Definition The trial balance is a list of all the closing balances of the general ledger at the end of the year. Or in other words, I can say that it is a statement showing debit and credit balances. A trial balance is prepared on a particular date and not in a specific period. Types of error in theRead more
Definition
The trial balance is a list of all the closing balances of the general ledger at the end of the year. Or in other words, I can say that it is a statement showing debit and credit balances.
A trial balance is prepared on a particular date and not in a specific period.
Types of error in the trial balance
Now let me explain to you that what are the errors of trail balance which are as follows :
• Error of principle
• Compensating error
• Transactions completely omitted
• Error of recording
• Error of posting
A trial balance is not conclusive proof of the accuracy of the books of accounts since certain types of errors remain even when it tallies. They are explained below :
Error of principle
This error arises due to the incorrect application of the principle of accounting is not disclosed by the trial balance.
Compensating error
It means the group of errors committed in such a way that one mistake is compensated by another and the trial balance still agrees.
Transaction completely omitted
When the transaction is entirely omitted from recording in the books of account cannot be detected.
Error of recording
When both aspects of recording a transaction twice in the books of account take place.
Error of posting
Posting the correct amount on the correct side but in the wrong account is not reflected in the trial balance.
Steps to locate errors
Differences in the trial balance, howsoever minor they may be, must be located and rectified. The following steps are useful in locating errors are :
• Two columns of the trial balance should be totaled again.
• The list of sundry debtors and creditors should be checked to find out whether all balances of debtors and creditors have been correctly written in the trial balance or not.
• It should be checked that the balances of every account including cash and bank balances ( from the cash book ) have been written in the correct column of the trial balance.
• If the errors remain undetected, try to locate the errors by trial and error techniques such as finding an account showing a balance difference from the trial balance.
• Ledger balances should be balanced again.
• Check the totals of subsidiary books.
• Check the posting of nominal accounts.
• And at last if not possible to locate the difference in the trial balance is temporarily transferred to a suspense account.
Importance
As the trial balance is prepared at the end of the year so it is important for the preparation of financial statements like balance sheets or profit and loss.
Purpose of trial balance
• To verify the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger accounts
This means trial balance indicates that equal debits and credits have been recorded in the ledger accounts.
It enables one to establish whether the posting and other accounting processes have been carried out without any arithmetical errors.
• To help in locating errors
There can be some errors if the trial balance is untallied therefore to get error-free financial statements trial balance is prepared.
• To facilitate the preparation of financial statements
A trial balance helps us to directly prepare the financial statements and then which gives us the right to not look or no need to refer to the ledger accounts.
