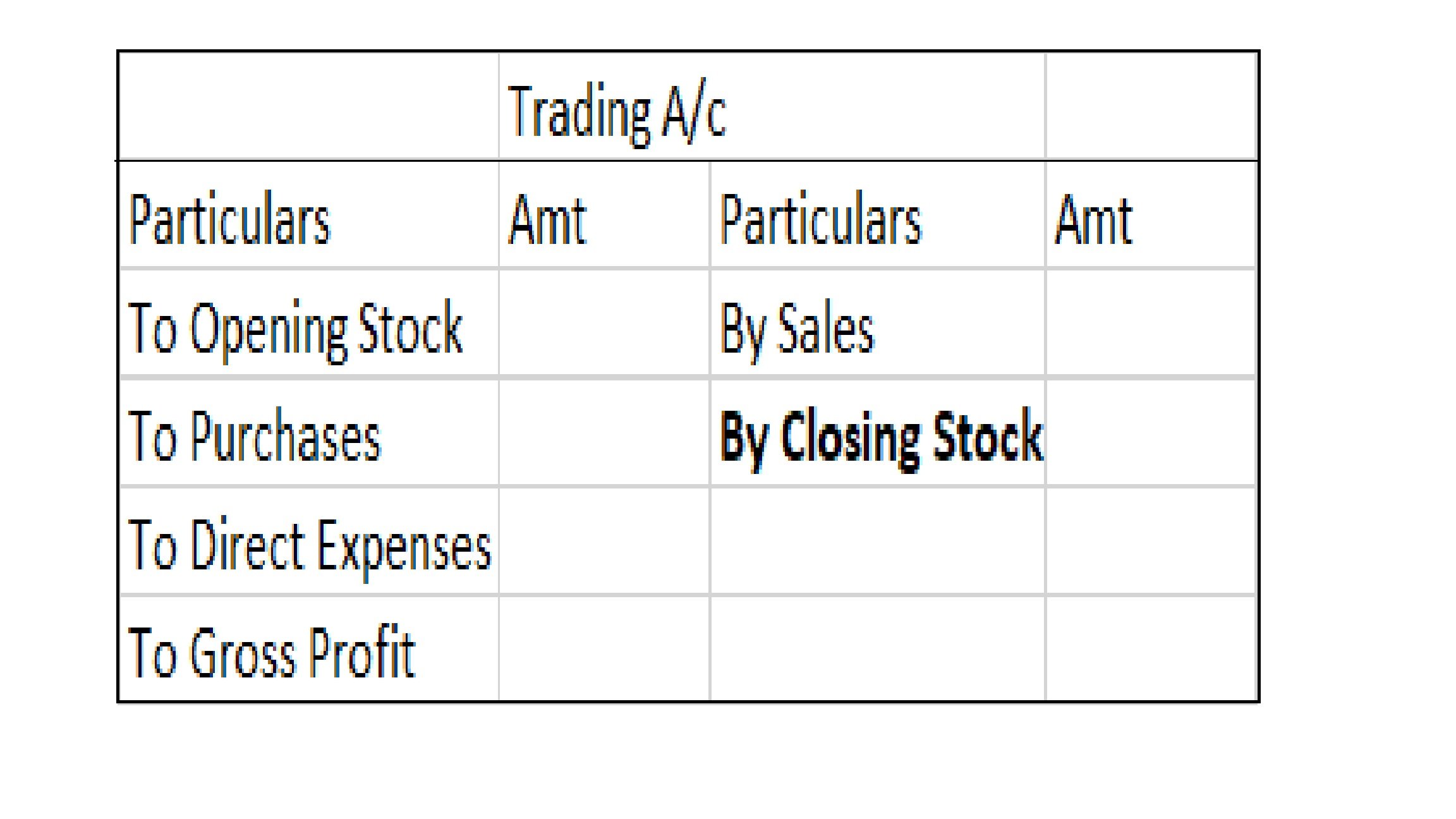
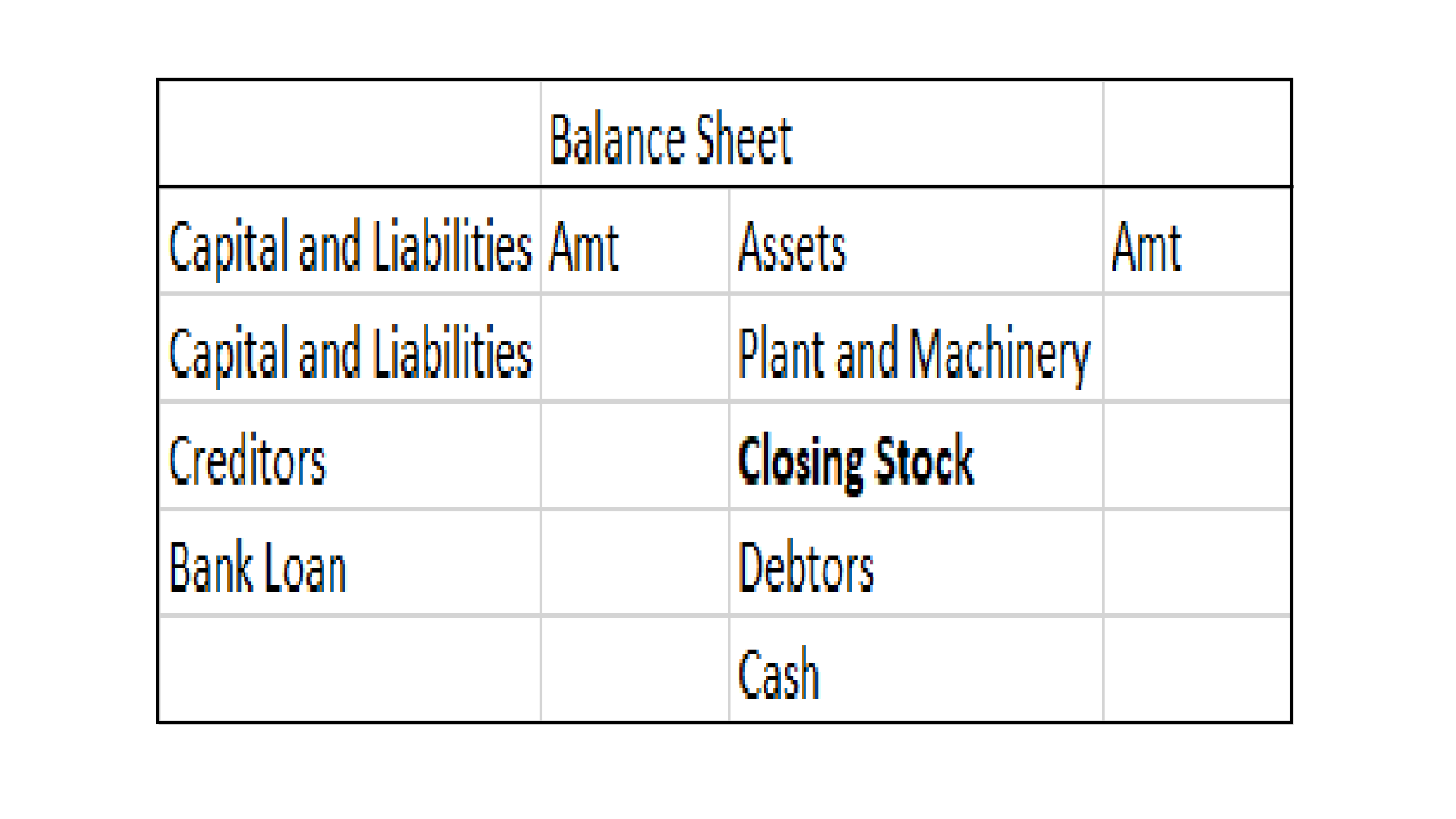
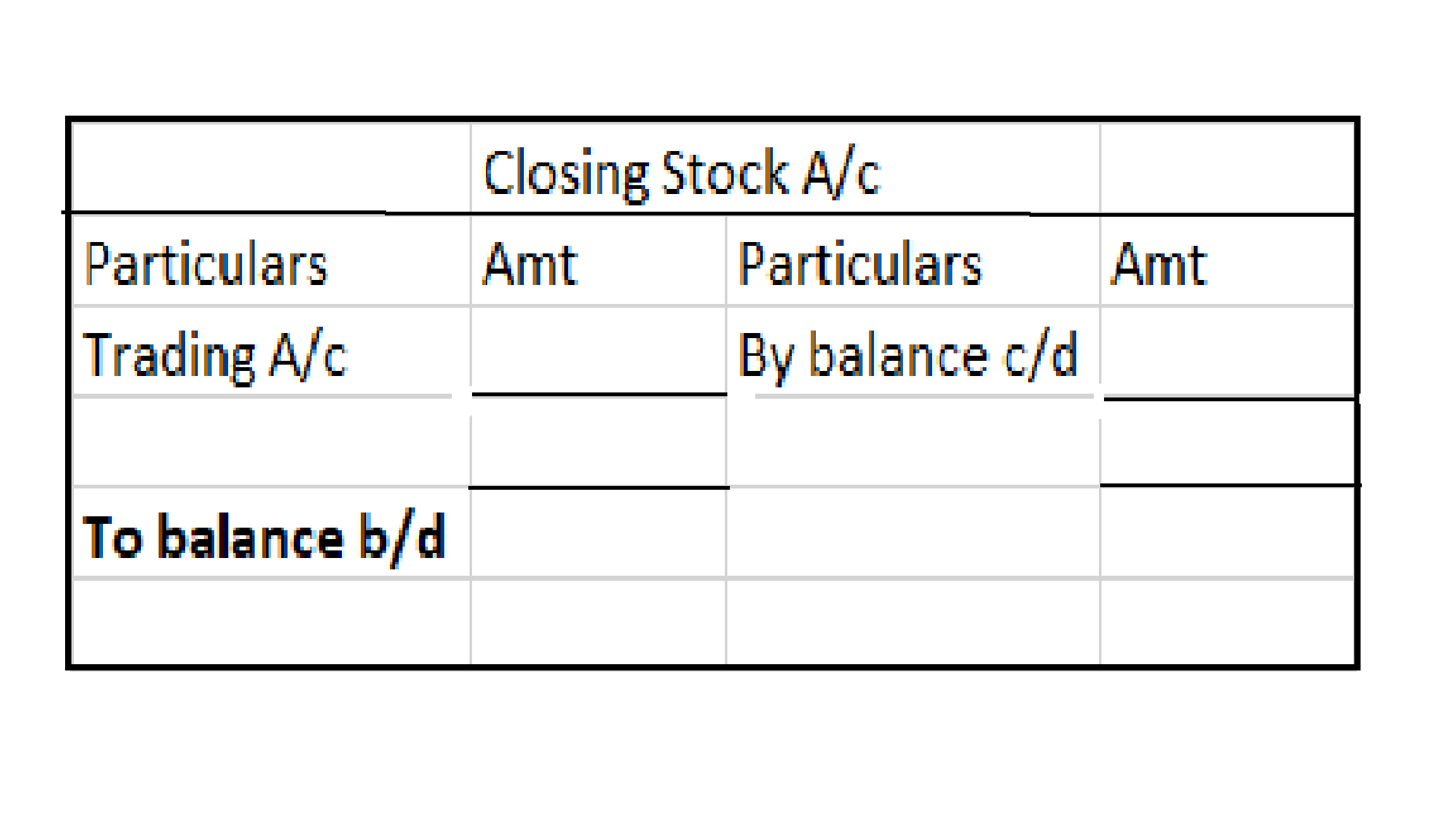
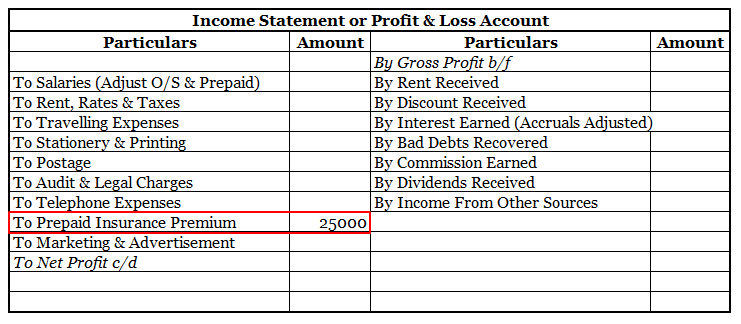
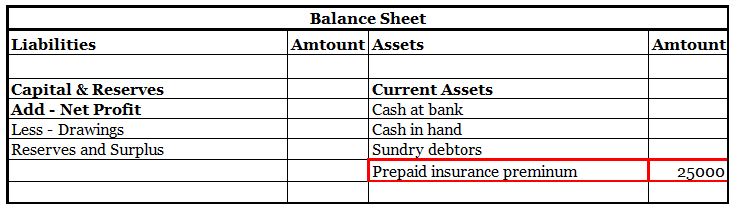
Definition Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period. For a business i.e. company/firm, it is a liability towards shareholders/promoters/partners/proprietors, etc. as it is their capital that has earned these profits. When the result of this computationRead more
Definition
Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period.
For a business i.e. company/firm, it is a liability towards shareholders/promoters/partners/proprietors, etc. as it is their capital that has earned these profits.
When the result of this computation is negative it is called a net loss.
Net profit may be shown before or after tax.
Formula :
Total Revenues – Expenses
