Income and Expenditure A/c of Charitable Trust Income and Expenditure A/c is like the Profit and Loss A/c in the Balance Sheet of the Charitable Trust. All the income and expenses are, therefore, recorded in this. It is used to determine the surplus or deficit of income over expenditures over a specRead more
Income and Expenditure A/c of Charitable Trust
Income and Expenditure A/c is like the Profit and Loss A/c in the Balance Sheet of the Charitable Trust. All the income and expenses are, therefore, recorded in this. It is used to determine the surplus or deficit of income over expenditures over a specific accounting period.
It shows the summary of all the income and expenditures done by the charitable trust over an accounting year. All the revenue items relating to the current period are shown in this account, the expenses and losses on the expenditure side, and incomes and gains on the income side of the account.
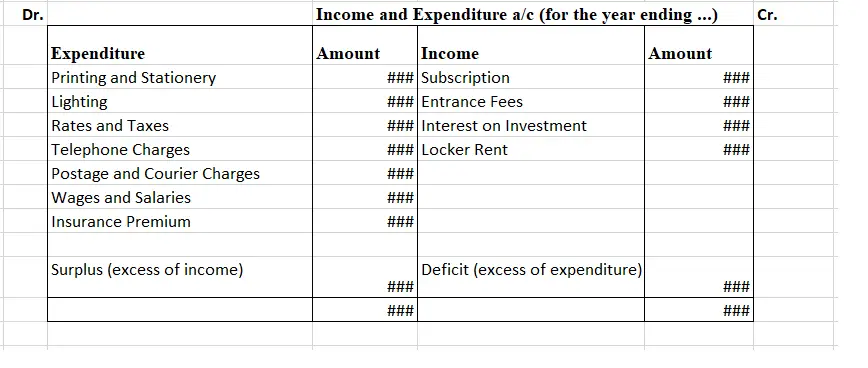
- Therefore, as you can see here, how a charitable trust may use MS Excel for making their Income and Expenditure A/c, the Surplus and Deficit are the balancing figures used for balancing both the debit and credit sides.
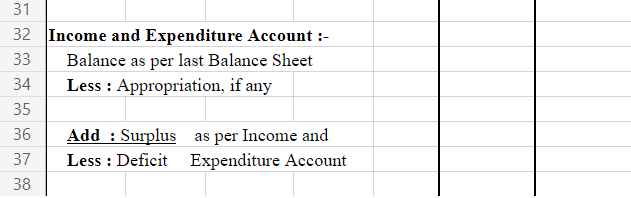
Later on, they are even used in the Balance Sheet. As follows-
On the Assets Side
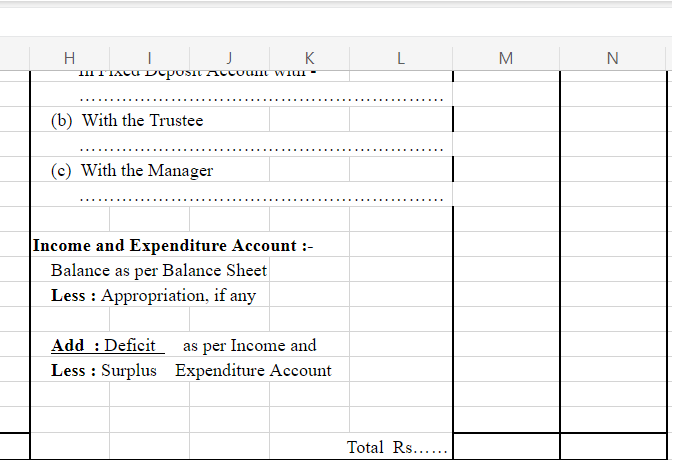
On the Liability Side
See less

The value of inventory at the end of the financial year or balance sheet date is called closing stock. Closing stock includes: Raw Material Work-in-Progress Finished Goods Example: If the value of raw material is Rs 10,000, value of WIP is Rs 5,000 and value of Finished Goods is Rs 15,000 then valueRead more
The value of inventory at the end of the financial year or balance sheet date is called closing stock. Closing stock includes:
Example:
If the value of raw material is Rs 10,000, value of WIP is Rs 5,000 and value of Finished Goods is Rs 15,000 then value of Closing Stock will be Rs (10,000 + 5,000 + 15,000) = Rs 30,000
Adjustment entries are done on the accrual basis of accounting, that is, income is recorded when earned and not received and expenses are recorded when incurred and not paid. Adjustment entries are usually made before or after the preparation of the trial balance at the end of the accounting period.
If the entries are made after the preparation of the trial balance, then two adjustment entries are recorded while preparing Trading and Profit & Loss A/c.
Since closing stock is an item outside the trial balance, the double-entry would be:
The journal entry
The second adjustment would be to show closing stock on the balance sheet and since the closing stock is an asset it is shown under the head Current Assets.
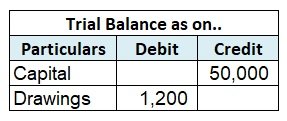
In case where adjustment for Closing Stock is to be done before preparation of Trial Balance, then it will be shown on the credit side of the Trial Balance, since it is an asset for the company and will have a credit brought down balance as shown in the image.
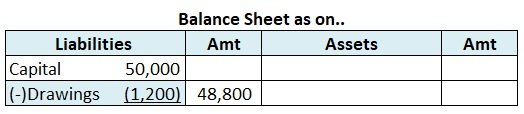
Later, while preparing Balance Sheet, Closing Stock will be shown on the Asset side of the Balance Sheet.
See less