Rules of trial balance
When we prepare a trial balance from the given list of ledger balances, the following rules to be kept in mind that are as follows :
• The balance of all
• Assets accounts
• Expenses accounts
• Losses
• Drawings
• Cash and bank balances
Are placed in the debit column of the trial balance.
• The balances of
• liabilities accounts
• income accounts
• profits
• capital
Are placed in the credit column of the trial balance.
See less

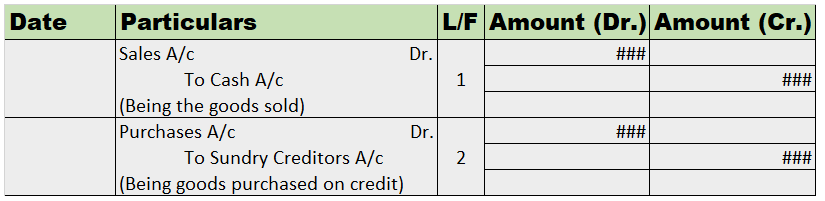
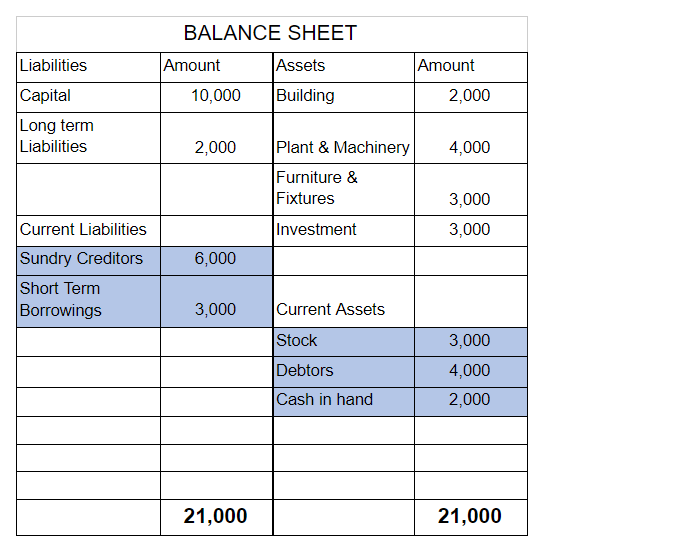
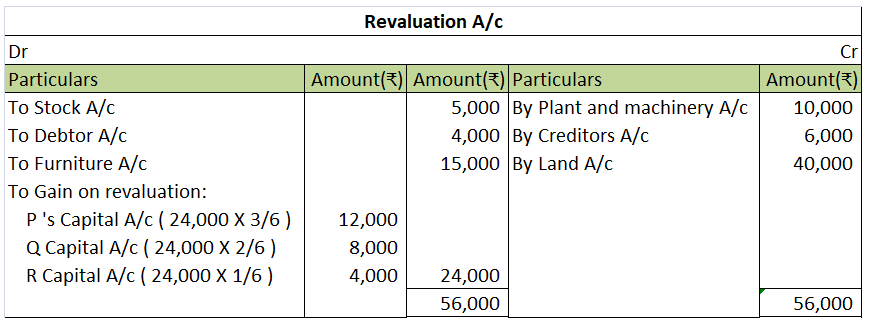
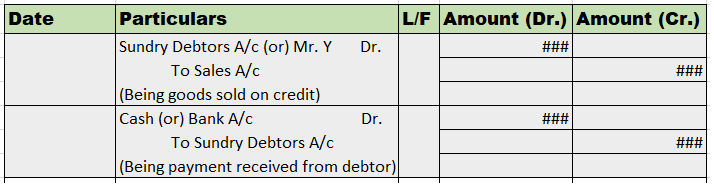
Goodwill In Accounting Aspect, Goodwill refers to an Intangible asset that facilitates a company in making higher profits and is a result of a business’s consistent efforts over the past years which can be the business's prestige, reputation, good name, customer trust, quality service, etc. GoodwillRead more
Goodwill
In Accounting Aspect, Goodwill refers to an Intangible asset that facilitates a company in making higher profits and is a result of a business’s consistent efforts over the past years which can be the business’s prestige, reputation, good name, customer trust, quality service, etc.
Goodwill has no separate existence although the concept of goodwill comes when a company acquires another company with a willingness to pay a higher price over the fair market value of the company’s net asset in simple words the goodwill can be only realized while at the time of sale of a business.
The formula for Goodwill
Types of Goodwill
there are two types of goodwill.
1. Inherent Goodwill/Self-generated goodwill
Inherent goodwill is the internally generated goodwill that was created or generated by the business itself. it is generally generated from the good reputation of the business.
Inherent Goodwill or Self-generated goodwill is generally not shown in the books or never recognized in the books of Accounts and no journal entry for the inherent goodwill is passed.
2. Purchased Goodwill/Acquired Goodwill
At the time of acquisition of a business by another business, any amount paid over and above the net assets simply refers to the amount of Purchased Goodwill or Acquired goodwill.
A Journal entry is passed in the case of the Purchase of goodwill.
Type of Account
generally, Goodwill is considered and recorded as an Intangible asset(long-term asset) due to its physical absence like other long-term assets.
Modern rule of accounting:
as per the Modern rule of accounting, all Assets or all possessions of a business are comes under the head Asset accounts.
as Goodwill is treated as an Intangible asset it is an Asset Account.
Journal entry for purchase of goodwill as per Modern rule
Goodwill A/c Dr. – Amt
To Cash/Bank A/c – Amt
(The modern approach of accounting for the Asset account is: “Debit the increase in asset and Credit the decrease in the asset“)
The golden rule of accounting
As per the golden rule of accounting, all assets or possessions of a business other than those which are related to any person (debtor’s account) are considered Real accounts.
Such accounts don’t close by the year-end and are carried forward.
As Goodwill is an Intangible asset it is treated as a Real account as per the golden rule of accounting.
Journal entry for purchase of goodwill as per Golden rule
Goodwill A/c Dr. – Amt
To Cash/Bank A/c – Amt
(The golden rule of accounting for the Real account is: “Debit what comes in and Credit what Goes out“)
See less