Deferred Revenue Expenditure Capital Expenditure Capital Gain Revenue Expenditure
Definition Prepaid expenses are those expenses whose payments are done in advance which can be for the goods or services whose benefit will accrue in the subsequent accounting period. A prepaid expense is a current asset. prepaid expenses are classified under the head current assets in the balance sRead more
Definition
Prepaid expenses are those expenses whose payments are done in advance which can be for the goods or services whose benefit will accrue in the subsequent accounting period.
A prepaid expense is a current asset. prepaid expenses are classified under the head current assets in the balance sheet.
This is because they provide future economic benefits to the company. As such, they are assets that can be used to generate revenue in the future.
For example prepaid rent, prepaid insurance, etc.
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business.
Or in other words, we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cycle period although it is more than the period of 12 months from the date of the balance sheet.
For example, goods are purchased with the purpose to resell and earn a profit, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Current liabilities are liabilities that are payable generally within 12 months from the end of the accounting period or in other words which fall due for payment in a relatively short period.
For example bills payable, short-term loans, etc.
Why current assets and not a current liability?
Now let me try to explain to you that prepaid expenses are classified as current assets and not as a current liability which is as follows :
-
- we can say that the expected realization period is less than the operating cycle period although it is more than the period of 12 months from the date of the balance sheet.
-
- expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or rendering of services in the normal course of business.
-
- In the business prepaid expense are treated as an asset which we can see on the asset side of the balance sheet.
-
- Or in other words, we can say that it is initially recorded as a prepaid expense as an asset in the balance sheet and subsequently its value is expensed over time in the profit and loss account.
Example
Now let us take an example for explaining prepaid expenses which are mentioned below.
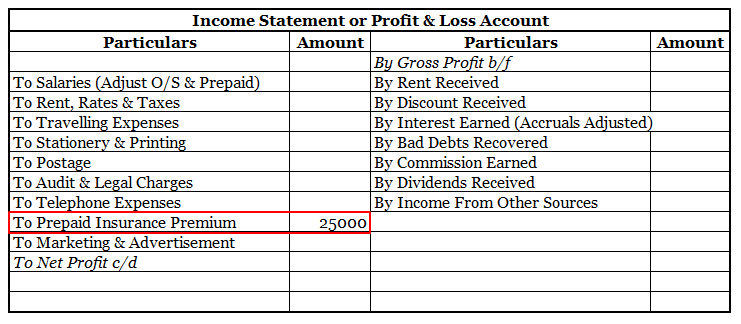
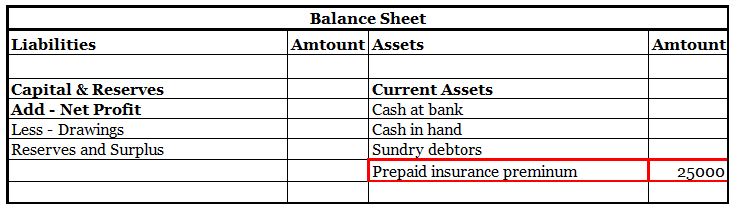
An insurance premium of Rs 50000 has been paid for one year beginning (previous year). The financial year ends on 31st march YYYY.
It means the premium for 6 months i.e., 1st April, YYYY(current year) to 30th September, YYYY(current year) amounting to Rs 25000 is paid in advance.
Thus, of premium paid in advance (Rs 25000) is a Prepaid Expense. It will be accounted as an expense in the financial year ending 31st march next year. In the balance sheet as of 31st march YYYY ( current year ) it will be shown as Current Asset.
Here is an extract of the profit /loss account and balance sheet of the above example:
Key points
There are a few things to keep in mind when dealing with prepaid expenses.
- First, is that the expenses are actually prepaid. This means that the expenses were paid for before they were used.
- Second, it is essential to track the number of prepaid expenses that have been used. That is to make sure that the prepaid expenses are not overstated on the company’s financial statements. This can happen if the company pays for more goods or services than it actually
- Last but not least it is important to keep in mind that changes in the value of prepaid expenses can impact the company’s net income. For example, if the company’s prepaid insurance increases in value, this will increase the company’s net income.
See less

The correct answer is 4. Revenue Expenditure. Depreciation is a non-cash expense and is charged on the fixed asset for its continuous use. Revenue expenditure is a day-to-day expense incurred by a firm in order to carry on its normal business. Depreciation is considered a revenue expense due to theRead more
The correct answer is 4. Revenue Expenditure.
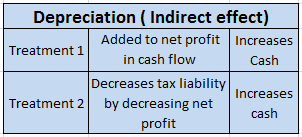
Depreciation is a non-cash expense and is charged on the fixed asset for its continuous use. Revenue expenditure is a day-to-day expense incurred by a firm in order to carry on its normal business. Depreciation is considered a revenue expense due to the regular use of the fixed assets.
Depreciation is the systematic and periodic reduction in the cost of a fixed asset. It is a non-cash expense. Mostly, depreciation is charged according to the straight-line method or written down method as per the policy of the company.
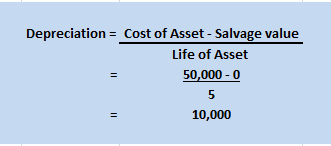
Depreciation is the systematic and periodic reduction in the cost of a fixed asset. It is a non-cash expense. Mostly, depreciation is charged according to the straight-line method or written down method as per the policy of the company. It is calculated as-
Depreciation = Cost of the asset – Scrap value / Expected life of the asset.
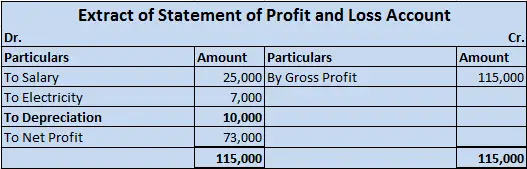
For Example, ONGC bought machinery at the beginning of the year for Rs 10,00,000
It charges depreciation @10% at the end of the year.
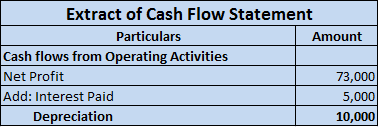
10,00,000 x 10/100 = 1,00,000 will be depreciation for the year and will be shown on the debit side of Profit & Loss A/c.
As the fixed assets are used in the day-to-day activities of the firm and hence the depreciation charged on it on the daily basis would be revenue in nature. so depreciation is said to be an item of revenue expenditure.
See less