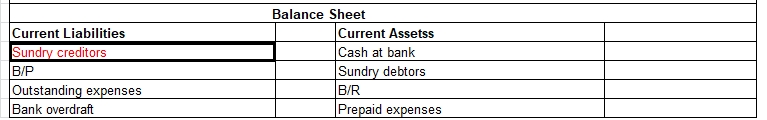
Prepaid expenses are those expenses that have not been expired yet but their payment has already made in advance. There are many examples of prepaid expenses such as rent paid in advance, interest paid in advance, unexpired insurance You might be wondering what kind of account it is? As the name sugRead more
Prepaid expenses are those expenses that have not been expired yet but their payment has already made in advance. There are many examples of prepaid expenses such as rent paid in advance, interest paid in advance, unexpired insurance
You might be wondering what kind of account it is? As the name suggests it should be an expense but actually it’s an asset. When we initially record prepaid expenses we consider them as current assets and show them in the balance sheet. It turns out to be an expense when we use the service/item for what we have paid for in advance.
The entry for the above explanation is as follows:
From the modern rule, we know Assets and expenses increased are debits while decrease in assets and expenses are credit.
As this is asset, increase in asset therefore we debit prepaid expense and on the other hand we pay cash/ bank on behalf of that asset in advance hence there is decrease in assets hence credited. The entry will be as follows:
| Prepaid Expense A/c …….Dr | XXX | |
| To Cash/ Bank | XXX |
when this prepaid expense actually becomes expense we pass the adjusting entry. The entry will be as follows:
| Expense A/c …….Dr | XXX | |
| To Prepaid expense | XXX |
Let me give you simple example of the above entry.
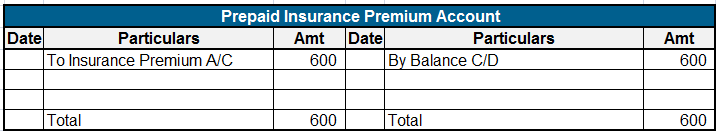
Suppose you pay advance rent of Rs 9,000 for six months for the space you haven’t used yet. So you need to record this as prepaid expense and show it on the asset side of the balance sheet under current assets. Since you paid for the same the entry would be as follows:
| Prepaid Rent A/c …….Dr | 9,000 | |
| To Cash/ Bank | 9,000 |
As each month passes we will adjust the rent with prepaid rent account. Since the rent was advanced for 6 months, therefore (9,000/6) Rs 1500 will be adjusted each month with the rent expense account. The adjustment entry will be:
| Rent A/c …….Dr | 1,500 | |
| To Prepaid rent | 1,500 |
The process is repeated until the rent is used and asset account becomes nil.
See less

Definition Posting refers to moving the transaction entries from the journal to the ledger books of the company. It is an important part of the accounting cycle. Posting helps us to classify transactions in a better manner. A journal is used to record transactions in chronological order while ledgerRead more
Definition
Posting refers to moving the transaction entries from the journal to the ledger books of the company. It is an important part of the accounting cycle.
Posting helps us to classify transactions in a better manner.
A journal is used to record transactions in chronological order while ledger books are used to classify transactions into assets, liabilities, expenses, and incomes.
Steps of Posting
• Create and name ledger accounts for different items of trial balance
• Identify those entries in the journal that relate to the relevant ledger book under consideration.
• Post the entry on the debit or credit side of the ledger account.
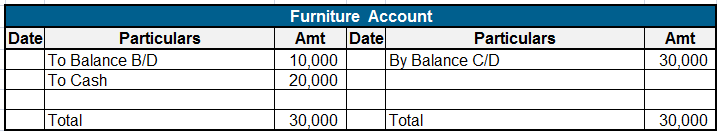
• For example, when salaries are paid a salary account is debited and a bank account is credited. When posting this transaction in the bank account we will debit the bank account and write “To salaries” under the head “particular”. This will indicate that salaries were paid from a bank account causing a reduction in the bank balance.
• After all the journal entries relevant to a particular ledger account have been posted in it, we will tally the total of the debit and the credit side of the ledger account to ascertain any balance left.
• Usually, asset accounts have the debit side exceeding the credit side. That is to say, they have a debit balance. Liability accounts usually have a credit balance.
• It is not necessary that every ledger account may have a balance left at the end. The total of the amounts on the debit side may be equal to the total of the amounts on the credit side in some ledger accounts.
• The last step is to recheck the ledger account to identify and correct any mistakes that may have occurred during the posting process.
Importance of Posting
• Posting helps us to classify transactions in a better and more efficient manner.
• Posting makes the books of accounts more readable.
• An accountant may choose to engage in posting once every month or even once every day as per the requirements of the business and the financial reporting norms.
• Posting is necessary for the creation of financial statements. A trial balance cannot be drafted without determining the balance of each ledger account.
• Posting helps us to know the balance of each account This helps to run the business smoothly by tracking balances timely and making up for any likely deficiency in advance.
• Analysis of how balances of various ledger accounts have changed over time helps us to draw valuable conclusions for the business.
Conclusion
We can conclude by saying that the process of posting refers to transferring the entries from the journal to the ledger accounts.
Posting is an essential step of the accounting cycle and without it, financial statements cannot be prepared. Any error while posting is bound to adversely affect the creation of the financial statements.
See less