The correct answer is 2. Credit balance in the bank column of the cash book. The credit balance in the bank column of Cash Book represents the overdraft facility utilized by the business. Overdraft is a credit extension facility offered by banks to both savings and current account holders. It allowsRead more
The correct answer is 2. Credit balance in the bank column of the cash book.
The credit balance in the bank column of Cash Book represents the overdraft facility utilized by the business. Overdraft is a credit extension facility offered by banks to both savings and current account holders. It allows the account holder to borrow a specified sum of money over and above the balance in their accounts.
It is a form of short-term borrowing offered by banks and is extremely useful for businesses to resolve short-term cash flow issues.
The account holder can withdraw money even when his/her account does not have enough balance to cover the withdrawal. Since the business is withdrawing money that is not in its account, an overdraft is represented by a negative bank balance. That is why they are shown as a credit balance in the bank column of the Cash Book.
Overdraft is a liability for the business. Hence, it is shown on the Equity and Liability part of the Balance Sheet under the head Current Liabilities and sub-head Short Term Borrowings.
Banks do not offer this facility to all customers. Only those who have a good reputation and credit score are eligible for this facility. Like any other borrowing, interest is charged on the amount utilized by the account holder as an overdraft.
See less
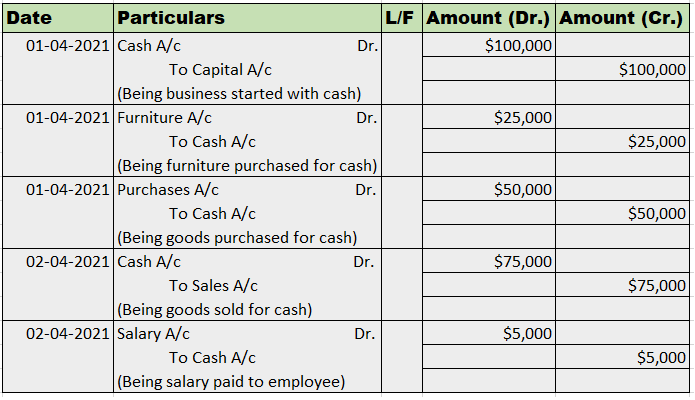
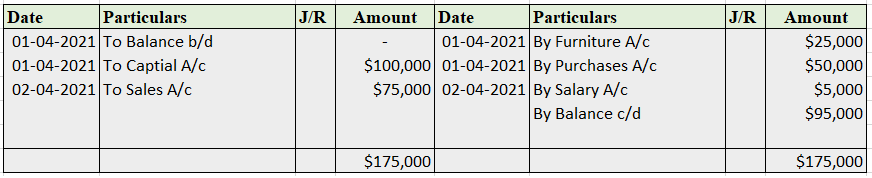
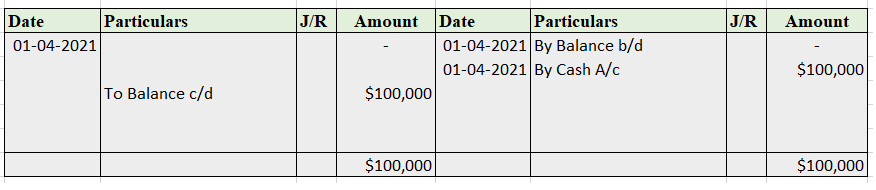
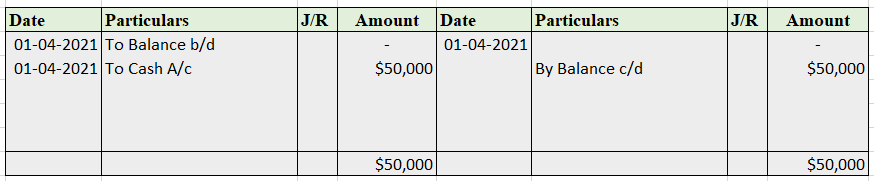
The accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is almost the same as in the case of the profit-oriented organisation. Let's first briefly understand what accounting equation and non-profit organisation are: Accounting Equation Accounting equation is an equation that depicts the relationship bRead more
The accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is almost the same as in the case of the profit-oriented organisation. Let’s first briefly understand what accounting equation and non-profit organisation are:
Accounting Equation
Accounting equation is an equation that depicts the relationship between assets, liabilities and capital of an entity.
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
As per this equation, the total assets of an entity are equal to the sum of its total liabilities and total capital. This equation holds good in every situation.
Non-Profit Organisation
A Non-Profit Organisation is an entity which exists for purposes other than for profit. Such organizations exist and operate for charitable purposes, promotion of culture and sports and welfare of society. The accounting for Non-profit organisation is slightly different from For-profit organisations. In the case of a non-profit organisation, the capital account is known as the capital fund.
Accounting Equation for non-profit organisations
The Accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Capital fund.
The difference is only in name. In the case of non-profit organizations, the capital is known as a capital fund. Rest everything is the same. The accounting equation will be prepared as normally prepared for business concerns.
See less