When a partnership firm decides to admit a new partner into their firm, the old partners have to forego a part of their share for the new partner. Therefore, sacrificing Ratio is the proportion in which the existing partners of a company give up a part of their share for the new partner. The partnerRead more
When a partnership firm decides to admit a new partner into their firm, the old partners have to forego a part of their share for the new partner. Therefore, sacrificing Ratio is the proportion in which the existing partners of a company give up a part of their share for the new partner. The partners can choose to forego their shares equally or in an agreed proportion.
Before admission of the new partner, the existing partners would be sharing their profits in the old ratio. Upon admission, the profit-sharing ratio would change to accommodate the new partner. This would give rise to the new ratio. Hence Sacrificing ratio formula can be calculated as:
Sacrificing Ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
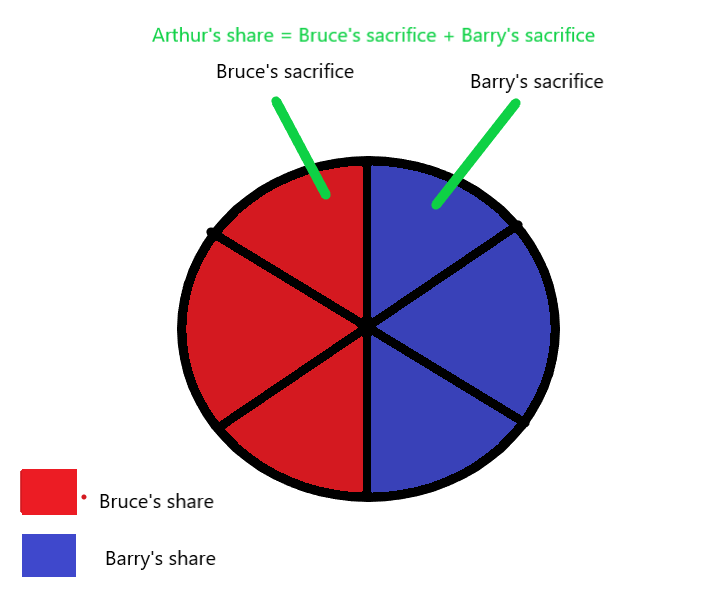
To further understand the formula, let’s say Bruce and Barry are sharing a pizza of 6 slices equally (3 slices each). They decide to share their pizza with Arthur such that they all get equal slices (2 slices each). Hence, we can use the formula to calculate their sacrifice as follows:
Bruce’s sacrifice = 3 – 2 = 1 slice
Barry’s sacrifice = 3 – 2 = 1 slice
Therefore, their sacrificing ratio = 1:1. In this same way, we can solve various problems to calculate the sacrifice of partners during a change in their profit sharing ratio.
For example, Joshua and Edwin are partners, sharing profits in the ratio 7:3. They admit Adam into their partnership such that the new profit-sharing ratio is 5:2:3. Therefore, their sacrificing ratio can be calculated as:
Joshua’s sacrifice = old share – new share = 7/10 – 5/10 = 2/10
Edwin’s sacrifice = old share – new share = 3/10 – 2/10 = 1/10
Hence, sacrificing ratio of Joshua and Edwin is 2:1. Once the denominators are equal, we ignore them and only consider numerators while showing sacrificing ratio.
See less
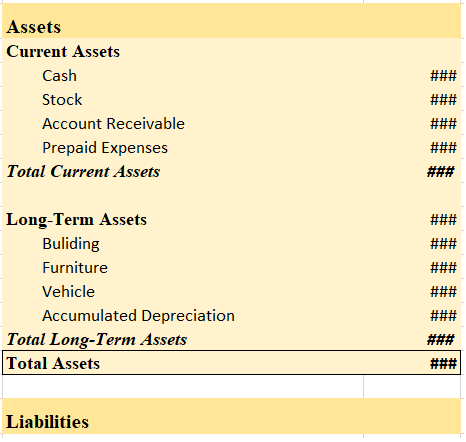
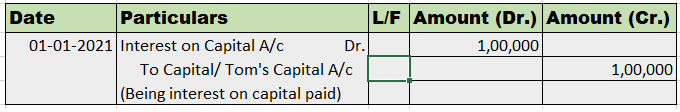
Definition Section 43 of the companies act 2013 prescribes that the share capital of a company broadly can be of two types or classes : Preference shares Equity shares Preference shares Preference shares are the shares that carry the following two preferential rights : Preferential rights to receivRead more
Definition
Section 43 of the companies act 2013 prescribes that the share capital of a company broadly can be of two types or classes :
Preference shares
Preference shares are the shares that carry the following two preferential rights :
Classes of preference shares
Preference shares are broadly classified as follows :
With reference to the dividend
Cumulative preference shares are those preference shares that carry the right to receive arrears of dividends before the dividend is paid to the equity shareholders.
Non-cumulative preference shares are those that do not carry the right to receive arrears of dividends.
Participation in surplus profit
Participating preference shares of the company may provide that after the dividend has been paid to the equity shareholders, the holders of preference shares will also have a right to participate in the remaining profits.
Non-participating preference shares are those preference shares that do not carry the right to participate in the remaining profits after the equity shareholders have paid the dividend.
Convertibility
Convertible preference shares are those preference shares that carry the right to be converted into equity shares.
Non-convertible preference shares are those that do not carry the right to be converted into equity shares.
Redemption
Redeemable preference shares are those preference shares that are redeemed by the company at the time specified for the repayment or earlier.
Irredeemable preference shares are preference shares the amount of which can be returned by the company to the holders of such shares when the company is wound up.
Equity shares
Equity shares are those shares that are not preference shares.
Equity shares are the most commonly issued class of shares that carry the maximum ‘risk and reward ‘ of the business the risks of losing part or all the value of the shares if the business incurs losses.
The rewards are the payment of higher dividends and appreciation in the market value.
See less