1) Liability 2) Asset 3) Expenses 4) Income
Yes, I agree with your statement that accounting information should be comparable. Comparability is one of the qualitative characteristics of accounting information. It means that users should be able to compare a company's financial statements across time and across other companies. Comparability oRead more
Yes, I agree with your statement that accounting information should be comparable.
Comparability is one of the qualitative characteristics of accounting information. It means that users should be able to compare a company’s financial statements across time and across other companies.
Comparability of financial statements is crucial due to the following reasons:
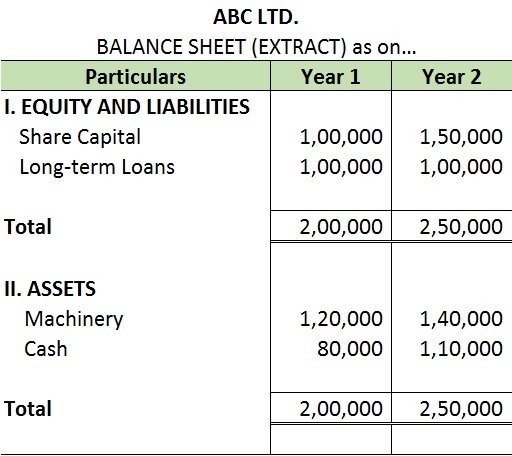
1. Intra-Firm Comparison:
Comparison of financial statements of two or more periods of the same firm is known as an intra-firm comparison.
Comparability of accounting information enables the users to analyze the financial statements of a business over a period of time. It helps them to monitor whether the firm’s financial performance has improved over time.
The intra-firm analysis is also known as Time Series Analysis or Trend Analysis.
To understand intra-firm analysis, I have provided an extract of the balance sheet of ABC Ltd. for two accounting periods.
2. Inter-Firm Comparison:
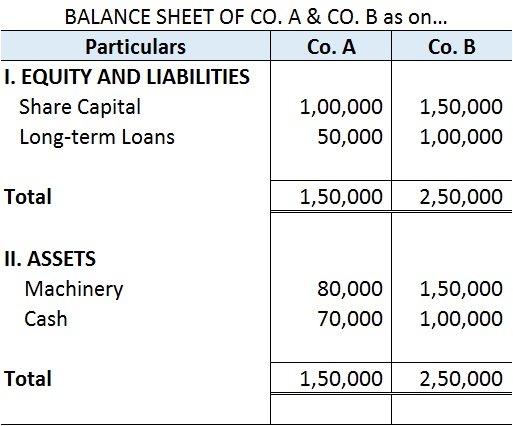
Comparison of financial statements of two or more firms is known as an inter-firm comparison.
Inter-firm comparison helps in analyzing the financial performance of two or more competing firms in an industry. It enables the firm to know its position in the market in comparison to its competitors.
Inter-firm comparison is also known as Cross-sectional Analysis.
I’ve provided the balance sheets of Co. A and Co.B to make an inter-firm comparison.
Here is a piece of bonus information for you,
Sector Analysis – it refers to the assessment of economical and financial conditions of a given sector of a company/industry/economy. It involves the analysis of the size, demographic, pricing, competitive, and other economic dimensions of a sector of the company/industry/economy.
One more important thing to note here is that comparability can only be achieved when the firms are consistent in the accounting principles and standards they adopt. The accounting policies and standards must be consistent across different periods of the same firm and across different firms in an industry.
See less
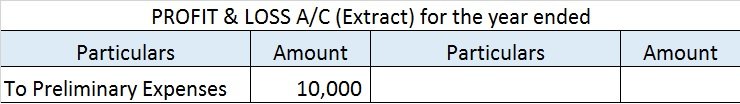
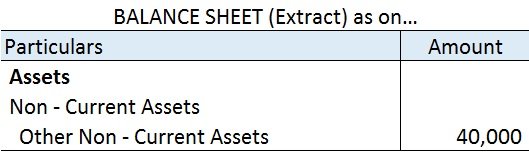
Therefore, 2) Asset is the correct option. Explanation The petty cash book is managed and made by not an accountant but the petty cashier and is done to record small incomes and expenditures that are not recordable in the cash book. Therefore, the desired result we obtain from the deduction oRead more
Therefore, 2) Asset is the correct option.
Explanation
The petty cash book is managed and made by not an accountant but the petty cashier and is done to record small incomes and expenditures that are not recordable in the cash book. Therefore, the desired result we obtain from the deduction of the total expenditure and total cash receipt is the closing balance of the petty cash book.
Petty cash refers to the in-hand physical cash that a business holds to pay for small and unplanned expenses.
Asset: The closing balance of the petty cash book is considered an asset because the petty cash book is a type of cash book. The petty cash book also deals in outflow and inflow of the cash, it also maintains and records income and expenditure that are similar to the cash book.
The petty cash book since being a part of the cash book, which records all the inflow and outflow of cash in a business, which is an asset, thus petty cash book’s closing balance is considered an asset. Also, the balance of the petty cash book is never closed. Their closing balance is carried forward to the next year.
Liability: The closing balance of the petty cash book is not considered a liability because that closing balance of the petty cash book doesn’t create a liability for the business. In fact, the closing of the petty cash book is placed under the head current asset in the balance sheet as mentioned above, it’s a part of the cash book which records the transactions of cash a/c which is an asset itself.
Expenses or Income: It is not an expense because the closing balance of the petty cash book is calculated by deducting the total expenditure from the total cash receipt.
That is an asset and it is considered to be a current asset, neither an income nor an expense. It is used for paying out petty expenses.
Therefore, the closing balance of the petty cash book is considered an asset.
See less