Every business requires research and development to create innovative products for consumers. More innovative and creative products and services are more popular among customers, leading to increased revenue and profits for the business. Creating new products or designing changes and testing existinRead more
Every business requires research and development to create innovative products for consumers. More innovative and creative products and services are more popular among customers, leading to increased revenue and profits for the business.
Creating new products or designing changes and testing existing products also forms a part of research and development.
Examples of Research and Development costs are –
- Salaries of employees
- Cost of making prototypes
- Cost of raw material
- Overhead expenses
Let us now understand how research and development costs are treated in Financial Statements.
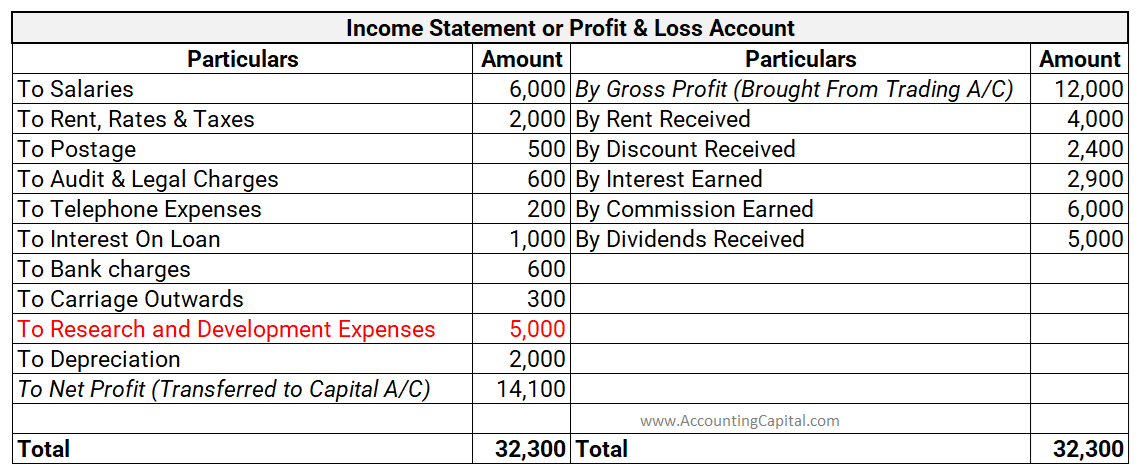
Research and Development Costs are generally shown as an expense in the Income Statement.
IAS-38
IAS-38 majorly governs the accounting of research and development costs. There are two phases in R&D:
- Research: During this phase, costs are incurred for understanding or designing the product. These costs are expensed as incurred costs as there is an uncertainty of a future benefit.
- Development: Economic value can be ascertained during this phase and hence, the costs incurred can be capitalized as Intangible assets. To be recognised as intangible assets, the following conditions shall be satisfied:
1. it is developed with the intention of putting it to use in the future
2. the asset shall hold an economic value
3. the costs can be measured reliably
Treatment of R&D costs in the Financial statements:
-
- Income statement: Research costs are shown as expenses in the income statement. However, development costs if capitalized as intangible assets can be amortised over time.
- Balance Sheet: Capitalised development costs are shown as intangible assets under the Assets head of the Balance Sheet.
Conclusion
The above discussion can be summarised as follows:
- Research and development is essential for creating innovative and creative products and services.
- Accounting standard IAS-38 governs the accounting for Research and Development.
- Research costs are usually shown as an expense in the Income statement of the business.
- Development costs when capitalised can be shown as Intangible assets in the Balance Sheet.



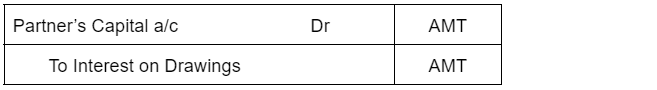
Definition Debit balance may arise due to timing differences in which case income will be accrued at the year's end to offset the debit. The amount is shown in the record of a company s finances, by which its total debits are greater than its total credits. The account which has debit balances are aRead more
Definition
Debit balance may arise due to timing differences in which case income will be accrued at the year’s end to offset the debit.
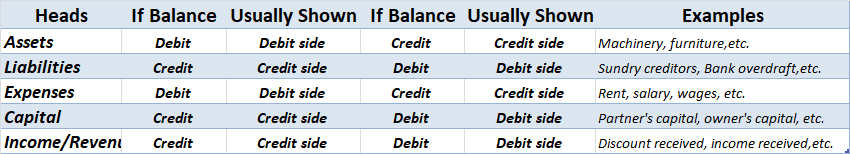
The amount is shown in the record of a company s finances, by which its total debits are greater than its total credits.
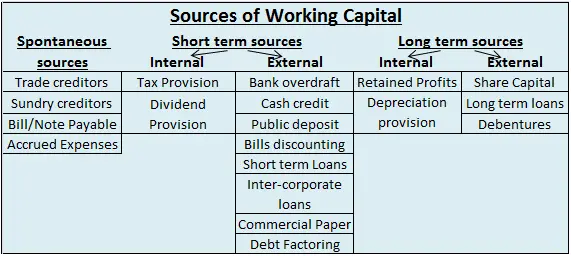
The account which has debit balances are as follows:
• Assets accounts
Land, furniture, building machinery, etc
• Expenses accounts
Salary, rent, insurance, etc
• Losses
Bad debts, loss by fire, etc
• Drawings
Personal drawings of cash or assets
• Cash and bank balances
Balances of these accounts
In class 11th, we learned about all these accounts that have debit balances.
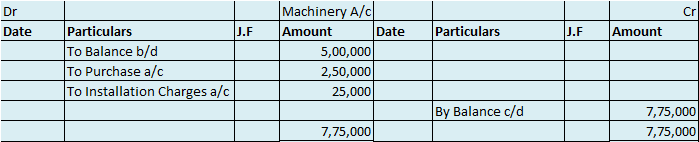
Where the total of the debit side is more than the credit side therefore the difference is the debit balance and is placed credit side as “ by balance c/d “
Here are some examples showing the debit balances of the accounts :

See less