Introduction Minority interest refers to the interest of the outsiders in the subsidiary or subsidiaries of a holding company. In the presentation of the consolidated balance sheet of a parent company and its subsidiaries, Minority Interest is shown just below Shareholders’ Funds. Explanation To undRead more
Introduction
Minority interest refers to the interest of the outsiders in the subsidiary or subsidiaries of a holding company. In the presentation of the consolidated balance sheet of a parent company and its subsidiaries, Minority Interest is shown just below Shareholders’ Funds.
Explanation
To understand the concept of minority interest, we need to first understand the relationship between a holding company and its subsidiary company or companies.
A holding company means a company that controls one or more companies by:
- Holding more than fifty percent of the total voting rights or equity share capital.
- having the power to appoint or remove the majority of the board members.
A subsidiary company is a company that is controlled by another company.
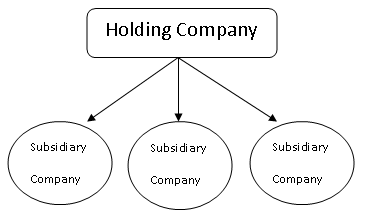
From the above, we can simply deduce that a holding company holds the majority of the equity in its subsidiary company or companies.
So, the equity of the subsidiary company which does not belong to the holding company, but to the outsiders is known as the minority interest as it is, in fact, the minority in comparison to the majority stake of the holding company.
Example
For example, A Ltd holds 75% of the equity in B Ltd, then the rest 25% which belongs to the outsiders will be the Minority Interest.
Minority Interest means the share of outsiders in the:
- Paid-up share capital of the subsidiary
- Reserve and Surplus
For example, B Ltd has the following particulars under Shareholders’ Funds.
| Equity Share Capital | Rs. 10,00,000 |
| Revaluation Reserve | Rs. 4,00,000 |
| Balance of Profit and Loss A/c | Rs. 1,00,000 |
| General Reserves | Rs. 5,00,000 |
B Ltd is a subsidiary company of the A Ltd. A Ltd holds 75% of B Ltd.
It means minority interest in B Ltd is 25% (100% – 75%)
Therefore, in the consolidated balance sheet of A Ltd and its subsidiary, the minority interest will be as follows:
Minority Interest in B Ltd (25%)
| Equity Share Capital | Rs. 2,50,000 (10,00,000 x 25%) |
| Revaluation Reserve | Rs. 1,00,000 (4,00,000 x 25%) |
| Balance of Profit and Loss A/c | Rs. 25,000 (1,00,000 x 25%) |
| General Reserves | Rs. 1,25,000 (5,00,000 x 25%) |
| Total | Rs. 5,00,000 |
See less


The provision for doubtful debts is the estimated amount of bad debts which will be uncollectible in the future. It is usually calculated as a percentage of debtors. The provision for a doubtful debt account has a credit balance and is shown in the balance sheet as a deduction from debtors. It is aRead more
The provision for doubtful debts is the estimated amount of bad debts which will be uncollectible in the future. It is usually calculated as a percentage of debtors. The provision for a doubtful debt account has a credit balance and is shown in the balance sheet as a deduction from debtors. It is a contra asset account which means an account with a credit balance.
When a business first sets up a provision for doubtful debts, the full amount of the provision should be debited to bad debts expense as follows.
In subsequent years, when provision is increased the account is credited, and when provision is decreased the account is debited. This is so because provision for doubtful debts is a contra account to debtors and has a credit balance, and is treated as a liability.
Effects of Provision for Doubtful Debts in financial statements:
For example, ABC Ltd had debtors amounting to Rs 50,000. It creates a provision of 5% on debtors.
Provision for Doubtful Debts = 50,000*5%
= 2,500
Journal entry for provision will be:
Effect on financial statements will be:
See less