Or
Total Revenues – Total Cost ( Implicit And Explicit Cost )
Liabilities
It means the amount owed (payable) by the business. liability towards the owners ( proprietor or partners ) of the business is termed an internal liability.
On the other hand, liability towards outsiders, i.e., other than owners ( proprietors or partners ) is termed as an external liability. For example – taxes owned, trade payables, etc.
For example creditors, bank overdrafts, etc.
Assets
An asset is a resource owned or controlled by a company and will benefit the business in current and future periods.
In other words, it’s something that a company owns or controls and can use to generate profits today and in the future.
For example – cash, building, etc.
Why debtors are treated as a liability?
Now let me explain to you why net profits are treated as a liability and not as an asset because of the following characteristics :
• Net Profit shows the credit balance of the Profit And Loss Account.
• It is treated directly in the balance sheet by adding or subtracting from the capital.
• Net Profit is a measure of the profitability of the company after taking into consideration all costs incurred during the accounting period.
• Net profit is the last line in an income statement and is the figure that concerns most people who use such a statement.
• Net income is reported on the income statement (profit and loss account) and forms a key indicator of a company’s performance.
Importance Of Net Profit
Now I will let you know the importance of net profit which is as follows :
Owners
Net profit allows owners to calculate the tax to be paid and how much earnings need to be distributed to the business owners.
Investors
Investors need to see net profit as they need to access the risk before investing they basically judge the revenue-generating capacity of a firm based on net profit.
Competitors
For making the comparison competitors tend to look at the net profit of the company to know how are they performing in the industry so that they can build themselves strong.
Creditors
Creditors look at the net profit for the purpose of obtaining business loans or we can say that determines a prospective debtor’s capacity to pay future debts.
Conclusion
Now after the above explanation, we can say that,
Net Profit is shown on the liability side as it belongs to shareholders so the company has to give it to shareholders so we are showing it under the liability side.
Net Profit with respect to the company is a liability as it has to pay it to shareholders.
Net Profit with respect to shareholders is an asset.
See less